Steel structures are the foundation of modern construction, providing unmatched strength and versatility. But here’s the thing—they don’t just stay reliable on their own. Regular inspections are crucial for ensuring their safety, durability, and adherence to specifications.
In this article, we will walk you through the main types of steel structure inspections, how they’re done, and why they matter. Whether you’re an engineer, architect, or project manager, understanding these checks is vital to ensuring your structures remain of the highest quality.
1. Material Inspection: The Foundation of Quality
Before any steel component becomes part of a structure, its material properties must be thoroughly evaluated. This step guarantees that the steel meets the necessary standards and is capable of withstanding the intended loads.
Chemical Composition Analysis
Advanced tools like spectrometers can be used to analyze carbon, silicon, manganese, sulfur, and phosphorus levels in steel. These elements have a direct impact on the material’s strength, weldability, and resistance to environmental factors. For instance, excessive sulfur can lead to brittleness, while the right carbon content enhances strength.
Mechanical Properties Testing
Mechanical tests, such as tensile, impact, and bending tests, provide critical data on the steel’s performance. Tensile tests assess yield strength and elongation, while impact tests measure toughness at low temperatures. These results allow us to confirm that the steel can withstand both static and dynamic loads without failure.
2. Welding Quality Inspection: Ensuring Structural Integrity
Welding is a critical process in steel construction, and its quality can make or break a structure. Even the smallest defect in a weld can compromise the entire system.
Visual Inspection
The first step consists of a thorough visual inspection of the weld surface. Common issues such as cracks, porosity, undercutting, and incomplete fusion are identified during this process. Although this method is simple, it is highly effective in detecting surface-level defects.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
For a more in-depth analysis, NDT techniques are employed:
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT): Ideal for detecting internal flaws in thick welds, such as cracks or inclusions.
- Radiographic Testing (RT): It uses X-rays or gamma rays to generate detailed images of internal defects.
- Magnetic Particle Testing (MT): It is effective for detecting surface and near-surface flaws in ferromagnetic materials.
- Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT): Used to identify surface cracks in non-porous metals.
Destructive Testing
In some cases, it’s recommended to perform destructive tests on sample welds to assess their mechanical properties. While these tests aren’t conducted on the actual structure, they offer valuable insights into weld strength and ductility, helping to ensure the overall integrity of the welding process. For example, a tensile test is often used, where a sample weld is stretched until it breaks, providing critical data on how the weld performs under stress.
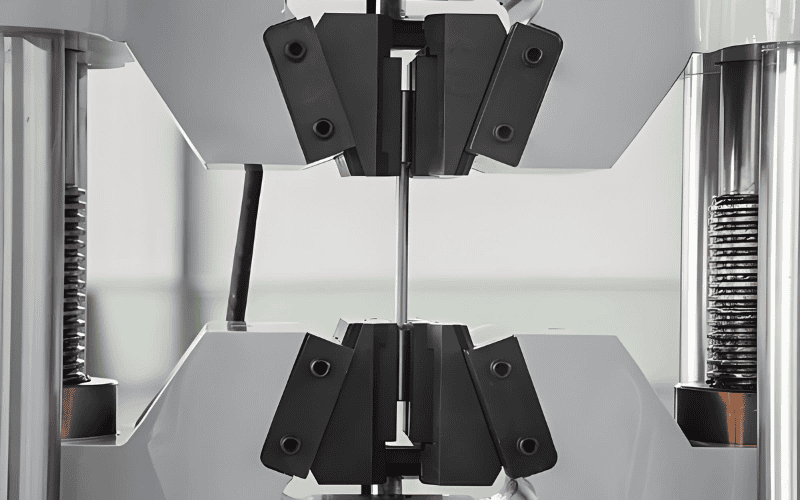
3. Bolt Connection Inspection: The Key to Stability
Bolted connections are a cornerstone in the assembly of steel structures, and their performance is directly tied to proper installation and ongoing maintenance. Ensuring these connections are secure is essential for the overall stability and safety of the structure.
Visual and Installation Checks
A thorough inspection should include all types of bolts used in steel structures, such as high-strength bolts, anchor bolts, and standard bolts. Key checks include looking for cracks, corrosion, and thread integrity.
For high-strength bolts, ensure pre-tensioning aligns with design specifications.
For anchor bolts, check for proper embedding and alignment with the foundation. Even a slightly loose or improperly installed bolt—whether it’s high-strength or a regular bolt—can lead to joint failure, making this step crucial.
Friction Surface Testing
For high-strength bolted connections, testing the slip coefficient of friction surfaces is important to ensure the connection can resist shear forces and maintain stability under load.
For regular bolts and anchor bolts, while friction testing is less critical, checking the condition of the contact surfaces and ensuring correct torque is applied during installation are essential steps to prevent structural issues.
For more insights, take a look at our related article: Steel Connections in Steel Structure Buildings.
4. Dimensional and Deformation Inspection: Precision Matters
Even minor deviations in dimensions or alignment can significantly impact a structure’s performance. Ensuring accuracy in these areas is crucial for preserving structural integrity and functionality.
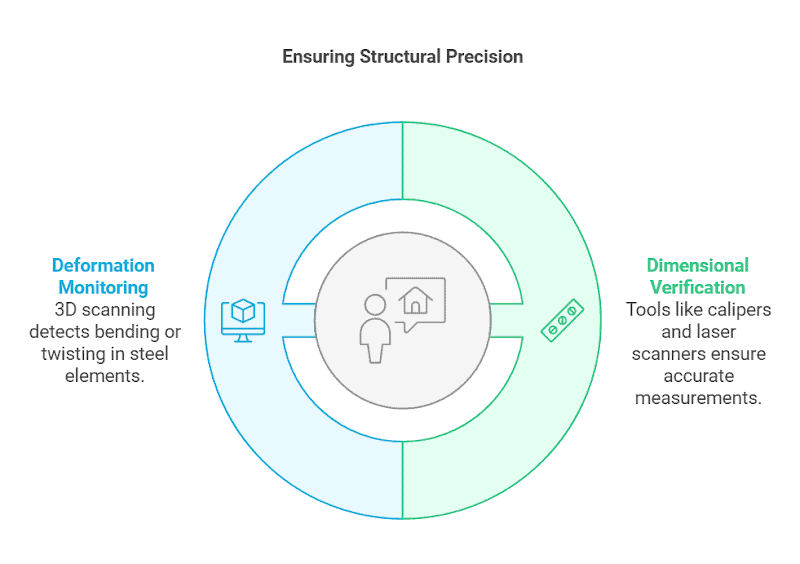
Dimensional Verification
It is advisable to use tools like calipers, laser scanners, and total stations to measure the length, width, thickness, and other dimensions of steel components. This step ensures that every piece aligns precisely with the design specifications, minimizing the risk of installation errors or structural weaknesses.
Deformation Monitoring
Over time, steel elements may experience bending, twisting, or sagging due to loads or environmental factors. Advanced surveying techniques, such as 3D laser scanning or digital photogrammetry, should be employed to continuously monitor these deformations. Early detection of excessive deformation allows for timely corrective measures, preventing potential structural failures.
5. Corrosion and Fire Protection Inspection: Longevity Assurance
Steel structures are often exposed to harsh environments, making corrosion and fire protection critical for ensuring their longevity and safety.
Related Reading: Fire Prevention for Steel Structures
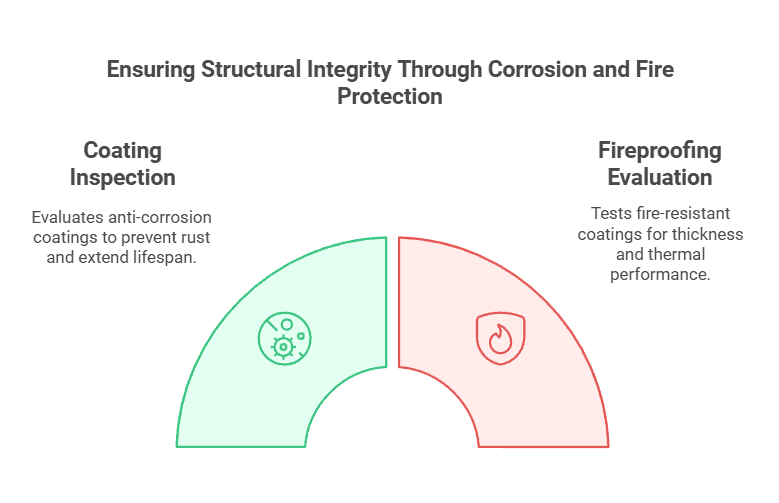
Coating Inspection
Measuring the thickness of anti-corrosion coatings using specialized instruments such as ultrasonic thickness gauges or magnetic induction coating thickness testers is recommended. Additionally, adhesion tests like cross-cut or pull-off tests should be performed to assess the bond strength between the coating and the steel surface.
A well-applied and properly maintained coating can significantly extend the structure’s lifespan by preventing rust and degradation.
Fireproofing Evaluation
Fire-resistant coatings should be tested for thickness, integrity, and thermal performance. Using advanced techniques, such as thermal imaging or flame exposure tests, ensures that these coatings can withstand high temperatures as per design requirements, providing critical protection in fire scenarios.
6. Seismic Performance Inspection: Preparing for the Unexpected
In earthquake-prone areas, seismic performance is a top priority.
We conduct specialized inspections of seismic connections and components to ensure they can absorb and dissipate energy during an earthquake. This includes checking the integrity of braces, dampers, and moment-resisting frames.
For a deeper dive into this topic, explore our article: Seismic Resistance in Steel Structures.
Steel Structure Inspection and Performance Assurance
At SteelPRO PEB, we understand that the safety and durability of a steel structure depend on meticulous inspection processes. From material testing to seismic performance evaluations, every step is designed to ensure that our structures stand the test of time. What sets us apart is our commitment to comprehensive structural performance testing, including static and dynamic load tests and modal analysis, which help us validate our designs and optimize for real-world conditions.
By following stringent standards and utilizing advanced technologies, we provide steel solutions you can rely on for decades. For more information on our inspection processes or to discuss your next project, feel free to reach out to our team. Together, we can create structures that are not only strong but also safe and sustainable.
Common Questions About Steel Structure Inspection
How do you inspect a steel structure?
Inspections involve a combination of visual checks, non-destructive testing, and performance evaluations to ensure compliance with design and safety standards.
What are the testing procedures for structural steel?
Procedures include material testing, weld inspections, bolt connection checks, and load testing, among others.
What is the NDT test for steel structures?
Non-destructive testing methods like ultrasonic, radiographic, and magnetic particle testing are used to detect flaws without damaging the structure.
What is the significance of load testing in steel structures?
Load testing is used to evaluate how much weight or pressure a steel structure can bear before failure. It helps ensure the structure can handle the intended loads, both static (constant) and dynamic (changing), without compromising safety or performance.
How often should steel structures be inspected?
Steel structures should be inspected according to their age and the environmental conditions they are exposed to. New structures need an inspection within 1 year, then annually for 5 years. Mature structures (5-20 years) should be checked every 2 years, and older ones (20+ years) every 1-2 years. In harsh conditions, inspections should be conducted more frequently, with additional checks following major events.

