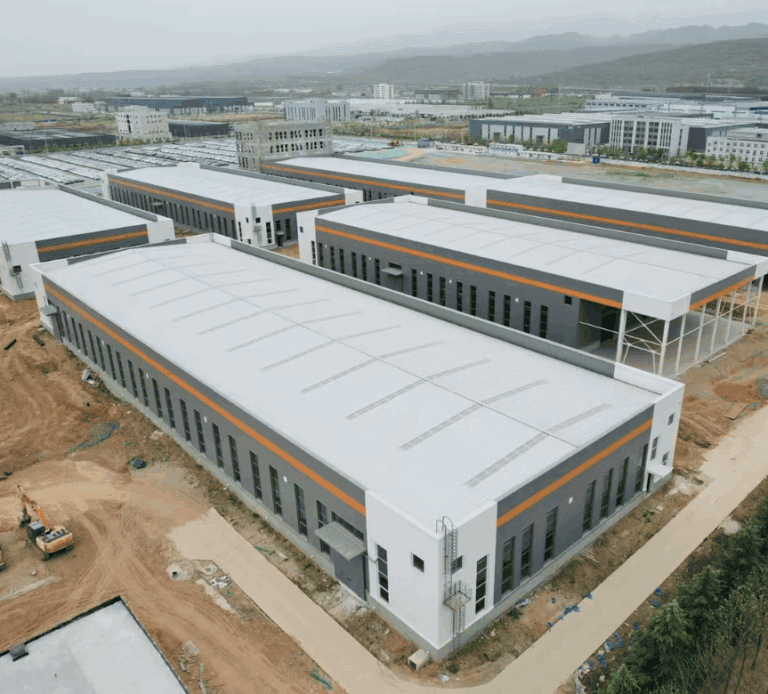
The modular building industry is growing quickly. Although it still makes up a small portion of the global construction market, its growth is hard to ignore. From new technologies to shifting market needs, and from global trends to local challenges, modular construction is changing the way we think about building speed, costs, and quality. What was once seen as an innovation is now becoming more common.
So, what is the current state of the modular building industry? What challenges does it face? And what opportunities lie ahead?
Let’s break it down.
#1 The Rise of Modular Construction: More Than Just a Trend

Modular construction involves building parts of a structure in a factory and then shipping those parts to the construction site for quick assembly. This method speeds up the building process, reduces construction time, and lowers risks on site. According to McKinsey & Co., modular construction can shorten project timelines by 20%-50%, while also improving the quality of the final building—without raising costs. A study by the U.S. Department of Energy (USDOE) also shows that modular projects are completed 30% faster on average than traditional site-built projects. This faster timeline benefits developers, especially for large-scale residential and commercial buildings.
What does this mean for developers? It means faster returns on their investment—projects often finish 6-12 months ahead of schedule. This allows developers to start earning sooner and lowers the overall project risks. For instance, a commercial building project in London was completed 6 months earlier than planned, saving about 5% on construction costs by switching to modular methods.
Related Reading: 5 Latest Trends in Modular Construction in 2024
#2 Technology Driving Modular Construction Forward
Technology is one of the main reasons modular construction is growing. Tools like Building Information Modeling (BIM), 3D printing, and digital twins are helping the industry move forward. BIM, for example, allows designers to catch errors early in the design process, saving 15%-30% on costs that would otherwise come from fixing mistakes. Harvard Business Review highlights that when BIM is combined with modular construction, projects can be finished faster and at lower long-term costs.
Automation is another key area of progress. Companies like Modular Works in Finland use robotic production lines to make modular units. This has improved their efficiency by 25%, while also making the modules more accurate and consistent. As technology continues to advance, automation and AI will make modular construction even more efficient and cost-effective.
The rise of digital supply chain management is also speeding up modular construction. Real-time monitoring and smarter scheduling allow companies to better track transportation and assembly, reducing delays and losses. For example, some international projects now use digital platforms to manage logistics, helping to cut transportation losses and control costs. One major project managed to keep logistics costs down by keeping transport loss rates below 5%.
#3 Regional Differences and Global Gaps

Although modular construction is growing fast in some parts of the world, its adoption varies widely from region to region. In countries like Finland, Sweden, and Japan, modular construction makes up nearly 50% of the building market. In these places, it’s already a major part of construction. However, in the U.S. and Canada, modular construction still accounts for less than 6% of the market. The American Institute of Architects (AIA) notes that while modular construction offers clear benefits in terms of time, cost, and quality, many developers in North America are still hesitant. They worry about the quality of modular buildings and whether they will last as long as traditional buildings.
Japan, on the other hand, has seen much faster growth. According to the Japan Architecture Association (JAA), modular construction now makes up 15% of the country’s residential market. This is partly because Japan places a high value on speed and quality, and modular construction meets these needs very well.
The difference in adoption rates also reflects local policies and cultural attitudes. For example, countries like the UK and the Netherlands have actively supported modular construction through government programs, which has helped boost its use in not only homes but schools, hospitals, and other public buildings. In contrast, North American markets still tend to favor traditional construction methods, especially in high-end commercial and residential sectors.
#4 Labor Challenges: The Balance Between Technology and People

One of the biggest challenges in the construction industry today is the shortage of skilled labor. According to a survey by the Associated General Contractors (AGC), 56% of U.S. construction firms report labor shortages, especially in skilled trades. This has a direct impact on the pace and quality of traditional construction.
However, modular construction helps address some of these challenges by moving much of the work off-site, to factory settings. This reduces the need for as many on-site workers. Still, the shift to factory-based work means there’s a growing demand for skilled workers to design, engineer, and manage these projects. The American Building Institute (ABI) points out that modular construction requires not just more factory workers, but also specialized talent to coordinate everything from design and manufacturing to on-site assembly.
This shift highlights the need for new training and skills development. As more automation and technology are introduced to modular production lines, traditional construction workers will need to adapt to new, tech-driven roles. This makes it clear that the future of construction will demand a new type of workforce—one that combines technical know-how with digital expertise.
#5 Supply Chain and Logistics: From Factory to Site

Managing the supply chain for modular construction is more complex than for traditional methods. This is because it involves not just manufacturing, but also transporting the modules to the site and assembling them. According to McKinsey & Co., the efficiency of supply chain management directly impacts project timelines and costs. This is particularly true for international projects with higher logistical risks. Problems like module damage or shipping delays can increase costs and cause project delays.
For international projects, the transportation of large, heavy modules presents specific challenges. This often requires specialized transport equipment and infrastructure, which isn’t always available. Research has shown that digital supply chain platforms can help reduce logistics issues, making tracking shipments and managing delays easier. One project managed to keep logistics costs low and reduce transportation losses to below 5%.
#6 Modular Construction and Sustainability: Meeting Modern Environmental Needs

As sustainability becomes a bigger focus in construction, modular construction is gaining attention for its environmental benefits. For one, modular construction reduces waste and pollution since much of the work happens in a factory, where materials are better controlled. According to the World Green Building Council (WGBC), modular construction can cut on-site waste by up to 30%. And because the process is more efficient, modular buildings tend to have a smaller carbon footprint compared to traditional buildings.
Modular buildings also tend to be more energy-efficient. Studies show that they usually have better air-tightness, which leads to lower energy consumption. According to ENERGY STAR™, modular buildings are 5%-10% more energy-efficient than traditional buildings, making them an attractive choice for environmentally conscious projects.
Modular construction is also being explored as a solution to the global housing crisis. Particularly in places where affordable housing is needed quickly, modular buildings offer a cost-effective way to address the problem. UN-Habitat has been experimenting with modular construction in developing regions to create affordable housing for rapidly urbanizing populations.
#7 The Future: Great Potential, but Challenges Remain
While modular construction has many advantages, it still faces several challenges. One of the biggest hurdles is the lack of industry standards. Without clear guidelines, the way modular construction is applied can vary widely between regions. The American Institute of Architects (AIA) also notes that financing remains a barrier, particularly in areas where traditional construction is still the norm. Developers and investors are often unsure about the long-term value of modular buildings, making it harder to secure funding for these projects.
Despite these challenges, the future of modular construction looks bright. As the global demand for housing and infrastructure grows, modular construction offers an efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable solution. According to McKinsey & Co., modular construction could triple its market share by 2030, reaching 15% of the overall construction market. This growth will likely drive major changes in the construction industry.
The potential for modular construction is huge. As cities grow, environmental regulations tighten, and labor costs rise, modular construction is well-positioned to become a mainstream method of building. With advances in technology, better industry standards, and more education for developers, the modular building sector will continue to break down barriers and become a key player in the future of construction.

