A gable roof remains one of the most practical and recognizable roof designs, but what are its real advantages and drawbacks in today’s construction? This guide explores every key aspect: what defines a gable roof, how it performs across different climates, its benefits in strength, ventilation, and cost-efficiency, and where its limitations appear. You’ll also discover the main gable roof types and how prefabricated and steel applications have transformed their durability and installation efficiency.
Drawing from SteelPRO PEB’s decade of manufacturing and engineering experience, this article translates technical expertise into practical insight, showing how advanced steel framing, certified fabrication, and global project data reshape the traditional “pros and cons” perspective. Whether you’re planning a home, warehouse, or modular cabin, understanding gable roofs through a structural and factory-engineered lens will help you choose the most reliable and cost-effective solution.
What is a Gable Roof?
A gable roof, also known as a pitched, peaked, or A-frame roof, is one of the most recognizable and practical roof styles. It features two sloping sides that meet at a central ridge, creating a triangular end wall known as the gable.
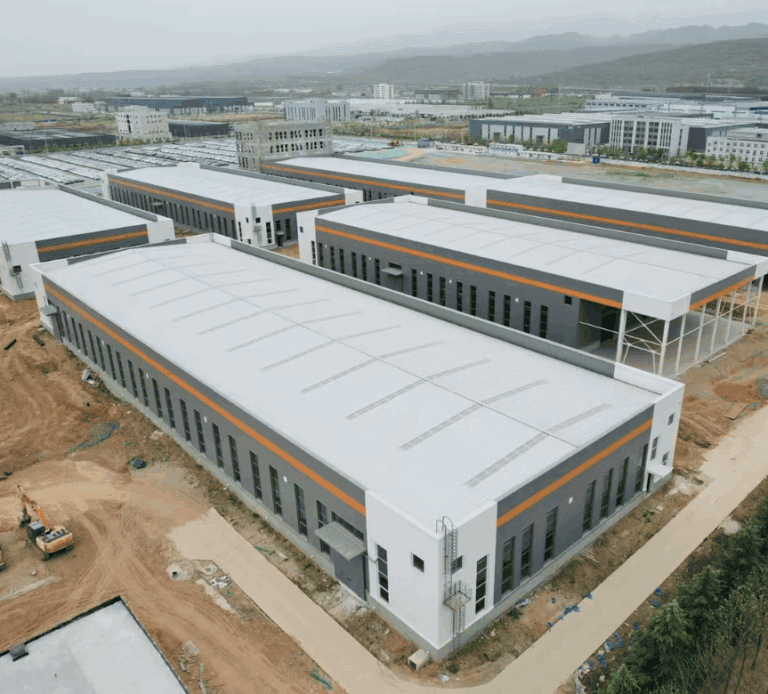
This simple geometry offers structural efficiency: steeper slopes shed snow and rain effectively, while moderate angles balance drainage with cost. Gable roofs are found in everything from homes to warehouses and are especially valued in steel and PEB (Pre-Engineered Building) structures, where the design enhances durability, speeds up construction, and optimizes material usage.
In modern prefabricated steel buildings, the gable form remains one of the most cost-efficient and weather-resistant profiles, making it ideal for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
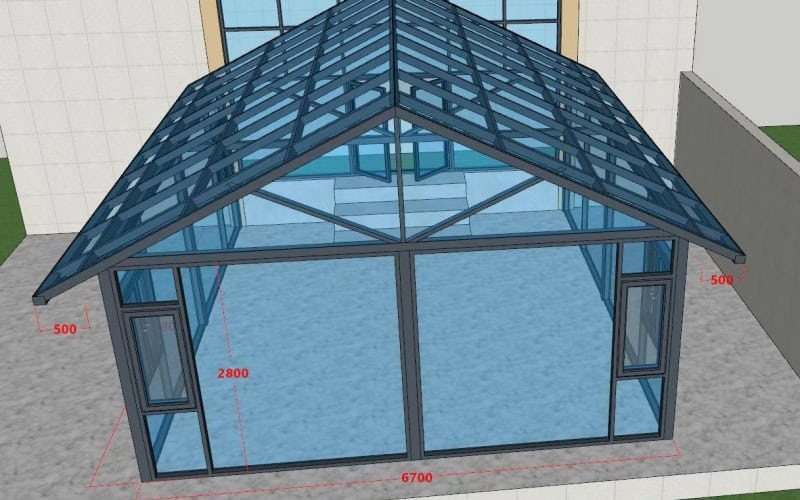
Advantages of Gable Roofs
Gable roofs have long been favored for their simplicity, efficiency, and cost-performance ratio—qualities that make them particularly well-suited for prefabricated and steel-framed buildings.
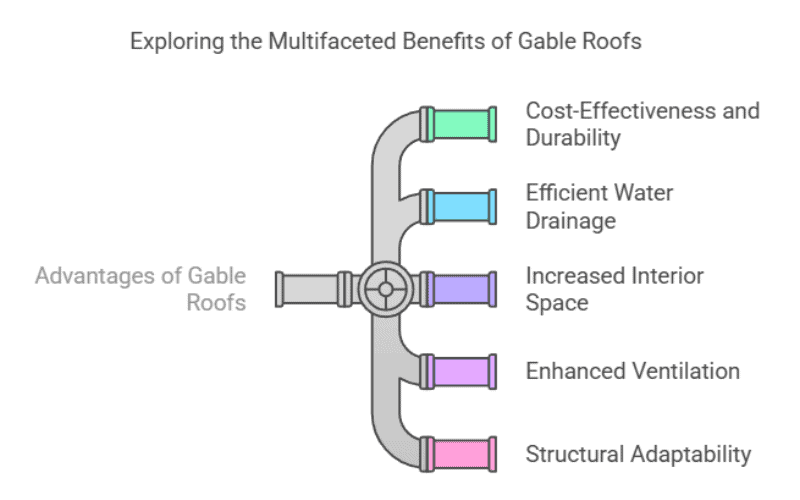
Cost-Effectiveness and Durability
The clean triangular structure of a gable roof minimizes material waste and simplifies installation, making it one of the most economical roof forms available. In practice, prefabricated steel gable roofs can reduce total project costs by up to 20%, especially when produced in large-scale manufacturing lines like SteelPRO PEB’s 120,000-ton annual facility. Combined with corrosion-resistant coatings and precise fabrication, these roofs provide decades of performance with minimal maintenance.
Efficient Water Drainage
The steep slope design naturally channels away rain and snow, preventing leaks and extending the lifespan of roof materials. For PEB and steel structures, this drainage efficiency reduces structural load stress and ensures long-term waterproofing reliability.
Increased Interior Space
The elevated ridge allows for additional headroom—ideal for ventilation, mezzanine storage, or even HVAC integration. This feature is especially useful in industrial or warehouse designs where vertical clearance translates directly into usable space.
Enhanced Ventilation
Warm air naturally rises to the ridge, where it can escape through vents or ridge openings. In climates with high humidity or heat, this airflow maintains thermal comfort and prevents condensation—important for metal buildings where insulation continuity matters.
Structural Adaptability
Gable roofs perform reliably across climates—from high-snow regions requiring steep pitches to tropical areas preferring moderate slopes. In PEB structures, this adaptability allows engineers to customize the roof geometry for load balance, cost efficiency, and assembly speed, optimizing both material use and on-site installation.
Superior Structural Integrity
The gable roof’s triangular geometry provides inherent strength by evenly distributing weight across the steel frame. This stability is further enhanced through precision-welded joints and braced truss systems that resist wind uplift and seismic stress. Especially when paired with steel framing, this structural integrity ensures decades of reliability under ISO and CE standards, delivering long-term security for both residential and industrial applications.
Disadvantages of Gable Roofs
While gable roofs offer many advantages, they come with a few challenges. But with the right design and materials, these issues can be effectively managed.
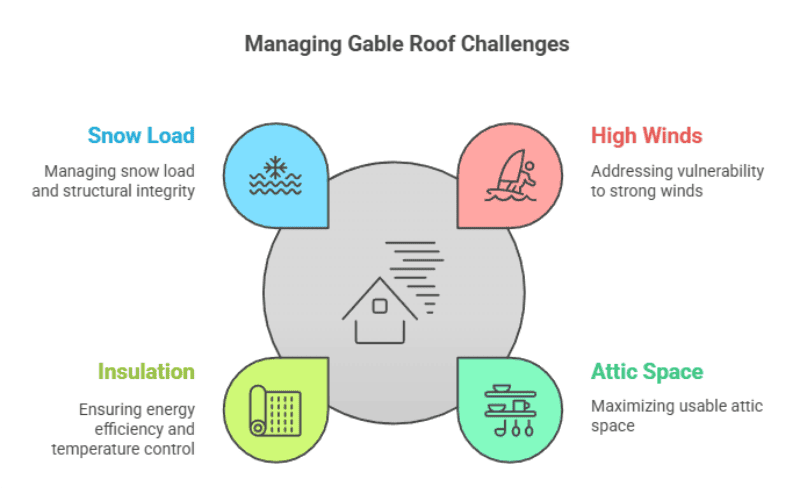
While gable roofs are efficient and durable, certain design challenges should be considered—especially in steel or prefabricated building applications. With proper engineering and materials, most of these drawbacks can be effectively managed.
Vulnerability to High Winds
Gable roofs can act like sails during strong winds, placing pressure on end walls and joints. Proper bracing and anchoring, especially in prefabricated steel systems, can significantly reduce uplift risk. In hurricane-prone or coastal regions, additional tie-downs and truss reinforcements are essential to maintain long-term structural stability.
Limited Usable Attic Space
While gable roofs create more vertical volume, the sloped surfaces can limit usable floor area within attics or upper levels. Solutions include raising knee wall height or incorporating modular framing systems that maximize interior clearance without increasing total height.
Insulation and Temperature Control
Insulating a gable roof requires precision to ensure uniform thermal coverage. Steel-framed buildings often use sandwich panels or PU-insulated cladding to maintain energy efficiency, preventing both heat loss and condensation inside the structure.
Snow Load Risks
Although steep slopes encourage snow shedding, excessive accumulation can still pose stress on the structure. In cold regions, snow load design must include reinforced trusses and optimized pitch angles.
Example: SteelPRO PEB’s prefabricated gable roof warehouses in Canada use strengthened rafters and engineered truss geometry to evenly distribute snow weight, maintaining safety under heavy winter conditions.
Moisture Issues at Gable Ends
Because gable ends are directly exposed, they are more prone to leaks and corrosion. Using galvanized steel panels, sealed flashings, and weather-resistant membranes prevents moisture ingress and prolongs the service life of the structure.
Maintenance Access Challenges
The steep angle that benefits drainage also makes roof access more complex. To ensure safe maintenance, prefabricated steel systems can integrate built-in anchor points or roof walkways during fabrication—allowing easy inspection and cleaning later on. This design-forward approach minimizes labor effort while maintaining safety standards.
Types of Gable Roofs
Gable roofs come in several variations, each with its own advantages. Here’s a quick look:
- Open Gable Roof: The traditional gable layout, featuring a central apex and symmetrical slopes on either side—straightforward, effective, and enduring.
- Side Gable Roof: The most prevalent variety, featuring gable ends positioned on the lateral sides. It’s straightforward and works well for rectangular buildings.
- Cross Gable Roof: Two gable sections intersect at a right angle, perfect for larger or more complex layouts.
- Front Gable Roof: The gable is oriented towards the front, frequently employed for classic aesthetic purposes.
- Dutch Gable Roof: A blend of gable and hipped roofs, providing supplementary loft space and a unique aesthetic.
- Box Gable Roof: Similar to a standard gable but with enclosed triangular extensions for added support.
For steel structures, custom gable designs enhance durability and simplify assembly. Cross gable roofs, for example, can be prefabricated in sections—speeding up installation without sacrificing strength.
Prefabricated and Steel Gable Roof Applications
In prefabricated and steel structure buildings, gable roofs are widely adopted for their balance of efficiency and strength.
- Industrial warehouses and workshops often use cross or box gable roofs to maximize span and drainage capacity.
- Residential steel buildings favor side or front gable roofs for improved ventilation and visual appeal.
- Commercial projects like retail spaces and modular offices benefit from prefabricated gable roof panels, which reduce installation time and cost.
This adaptability makes gable roofs a cornerstone design across SteelPRO PEB’s prefabricated steel structure systems, combining visual simplicity with certified performance and long service life.
Why Steel Gable Roofs Are a Game-Changer
Steel gable roofs redefine how durability and efficiency coexist in modern construction. By combining triangular geometry with prefabricated steel framing, these systems achieve exceptional load resistance and installation speed — solving the wind, snow, and maintenance issues typical of conventional roofs. Their modular design minimizes waste and ensures precise alignment, giving every project predictable strength and long-term performance.
At SteelPRO PEB, advanced fabrication and ISO/CE-certified production translate engineering precision into real-world reliability. Our experience in designing gable roof systems for warehouses, residential buildings, and modular cabins has shown that prefabricated steel not only lowers total project costs but also extends service life under extreme climates. If you’re exploring compact or portable applications, see how the Gable Roof Portable Cabin integrates this efficiency into a ready-to-install solution.

