Wondering what the best material for your solar panel structure is? The answer depends on factors like your project’s size, budget, and location. Whether you’re installing solar panels at home or managing a commercial project, the material you choose will directly affect the system’s durability, performance, and long-term savings.
In this article, we’ll help you make an informed decision by comparing common materials like steel, aluminum, galvanized steel, stainless steel, and concrete. By the end, you’ll know exactly which material is best for your solar installation, ensuring a reliable, cost-effective, and long-lasting system.
What to Expect in This Blog:
What Are Solar Panel Structures and Why Do They Matter?
Solar panel structures are the frameworks that support and secure solar panels, ensuring they stay in place, absorb sunlight efficiently, and endure harsh weather conditions. These structures can be installed on rooftops, on the ground, or even on other surfaces, depending on the type of system you’re setting up.
Choosing the right material for these structures is crucial. It affects the durability of the system, how well it resists weather conditions like rain, snow, and strong winds, and even how cost-effective the overall setup is. A good structure not only helps secure the solar panels, but it also plays a big role in the performance and longevity of the solar system.
Whether you’re working on a residential rooftop system or a large commercial installation, selecting the best material ensures that your solar panel system will stay reliable and efficient for many years to come. The right choice also helps keep maintenance costs low, as some materials may require less upkeep over time.
Now, let’s dive into the key factors you should consider when choosing a material for solar panel structures.

Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Solar Panel Structure Materials
When it comes to selecting the material for your solar panel structure, there are several key factors that directly impact your decision. These factors will help ensure the structure is strong, cost-effective, and suitable for your specific installation needs. Let’s take a look at the most important aspects to keep in mind:
Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
The material you choose needs to support the weight of the solar panels, which can be quite heavy, especially for larger systems. It’s essential that the structure can handle not just the weight of the panels themselves but also any additional loads, such as snow or wind pressure. Materials like steel and galvanized steel are often preferred for their high strength and load-bearing capacity, especially in commercial installations or large solar farms.
Weather Resistance
Solar panel structures are exposed to outdoor elements day in and day out. The material needs to resist corrosion, rust, and UV damage from the sun. For example, aluminum is naturally corrosion-resistant, making it a good option for coastal areas with salty air. On the other hand, galvanized steel is coated with a layer of zinc, providing excellent protection against rust, making it ideal for areas with high moisture or fluctuating weather conditions.
Cost and Budget Considerations
While strength and weather resistance are key, it’s also important to consider your budget. Some materials may have a higher upfront cost but could save you money in the long run due to their durability and low maintenance requirements. For instance, steel is generally more affordable than stainless steel but still offers great strength and corrosion resistance. Balancing cost with the expected lifespan of the material is crucial for getting the best value.
Ease of Installation
Installation can be a time-consuming and costly process, so it’s worth considering how easy it is to work with the chosen material. Aluminum, being lightweight, is easier to handle and install compared to heavier materials like steel. This can save on labor costs and reduce installation time. However, if the project requires very strong and stable support, materials like steel may be more suitable despite the extra weight.
Longevity and Maintenance
Lastly, the long-term performance of the structure is a major factor. Some materials, like stainless steel, may cost more initially but will last longer and require less maintenance. On the other hand, materials like aluminum may need occasional cleaning but generally offer a longer lifespan than other options that could corrode more quickly in certain climates.
By keeping these factors in mind—strength, weather resistance, cost, ease of installation, and longevity—you’ll be able to make a more informed choice on which material works best for your solar panel structure. Each factor plays a role in the overall performance and lifespan of the solar system, so it’s important to prioritize what matters most for your specific situation.
Common Materials Used for Solar Panel Structures
Now that we’ve covered the key factors to consider when choosing a material for solar panel structures, let’s take a closer look at the most common materials used. Each material has its own set of strengths and weaknesses, and the right choice for your system depends on factors like installation type, climate, and budget. In this section, we’ll explore the most widely used materials, their advantages, and where they’re best applied.
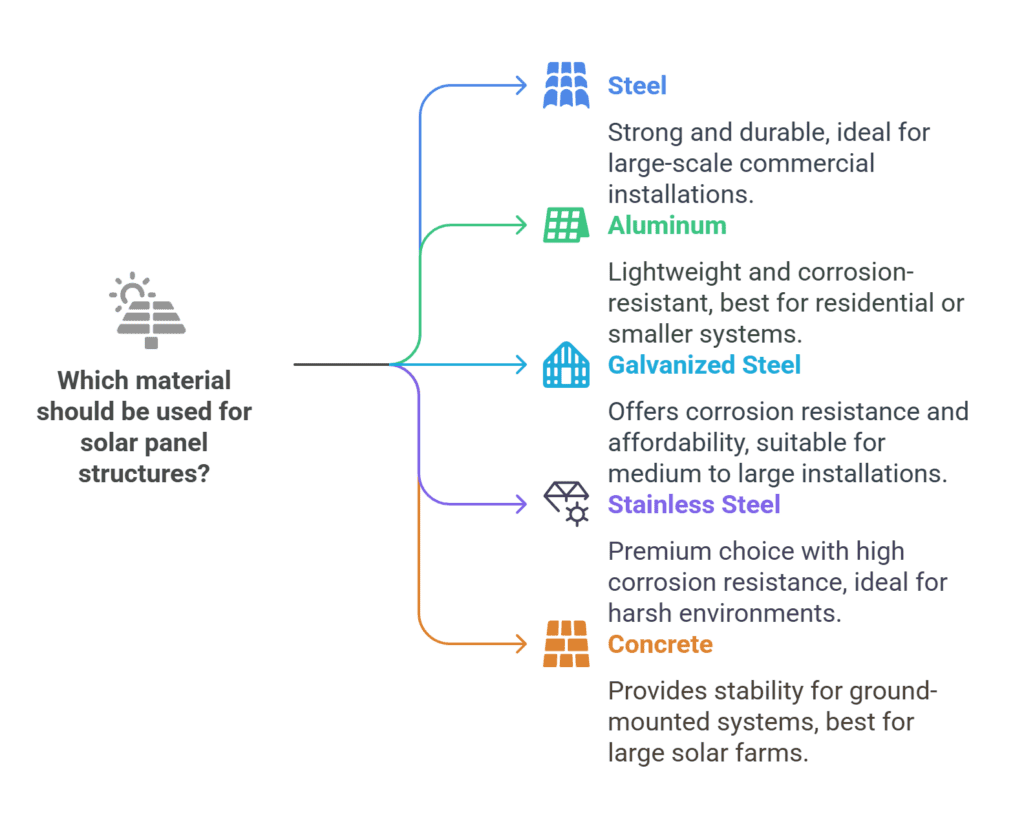
Steel
Steel is one of the most commonly used materials for solar panel structures, especially in large-scale commercial installations. It’s known for its strength and load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for systems that need to withstand harsh conditions.
Pros:
- Strong and durable, able to support large solar arrays
- Excellent resistance to weathering, especially when treated (galvanized or powder-coated)
- Widely available and relatively affordable
Cons:
- Heavier than other materials, which can make installation more challenging
- Can corrode if not properly treated (hence the need for galvanization)
Best For: Large-scale commercial solar farms or systems in areas where high strength is a priority. Galvanized steel is particularly useful in regions with high moisture.
Aluminum
Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to work with, making it a popular choice for residential and smaller solar systems.
Pros:
- Lightweight, making installation easier and faster
- Naturally corrosion-resistant, ideal for coastal or humid environments
- Low maintenance and high durability over time
Cons:
- Generally more expensive than steel
- Not as strong as steel for large, heavy installations
Best For: Residential solar installations or small-scale commercial projects, especially in coastal or humid climates where corrosion resistance is key.
Galvanized Steel
Galvanized steel is regular steel coated with a layer of zinc, which provides extra protection against rust and corrosion, making it a more durable choice than untreated steel.
Pros:
- Good corrosion resistance, even in humid or rainy climates
- Affordable and strong
- Ideal for medium to large-scale installations
Cons:
- Heavier than aluminum, which can complicate installation
- While resistant to corrosion, it can still corrode under extreme conditions if the coating is damaged
Best For: Areas with moderate to high rainfall or humidity, where durability and rust resistance are crucial but the cost needs to be kept down.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a premium material known for its high corrosion resistance and long lifespan. It’s a great choice for installations in very harsh environments, such as coastal areas or places with extreme weather.
Pros:
- Excellent resistance to rust and corrosion
- Very durable, with a long lifespan
- Requires minimal maintenance
Cons:
- More expensive than both galvanized steel and aluminum
- Heavier, which could increase installation time and labor costs
Best For: Areas with extreme weather conditions, coastal environments, or situations where the system must last many decades with minimal maintenance.
Concrete (for Ground-Mounted Systems)
Concrete is used primarily in ground-mounted solar systems. It’s a heavy-duty material that provides great stability and durability for large-scale solar farms.
Pros:
- Extremely stable and durable
- Excellent at handling extreme weather conditions
Low maintenance once installed
Cons:
- Very heavy, making transportation and installation more expensive and complex
- Not as flexible or adjustable once installed
Best For: Large ground-mounted commercial solar farms or installations in areas where soil stability is a concern.
Which Material is Best for Your Solar Panel System?
Now that you have an idea of the materials commonly used for solar panel structures, it’s time to dive into how to choose the best one for your specific project. The right material depends on several factors, including the type of installation (residential or commercial), the installation surface (roof or ground), and environmental conditions. Let’s break it down based on different scenarios:

Residential Installations
If you’re setting up solar panels on your home, your main considerations will likely be cost, lightweight options, and ease of installation. In this case, aluminum is often the best choice. It’s easy to handle, resistant to corrosion, and doesn’t weigh as much as steel, making it ideal for roof installations where weight can be a concern. While aluminum may be slightly more expensive than steel, its long-term durability and low maintenance make it a solid investment.
However, if you’re on a tighter budget and need a more affordable option, galvanized steel can still be a great choice for residential systems. It offers good corrosion resistance, especially in areas with moderate weather conditions, and provides excellent strength at a lower cost than stainless steel.
Commercial Installations
For larger-scale installations, especially in commercial solar farms, steel or galvanized steel is often the preferred choice due to their strength and load-bearing capacity. Commercial installations often require materials that can support heavy, large arrays and withstand the elements for many years. While stainless steel offers the best corrosion resistance and longevity, its higher cost may not always be justified for most commercial applications. Instead, galvanized steel offers a good balance of affordability and durability.
In regions where extreme weather is a concern, like coastal areas with high humidity or salt in the air, stainless steel may be worth the investment for its superior rust resistance and long-term durability.
Roof-Mounted vs. Ground-Mounted Installations
The choice of material may also depend on whether your solar system is roof-mounted or ground-mounted.
- For roof-mounted systems, where weight and ease of installation are more critical, aluminum is often preferred. Its lightweight nature helps reduce the load on your roof, and it’s relatively easy to handle during installation.
- For ground-mounted systems, where the structure doesn’t need to account for weight limitations, steel or concrete might be better suited. Concrete is especially popular for large commercial ground-mounted systems as it provides excellent stability, while steel offers great strength to handle large panels and withstand wind and weather conditions.
Environmental Considerations
Different environmental conditions can significantly affect the material choice. For example:
- Coastal Areas: If your solar system is near the ocean, materials like aluminum or stainless steel are ideal due to their excellent resistance to saltwater corrosion.
- Wet or Humid Areas: In places with frequent rain or high humidity, galvanized steel or stainless steel will offer better protection against rust and corrosion.
- Extreme Weather: For regions with strong winds, snow, or high temperatures, steel (either galvanized or stainless) is often the preferred choice due to its strength and ability to handle heavy loads.
By understanding your installation needs and environmental conditions, you can make a more informed decision about which material will give your solar panel structure the best performance and longevity.
Emerging Trends: What’s Next in Solar Panel Structure Materials?
The solar energy industry is constantly evolving, and as technology advances, so do the materials used in solar panel structures. Several emerging trends are reshaping the way solar systems are designed and built. Let’s explore the most exciting developments that could change the future of solar panel structures:
New Alloys and Composite Materials
One of the most promising trends in solar panel structure materials is the development of new alloys and composite materials. These materials combine the strength and durability of metals like steel with the lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties of polymers or composites. By using these innovative materials, solar structures can become both lighter and stronger, offering improved performance without sacrificing stability.
For example, advanced titanium alloys or carbon fiber composites are being tested for their potential to offer high strength-to-weight ratios, ideal for applications where weight is a concern, such as roof-mounted systems. These materials could lead to smaller, lighter structures that are easier to install and more cost-effective over the long term.
Lightweight and Flexible Materials
The demand for more flexible and lightweight materials is growing, especially for solar panel systems in areas with space constraints or challenging installations. Flexible solar panel structures, made from materials like carbon fiber or fiberglass, are increasingly being developed. These materials allow for easier adjustment and customization of solar panel placements, enabling panels to be integrated into unconventional spaces like curved roofs or unique architectural designs.
Lightweight materials also reduce the overall load on structures, making them particularly attractive for roof-mounted installations, where weight and roof integrity are key concerns. As these materials become more widely available, they could drive more innovation in solar integration into buildings, offering new possibilities for urban and residential solar applications.
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Materials
As sustainability becomes a higher priority in the construction and energy sectors, the solar industry is focusing on eco-friendly and sustainable materials. Many manufacturers are working on creating materials that not only last longer but are also made from renewable or recycled resources. For example, recycled steel and biodegradable composite materials are being explored as ways to reduce the environmental impact of solar installations.
The move towards more sustainable materials is also driven by the desire to minimize the carbon footprint of solar panel systems. The production process of some traditional materials, like steel or aluminum, can be energy-intensive. As eco-friendly materials become more affordable, the solar industry will be able to offer greener, more environmentally responsible options for consumers.
Cost-Effective Materials Technology
One of the key trends in emerging solar panel structure materials is the drive towards cost-effective solutions. New technologies are making it possible to create high-quality materials at lower costs. For example, 3D printing technologies are being used to create customized solar panel mounts and structures that can be produced at a fraction of the cost of traditional manufacturing methods.
Additionally, mass production of certain materials is driving down costs. As manufacturers scale up production of new alloys or composite materials, their prices will likely drop, making them more accessible to homeowners and businesses alike. This trend will make advanced solar systems more affordable, potentially expanding the market for solar energy even further.
Conclusion
Choosing the right material for solar panel structures is more than just a technical decision—it’s a key factor in ensuring the long-term success and reliability of your solar system. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to maximize efficiency on your roof, or a business investing in a large-scale solar farm, understanding the strengths, weaknesses, and applications of different materials will help you make smarter, more cost-effective choices.
The future of solar panel structures is exciting, with emerging materials offering new possibilities for lighter, stronger, and more sustainable solutions. From advanced composites to eco-friendly innovations, these trends are not just about improving performance—they’re about making solar energy more accessible, affordable, and environmentally responsible for everyone.
As the industry evolves, staying informed about the latest material developments can give you a competitive edge. By understanding both current options and future trends, you’ll be better equipped to build a solar system that not only meets today’s needs but also adapts to tomorrow’s challenges. Choose wisely, and your investment will continue to pay off for years to come—both in energy savings and in contributing to a greener, more sustainable future.

