Due to their robust, stable, and versatile characteristics, steel structures are extensively utilized in numerous construction projects. However, although steel is strong, it also has a common “enemy” – corrosion.
At this time, steel structure painting is very important. Painting can not only effectively isolate air and moisture and prevent steel from being corroded, but also make the steel structure look more beautiful and meet design requirements.
Here we will provide you with a comprehensive guide to steel structure painting to help you better complete the work of steel structure painting. We will introduce in detail the preparation for painting, material selection, construction methods, and maintenance and care after painting.
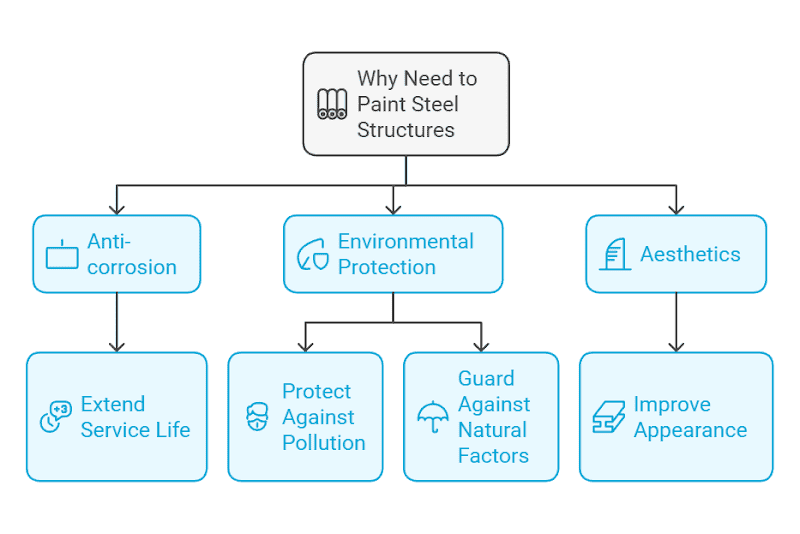
Why paint steel structures
The basis of steel structure painting: surface treatment
Surface treatment is a pivotal step in the painting process, as it directly influences the adhesion and longevity of the coating. If the surface is not clean enough, the paint will not adhere firmly, which may cause the coating to fall off, peel off or age prematurely. Therefore, ensuring that the surface treatment of the steel structure is in place is the basis for obtaining high-quality painting.
The purpose of surface treatment: to remove all impurities that may affect the adhesion of the coating, such as rust, scale and oil. One is to improve the adhesion of the coating and avoid the coating from falling off or peeling off, thereby ensuring the long-term effect of the coating.
Common surface treatment methods
- Sandblasting: This is a common and efficient surface treatment method. By spraying high-speed sand particles to remove rust, scale and old coatings, a clean and rough surface can be cleaned to help the coating adhere better.
- Chemical cleaning: Use solvents or acidic cleaning fluids to remove surface oil, rust and contaminants. It is suitable for stains that cannot be removed by physical methods. Chemical cleaning can penetrate the surface of steel and lay a good foundation for painting.
- Power tool cleaning: Suitable for cleaning small areas or local areas. Common tools include electric grinding wheels, wire brushes, etc., which are suitable for quick cleaning in places with limited space.
Surface preparation standards
In order to ensure the quality of coating, surface preparation must meet certain standards. Common standards include SSPC (Steel Structure Coating Engineering Association) and ISO standards. For example:
- SSPC-SP 6: Clear to standard cleaning level, suitable for heavy cleaning requirements.
- SSPC-SP 10: Nearly perfect cleanliness, usually used in situations requiring the highest coating quality.
Our steel structure products strictly follow these surface treatment standards to ensure that the coating quality meets international certification requirements and provides customers with long-lasting protection and excellent performance.
What Paint is Used on Structural Steel?
Choosing the right paint for structural steel is essential to ensure long-term protection and durability. The right combination of primer, intermediate coat, and topcoat provides the necessary defense against corrosion, UV degradation, and other environmental factors. Let’s break down the common types of paints used for steel structures.
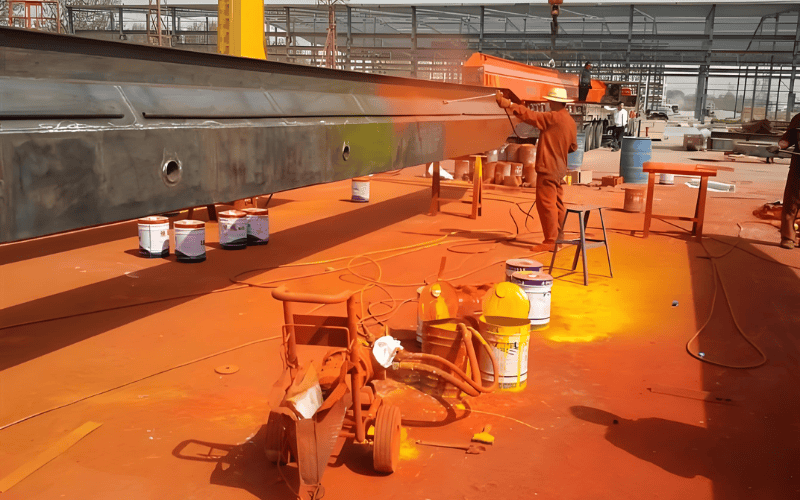

1. Primer
Epoxy Zinc-Rich Primer: This type of primer contains zinc particles that provide cathodic protection, preventing corrosion. The zinc functions as a sacrificial anode, undergoing corrosion first to safeguard the underlying steel. This method is frequently employed in harsh environments.
Inorganic Zinc-Rich Primer: Known for its high durability in harsh environments, inorganic zinc-based primers offer excellent resistance to extreme conditions such as high humidity, salty air, or industrial pollution.
2. Intermediate Coat
Epoxy Mica Iron Oxide Intermediate Coat: This paint provides barrier protection, helping to increase the overall thickness of the coating. It is designed to enhance the durability and resistance to moisture and corrosion, forming an effective intermediate layer that strengthens the coating system.
3. Topcoat
Polyurethane Topcoat: Known for its outstanding UV resistance and color retention, polyurethane topcoats are often chosen for steel structures exposed to sunlight. They not only provide a beautiful finish but also help protect the coating system from UV damage, ensuring that the color does not fade quickly.
Fluorocarbon Coatings: Offering exceptional weathering resistance, fluorocarbon coatings are ideal for extreme environmental conditions, including industrial zones and coastal areas. They offer durable protection against UV radiation, moisture, and environmental pollutants.
4. Special Coatings
Zinc-Rich Coatings: These coatings are especially effective in highly corrosive environments, such as marine settings or areas exposed to salt. Zinc-rich coatings offer galvanic protection, similar to the zinc primer, but in a complete topcoat form.
Acrylic Coatings: Acrylic paints are ideal for decorative purposes or areas with low maintenance needs. They offer good color vibrancy and moderate protection, often used in applications where appearance is more important than extreme durability.
What is the Best Paint for Steel Buildings?
The best paint for steel buildings depends on the specific environment and performance requirements:
- For highly corrosive environments, such as coastal or industrial areas, a combination of inorganic zinc-rich primer and fluorocarbon topcoat would offer the highest durability and weather resistance.
- For general use, an epoxy zinc-rich primer with a polyurethane topcoat provides a balanced solution of corrosion protection and UV resistance, ensuring the steel structure lasts long while maintaining a good appearance.
Ultimately, the choice of paint should align with the building’s exposure to environmental factors, its location, and the required maintenance intervals.
How to paint steel structures?
There are many methods for painting steel structures, and the terminal method is suitable for different situations. The specific choice should be determined based on factors such as the painting area, the complexity of the steel structure, and the type of paint being utilized. Here are several common painting methods:
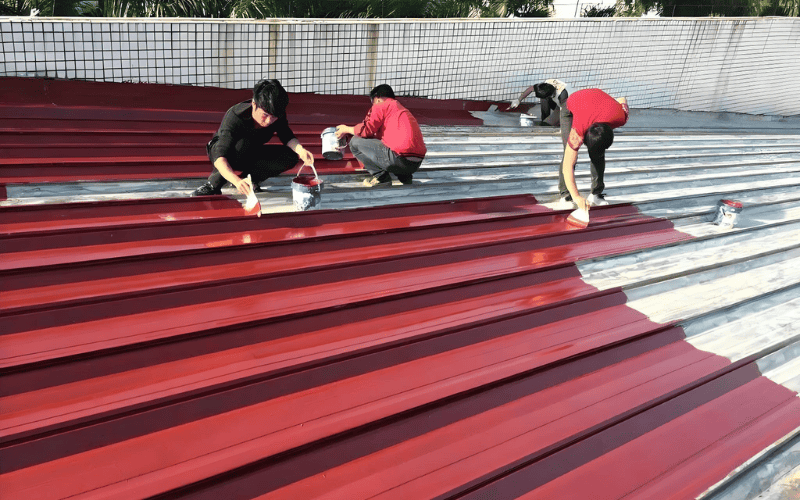

Spraying
- Airless spraying: This method is suitable for large-area painting, with high efficiency and uniform coating. Airless spraying uses a high-pressure pump to atomize the paint and compress the air, which can quickly form a large area, such as beams, steel columns and other structures.
- Air spraying: Suitable for parts with complex shapes or requiring fine painting. Air spraying uses air to spray the paint, which can provide better control and is suitable for purple, edges and other places that are difficult to approach.
Brushing and rolling
For small-scale painting or local repairs, brushing and rolling are simple and common methods. Although slower than spraying, brushing and rolling are suitable for small-scale touch repairs or surface painting details, especially when working on site, and can effectively solve difficult-to-spray areas.
Impregnation
An important part of the dip coating method is to completely immerse the workpiece in the coating, which is suitable for complex or irregular workpieces. Dip coating can ensure that each surface is treated evenly, especially in shapes and places that are difficult to coat, the effect is better.
Powder coating
Powder coating is to adsorb powder coating to the coating surface by electrostatic spraying, and then heat and cure to form a uniform and durable coating. This method is suitable for occasions that require coating uniformity and easy occurrence, and is common in industrial equipment, decorative steel structures, etc.
As a professional steel structure supplier, we not only provide high-quality steel products, but also provide customers with a full range of coating services. Whether it is the application of anti-corrosion coatings or weather-resistant coatings in special environments, we can provide customized coating solutions according to customer needs.
Our coating team has rich experience and can use various coating methods such as spraying, brushing and dipping to ensure that the surface of the steel structure is effectively protected, extend the service life and improve the aesthetics.
Factors affecting steel structure painting
During the coating process of steel structures, the following factors will directly affect the coating effect and durability:
1. Temperature and humidity
The ideal coating conditions are temperatures above 5°C and humidity below 85%. Too low a temperature will cause the coating to dry incompletely, while too high a temperature may cause the coating to dry too quickly, affecting adhesion. When the humidity is too high, moisture can cause coating quality problems, such as blistering or peeling.
2. Dew point
The dew point is the temperature at which water vapor in the air begins to condense. When coating, ensure that the surface temperature of the steel is higher than the dew point, otherwise moisture may condense on the surface of the steel, affecting the adhesion and anti-corrosion effect of the coating, resulting in a decrease in coating quality.
3. Corrosive environment
Different environments have different degrees of corrosion on steel structures, so environmental factors need to be considered when choosing coatings. According to the ISO 12944 standard, the corrosion environment in which steel structures are located can be divided into several levels (such as C3, C4, C5, etc.).
- C3 environment: moderately corrosive environment, such as cities and light industrial areas.
- C4 environment: highly corrosive environment, such as industrial areas and areas with heavy traffic.
- C5 Environment: An extremely corrosive environment, including coastal regions or chemical industrial zones.
Based on your project requirements, we can help you choose the right coating to ensure that the steel structure can resist environmental erosion and achieve the best protection effect.

Quality control and inspection of steel structure painting
Ensuring the quality of painting is a key link in the painting process. The following aspects are the focus of quality control and inspection:
Dry film thickness (DFT): DFT is the final thickness of the coating after completion. It is imperative to guarantee that the coating attains the thickness stipulated by the design. This is measured using specialized instruments to ascertain the protective efficacy and longevity of the coating.
Wet film thickness (WFT): The thickness of the coating just applied. During the painting process, the WFT should be monitored in real time and the coating amount and method should be adjusted to ensure that the final DFT meets the requirements.
Visual inspection: After painting, visual inspection is required to check whether the coating is uniform, whether there are bubbles, cracks, peeling or incomplete coating. Any visible defects need to be repaired.
Adhesion test: Coating adhesion is a key indicator to evaluate the bonding strength between the coating and the steel surface. Common adhesion test methods include cross-cutting or pulling methods to ensure that the coating is firmly attached and avoid coating shedding due to environmental factors.
The steel structure products we provide are strictly inspected to ensure that each coating meets high standards, achieves the best protection effect, and meets customer needs and industry requirements.
Steel structure painting maintenance
The effect of steel structure coating not only depends on the quality of the initial coating, but also requires proper maintenance and care during use. The following are several key steps for coating maintenance and long-term care:
- Regular inspection: Regularly check the status of the coating, especially in exposed areas. Check for signs of wear, cracks, bubbles or other damage, and detect potential problems in time to avoid small problems from turning into large corrosion risks.
- Local repair: For small areas of damage found, repairs should be made in time. Through local repairs, the protection of the coating is supplemented, the damage area is prevented from continuing to spread, and the long-term protection effect of the steel structure is ensured.
- Re-coating: Over time, the protective performance of the coating may gradually decrease. Re-coat in time according to environmental conditions and the wear of the coating.
- Use environmentally friendly coatings: Environmentally friendly coatings can not only decrease the emission of harmful substances but also minimize the waste produced during the coating application process.
Through these maintenance and care measures, you can ensure the long-term effectiveness of steel structure coatings, extend the service life, reduce maintenance costs, and improve the overall performance of the structure.
Alternatives to Steel Structure Painting
In addition to traditional painting methods, there are some alternatives that can provide long-term protection for steel structures, especially under some special needs and environmental conditions. The following are several common alternatives:
1. Hot-dip galvanizing
Hot-dip galvanizing is to immerse steel in molten zinc so that the zinc layer forms a chemical bond with the steel, thereby providing long-term corrosion protection. This technique can create a robust protective layer on the steel surface, making it particularly suited for highly corrosive environments like coastal regions and chemical plants. Hot-dip galvanizing is not only durable, but also reduces the frequency of painting maintenance.
2. Arc spraying zinc
Arc spraying zinc melts the zinc material and sprays it onto the surface of the steel using an electric arc to form a protective film. This method is suitable for large structures or areas that are difficult to paint, such as viaducts, towers, etc. Arc spraying zinc is flexible in operation, can be carried out on site, and can provide good corrosion protection.
3. Pre-coating primer
Pre-coating primer is a temporary coating that is usually used for short-term protection of steel during steel manufacturing and transportation. This primer can protect steel from corrosion or other damage during transportation and is particularly suitable for steel that needs to be further coated at the construction site.
Practical application of steel structure coating

Bridge coating: Bridges are often exposed to harsh environments such as high humidity and salt spray. By using anti-corrosion coatings such as epoxy primers and weather-resistant topcoats, the life of bridges can be extended and corrosion and damage can be effectively prevented.
Industrial facilities: Steel structures in chemical plants and refineries face highly corrosive environments. The use of high-temperature resistant and anti-corrosion coatings can protect steel structures from chemicals and high temperatures, reduce maintenance costs and extend service life.
Building steel structures: In modern buildings, steel structures require not only bearing capacity but also aesthetics. High-quality coatings can enhance the appearance of steel while enhancing corrosion resistance and ensuring the long-term durability of the building.
Investing in high-quality steel structure coatings not only improves the corrosion resistance and damage resistance of the structure, but also improves the overall aesthetics and safety of the building.
If you are considering a steel structure coating project, we recommend that you consult our professionals and strictly follow industry standards to ensure the best coating effect and achieve lasting protection.

