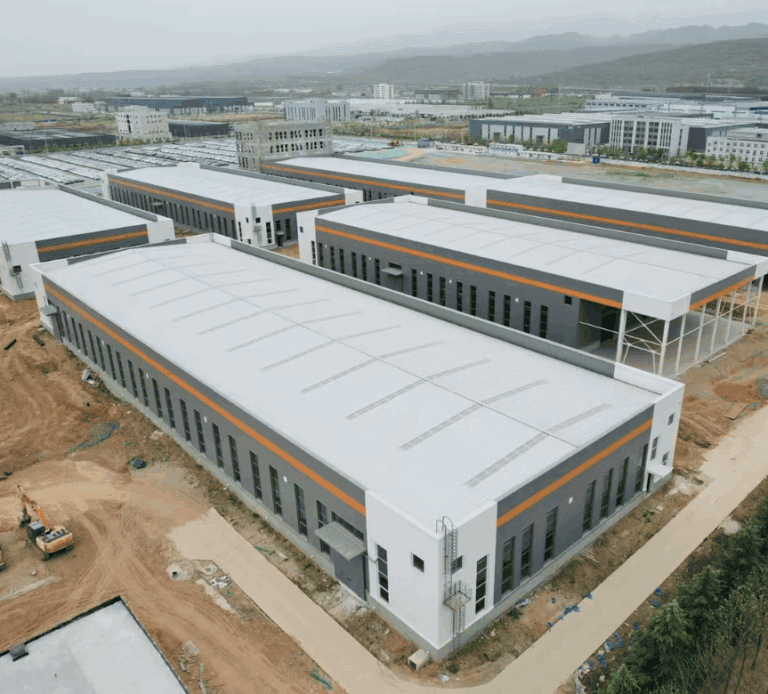
Have you ever thought that building a building can be as simple as building blocks? In 2015, China “built” a 57-story skyscraper in 19 days, shocking the world – this is the magic of modular construction! This subversive method disassembles the building into “boxes” prefabricated in the factory and transports them to the site for assembly. It is fast, low-cost, and can even reduce 90% of construction waste.
But modular building is not just a “fast food” temporary house. From luxury hotels, smart hospitals to space bases, it is redefining how humans design future spaces. Why has the IKEA-inspired house-building model emerged as the “new darling” of the construction industry? Does it indeed offer superior cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits compared to traditional approaches?
If these ideas are new to you, fear not; this article is tailored for your understanding. We will start with the most basic definition and take you to understand how it works, its advantages and challenges, its applicable scenarios, and even talk about its future development. You can easily understand it without any architectural background!
What is Modular Construction?
Modular Construction refers to an innovative method of breaking down a building into standardized modules, prefabricating them in a factory, and transporting them to the site for assembly. These modules can be rooms, walls, floors, roofs, and even internal structures such as water and electricity pipelines, windows, and doors. On-site, they are pieced together like a puzzle, creating a fully formed building.
Modular construction is a type of prefabricated construction, commonly used in residential, office buildings, schools, hospitals, hotels and other scenarios. Modularity does not mean temporary structures, it can be permanent buildings with structural strength comparable to traditional buildings, and even more advantages in some aspects.
Brief History of Modular Construction
Modular construction is not a “new thing”. As early as the mid-19th century, some people tried to prefabricate houses in parts and transport them over long distances, such as the “assembled houses” designed for immigrants. In the 20th century, especially during World War II, modular construction technology was widely used to quickly solve the needs of a large number of housing and medical facilities.
Entering the 21st century, with the advancement of manufacturing technology, transportation capabilities and design software, modular construction has ushered in a second peak of development. Today, in the era of pursuing efficiency, environmental protection and customization, it is gradually becoming a mainstream solution, favored by more and more developers, designers and owners.
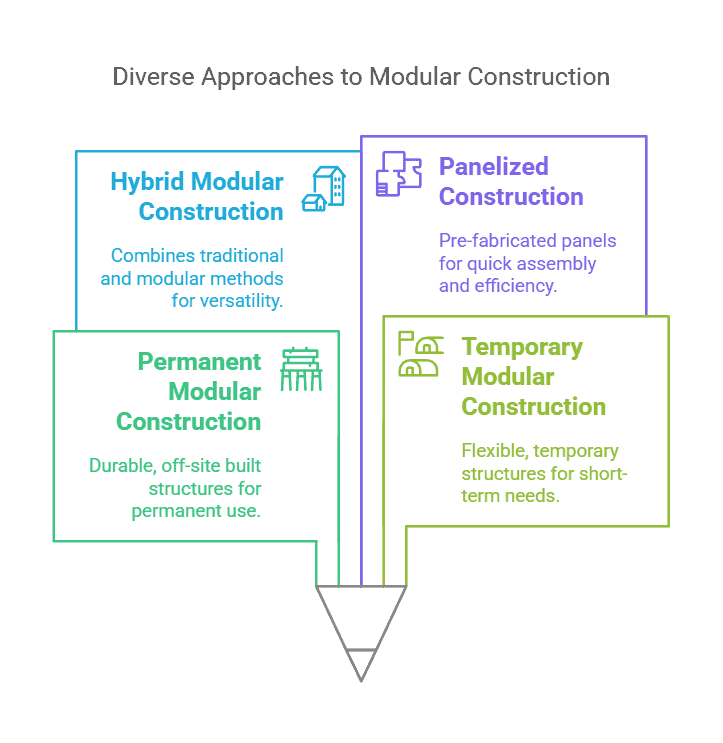
Types of Modular Construction
Modular construction is not a single model. It can be categorized into several types based on its intended use, module configuration, and assembly technique. Understanding these classifications will help to more clearly identify which projects are suitable for modular construction.
1. Permanent Modular Construction (PMC)
Permanent Modular Construction is a type of building designed for long-term use. Their modules are usually made of durable materials such as steel, concrete or wood, and their structural performance is the same as that of traditional buildings, or even stronger. PMC is widely used in places that require long-term operation, such as residential communities, hotels, apartments, schools, hospitals, etc.
Features include:
- Meet building regulations and long-term use standards
- Can be integrated with traditional structures to create multi-story buildings
- Flexible design, customizable appearance and functional space
2. Temporary Modular Construction (RMC)
Temporary Modular Construction focuses more on flexibility and reuse, and is usually used for temporary purposes, such as temporary classrooms, site offices, exhibition halls, emergency medical stations, etc. The structural design of these modules allows them to be transported, installed and dismantled multiple times.
Features include:
- Lightweight structure, easy to disassemble and transport
- Short construction period, suitable for emergency scenarios
- Usually not used as permanent facilities, but also has good performance
3. Hybrid Modular Construction
Hybrid modular construction merges modular components with traditional building elements. For example, the core areas of the building (such as stairwells and elevator shafts) use traditional construction methods, while the remaining spaces (such as room units and exterior walls) are completed using modular units. This method is particularly suitable for high-rise buildings or projects with complex functions.
Features include:
- Increase structural flexibility
- Conducive to construction in limited spaces or complex construction sites
- The modular ratio can be flexibly adjusted according to project requirements
4. Panelized Construction
Unlike integral modules, panelized modular construction only prefabricates some components of the building, such as wall panels, floor slabs, roofs, etc. These components undergo processing in a factory and are subsequently assembled into a complete structure at the construction site. It is faster than traditional construction, but slightly slower than volume modularization.
Features include:
- Easier to transport, suitable for road restricted areas
- More suitable for self-built projects and low-rise buildings
- The construction method is between traditional and modular
There is no absolute advantage or disadvantage between different types of modular construction methods. The key factor lies in the specific requirements of the project. Does it need to be moved? How long is the service life? Is the spatial layout complex? These are all issues that need to be considered when choosing a suitable construction type.
How Modular Construction Works?
The construction process of modular buildings is like a collaborative performance with clear division of labor and tight rhythm. The whole process can be divided into the following main stages:
1. Design stage
Everything starts with design. Architects and engineers will develop a design plan suitable for modular construction according to project requirements. Unlike traditional buildings, the design of modular construction must consider factors such as transportation size, assembly method, and on-site connection. BIM (Building Information Modeling) technology is usually used to accurately plan the location and function of each module.
2. Factory Prefabrication
Once the design is finalized, each module will be manufactured in a controlled factory environment. These modules can be room units, wall systems, or even an entire bathroom or kitchen. They usually contain components such as structure, insulation layer, water and electricity system, windows and doors, and are highly completed. At the same time, on-site construction of the building foundation is also carried out, which greatly saves the total construction period.
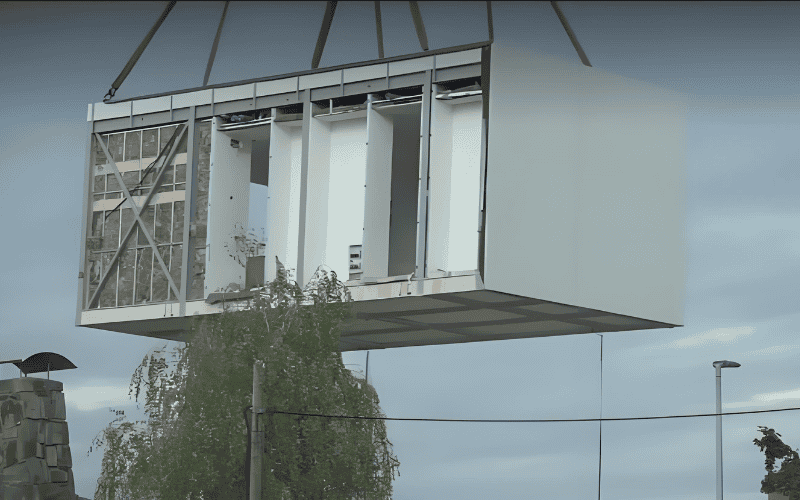
3. Transportation & Assembly
After the modules are built, they will be transported to the construction site and hoisted and spliced using lifting equipment. This process is typically completed within a matter of days or weeks, significantly faster than traditional construction methods. The modules are firmly spliced by connectors, bolts, welding, etc. to ensure the strength and safety of the overall structure.
4. Finishing & Commissioning
After all modules are assembled, the construction workers will perform the final sealing, connection, and decoration. This includes trimming the internal and external wall interfaces, water and electricity commissioning, and ground trimming. Finally, the building can be delivered for use.
Common module types
In modular buildings, common modules include:
- Structural modules: including structural components such as columns, beams, and floor slabs;
- Volumetric modules: such as overall spaces such as bedrooms, offices, and bathrooms;
- System modules: including system components such as electromechanical, water pipes, and cables;
- Panelized modules: such as wall panels and roof panels, used for semi-assembled structures.
Building materials and structural types
Modular buildings can use a variety of materials, depending on different application requirements:
- Steel structure: high strength, suitable for multi-story buildings or industrial sites;
- Wood structure: Ideal for low-rise residential buildings, offering excellent thermal insulation and being environmentally friendly;
- Concrete structure: used in scenarios requiring high load-bearing capacity and stability;
- Composite materials: such as steel-wood combination, lightweight panels, etc., suitable for convenient buildings.
In terms of structural form, modular buildings can be classified into:
- Light steel structure system
- Heavy steel structure system
- Wood structure system
- Hybrid structure system
Different systems are suitable for different scenarios, but they all have one thing in common: factory prefabrication + on-site assembly.
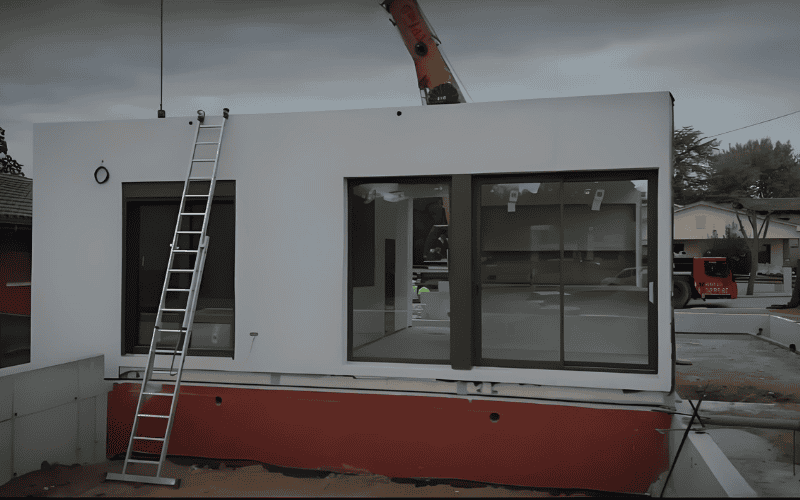
What is a Modular Building?
Simply put, a modular building is a complete building assembled from prefabricated modules (rooms, stairs, corridors, etc.), and 80%-90% of the construction of the modules can be completed in the factory. Many people mistakenly believe that modular buildings are just simple “temporary board houses” or “mobile buildings”, but in fact:
Modern modular buildings have long reached or exceeded the standards of traditional buildings in terms of structural strength, sound insulation, fire protection, insulation, and appearance design. Especially in terms of customized design and rapid deployment, modular buildings have natural advantages and are very suitable for projects with high requirements for delivery cycle and spatial flexibility.
Types of modular buildings:
- Permanent Modular Buildings: suitable for long-term use, with a solid structure, suitable for residences, schools, hospitals, commercial complexes, etc.;
- Relocatable Modular Buildings: used for temporary or flexible purposes, such as temporary office areas, construction site dormitories, mobile medical stations, etc.
Common modular buildings application
- Modular Homes: From single-family homes to multi-family homes, they can be flexibly combined according to the plot and budget;
- Modular Offices: Suitable for start-ups, temporary offices, construction site project command centers, etc.;
- Modular Restaurants: Kitchens, lobby, and dining areas can be preset according to the operation process to save design and decoration time;
- Modular Classrooms & Modular Schools: Suitable for school expansion, sinking of educational resources, etc.;
- Modular Healthcare Buildings: Clinics, isolation wards, and testing centers are quickly built to ensure emergency response;
- Modular Camp Buildings: Serving high-frequency mobility projects such as mining, oil and gas, and field construction.
The modular buildings we provide support a variety of structural systems (such as steel structures, lightweight composite structures, etc.), and can be customized according to customer needs, including interface pre-buried, functional zoning, weather resistance and other configurations. Whether you are a business owner, project manager, or a developer with building landing needs, modularization is an efficient solution worth considering.

Benefits of Modular Construction
Modular construction has attracted more and more attention not only because it is “fast”, but also because it has obvious advantages in many aspects:
Faster construction period: Module manufacturing and foundation construction can be carried out simultaneously, significantly shortening the total construction period, and the project can be delivered weeks or even months in advance.
More controllable costs: Although the initial investment is slightly higher, the overall cost is easier to control due to the short construction period, less manpower, and less rework, saving indirect costs.
More consistent quality: The modules are completed in the factory, with smaller errors in a controlled environment, unified construction standards, and are not affected by weather and on-site environment.
More environmentally friendly: less construction waste, higher material utilization, less on-site interference, in line with the concept of green and sustainable construction.
High flexibility: modules can be disassembled, moved or expanded, suitable for rapidly changing needs, such as school expansion, field camps, etc.
Safer construction: most of the work is completed in the factory, reducing on-site construction risks and improving overall construction safety.
These advantages make modular construction an efficient, flexible and environmentally friendly choice in modern construction.
Related Reading: Modular construction benefits
Limitations & Disadvantages of Modular Construction
Although modular construction has many advantages, there are also some limitations and challenges in practical application. It is crucial to understand these issues prior to considering this construction method.
Transportation restrictions: Modules are usually large in size, and the transportation process needs to consider road width, height restrictions, traffic permits and other issues. It may not be applicable to remote or narrow areas.
Limited design freedom: Although modularization can also be customized, it still needs to follow standardized design in terms of size, connection method, etc., and some complex shapes or structures may be difficult to achieve.
Slightly higher initial investment: Compared with traditional buildings, modularization may have higher initial costs in the design stage, factory manufacturing and equipment investment, and budget planning is required.
Early coordination is required: Modular projects require a high degree of design integration and engineering coordination in the early stage. Once the finalization is completed, the cost of changes is high and the flexibility is low.
Life cycle and maintenance: Although high-quality modular buildings can last for decades, the actual service life still depends on materials, structural design and daily maintenance.
Cost of Modular Construction
Cost is always the core factor in evaluating whether a construction method is suitable. Although many people think that modular construction is “more expensive” or “cheaper”, the actual situation needs to be analyzed in detail.
Cost composition
The total cost of modular construction mainly includes the following parts:
- Design cost: Because modularization requires precise design, the initial design cost is slightly higher;
- Factory manufacturing cost: Including modular processing costs such as structure, interior decoration, water and electricity systems;
- Transportation and hoisting: Logistics costs for transporting modules from the factory to the site and rental costs of lifting equipment;
- On-site foundation construction and assembly: foundation preparation, assembly, joint treatment, etc.;
- Finishing and commissioning: final sealing, commissioning and internal adjustments, etc.
Cost-influencing factors
The key factors affecting modular cost include:
- Project scale and number of modules
- Structural materials used (such as steel, wood, concrete)
- Required degree of customization
- The distance between the factory and the project site
- Hoisting difficulty and on-site construction conditions
Applications of Modular Buildings
Modular buildings exhibit great versatility and can be utilized across diverse sectors. From residential housing to commercial spaces, public facilities, and industrial use, modular construction offers fast and flexible solutions. Here are some common applications:
Residential
- Modular Homes: Including single-family homes, multi-unit apartments, and townhouses. They offer flexible layouts and shorter construction timelines.
- Expandable Homes: Homes designed to be adaptable or expandable in accordance with changing family needs.
Commercial
- Modular Offices: Ideal for temporary workspaces, construction site offices, and scalable office expansions.
- Retail & Food Spaces: Modular restaurants, cafes, and pop-up shops that are quick to deploy and easy to relocate.
Public & Educational
- Modular Classrooms & Schools: Perfect for school expansions or remote educational facilities.
- Other applications include daycare centers, libraries, and training rooms.
Healthcare & Emergency
- Medical Modules: Clinics, isolation wards, and testing centers that require quick installation.
- Emergency Facilities: Temporary shelters or housing in response to natural disasters or urgent needs.
Industrial & Camp Use
- Modular Camp Buildings: Serve industries like mining, oil & gas, and construction with sleeping quarters, offices, dining areas, etc.
- Control Rooms & Data Centers: For technical management in industrial environments.
The adaptability and swiftness of modular buildings render them ideal for a multitude of applications.

What is the difference between modular and non-modular construction?
| Category | Modular Construction | Non-modular Construction |
| Construction Method | Factory fabrication + on-site assembly | Entirely built on-site |
| Timeline | Much faster; multiple phases can run in parallel | Longer; steps proceed sequentially |
| Quality Control | Factory conditions ensure consistency | More variability; affected by weather & site |
| Cost Control | More predictable long-term costs; less labor | Higher labor costs; more risk of rework |
| Environmental Impact | Less waste, lower noise/dust, higher material efficiency | More waste and disruption to surroundings |
| Design Flexibility | Limited by module size and connection methods | Highly flexible for complex or custom designs |
| Best Use Cases | Education, healthcare, camps, housing, commercial | Suitable for all types, especially complex ones |
In short, modular construction is faster, greener, and more standardized, while traditional construction offers greater flexibility for highly customized or intricate projects. The optimal choice hinges on your project’s objectives, timeline, budget, and intended purpose.
Related Reading: Traditional or modular construction
Future of Modular Construction
Modular construction is gradually changing from an “emerging option” to an important development direction in the construction industry. The future development of modular building is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
Technology drives higher efficiency: As technologies such as BIM modeling, automated manufacturing, and intelligent management continue to mature, modular construction will be more accurate and efficient.
Environmental protection and sustainable development: Modular construction has excellent performance in reducing construction waste and reducing energy consumption, and will play a greater role in green construction in the future.
Responding to urbanization and housing needs: In the face of rapid urbanization and housing shortages, modularization provides a fast, flexible, and scalable construction solution, which is particularly suitable for public projects and emergency facilities.
Continuous expansion of application scenarios: In the future, modular buildings will be more flexible, and modules can be combined, replaced, and even migrated, suitable for residential, office, school, commercial and other fields.
As demand for cost-effective, sustainable and scalable building solutions grows, now is the perfect time to explore what modular construction can do for your project.
Want to build smarter and faster?
We offer a variety of customizable modular building solutions to fit your needs – whether permanent or transportable, residential or industrial.
Reach out to us today to discuss your project or request a quotation. Allow us to leverage the strength of modularity to bring your vision to life.

