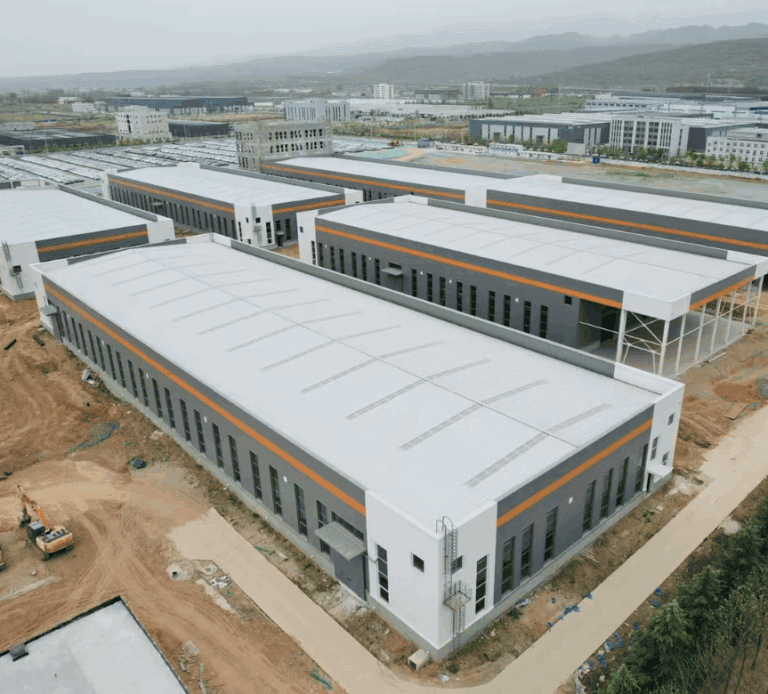
As society focuses more on sustainability and adaptable solutions, temporary buildings are becoming increasingly popular with their modular and prefabricated designs. These structures can be quickly set up and easily adjusted to changing needs. But here’s the big question: how long can they actually last? While they’re great for short-term projects, their long-term durability and ability to adapt to new uses are key factors.
In this article, we’ll dive into the lifespan of temporary buildings, factors affecting their lifespan, and how they can work for short- and long-term needs. Keep reading to see if temporary buildings are the flexible, cost-effective solution you’ve been looking for!
What Are Temporary Buildings?
Temporary buildings, often referred to as Temporary Modular Buildings, are designed for short-term needs with the flexibility to be quickly assembled, disassembled, and relocated. They are commonly used for exhibitions, offices, storage, or disaster recovery. While ideal for temporary use, their modular design ensures adaptability while typically offering a lifespan of 5 to 20 years. Let’s take a closer look at the factors that affect their durability—keep reading!
Related Reading: What Is The Difference Between Temporary And Permanent Modular Buildings?
Factors Affecting the Lifespan of Temporary Buildings
The lifespan of temporary buildings is influenced by a variety of factors that can determine whether they last a few years or decades. From the choice of materials to the construction quality and environmental conditions, these elements all play a crucial role in how well a structure can stand the test of time.
Materials
The materials used in temporary buildings are key to their longevity. Different materials handle wear, weather, and maintenance needs differently.
- Steel: With our expertise in steel structures, we highly recommend galvanized steel (grade Z275 or Z350) for temporary buildings. Its excellent corrosion resistance and high tensile strength make it the ideal choice for long-lasting durability, especially in harsh environments. Additionally, weathering steel (such as COR-TEN A) is another great option, providing exceptional resistance to corrosion and requiring minimal maintenance over time. This can extend the lifespan of a temporary building by 10 to 15 years compared to other materials.
- PVC Membranes: While lightweight and easy to install, PVC membranes are prone to UV damage and wear, making them less durable in the long run. Over time, exposure to UV rays can reduce their lifespan by up to 50%, typically shortening it to around 5-8 years.
- Wood: Wood is susceptible to moisture and pests, which can shorten its lifespan. Without regular treatment and maintenance, wood may last only 5 to 10 years, depending on environmental conditions.
- Aluminum: Although resistant to corrosion, aluminum doesn’t offer the same strength under heavy loads as steel does. In high-stress environments, aluminum may degrade more quickly, reducing the lifespan by 5-7 years compared to steel.
For maximum durability and cost-effectiveness, galvanized steel or weathering steel (like COR-TEN) are the best options for temporary buildings. These materials provide the strength and longevity needed for both short-term and long-term use.
Construction Quality
The quality of construction plays a critical role in the lifespan of temporary buildings. Poor workmanship, such as loose joints, inadequate sealing, or foundation issues, can lead to cracks, instability, and premature failure. Our steel structure company prioritizes precise design, professional welding, and secure connections to ensure durability.
We suggest that you perform appropriate foundation treatment, such as soil stabilization or pile driving, before installing temporary buildings to prevent uneven settlement and structural damage.
Usage Environment
The environment in which a temporary building is used significantly affects its lifespan. Several factors, such as climate conditions and geographic location, play key roles.
Climate Conditions
- Temperature Fluctuations: Extreme temperature changes can cause materials to expand or contract, leading to cracks or material degradation.
- Humidity: High humidity or rainy regions accelerate material corrosion, weakening the structure.
Geographic Location
- Coastal Areas: High salt concentrations in the air can speed up corrosion, especially in steel and concrete structures.
- Mountainous Regions: Complex terrain can make construction more challenging, affecting stability and durability.
Surrounding Environment
- Pollution: Industrial areas with high pollution levels can damage materials and shorten the building’s lifespan.
Biological Factors
- Pests and Fungi: Areas with a high presence of pests or fungal growth can damage wooden structures, leading to rot and decay.
| Building Type | Urban Environment | Coastal Environment | Mountainous Region | Severe Corrosive Environment |
| Wooden Temporary Building | 5-7 years | 3-5 years | 4-6 years | 2-4 years |
| Steel Temporary Building | 7-12 years | 5-8 years | 6-10 years | 3-5 years |
| Steel (with corrosion-resistant materials) | 12-15 years | 8-12 years | 10-15 years | 5-8 years |
| Steel (with weathering steel – COR-TEN A) | 15-20 years | 12-18 years | 18-25 years | 10-15 years |
| Modular Temporary Building | 7-10 years | 5-8 years | 6-9 years | 3-6 years |
| Modular (with high-strength, corrosion-resistant materials) | 12-18 years | 10-15 years | 12-18 years | 8-12 years |
We recommend using galvanized steel (Z275 or Z350) or weathering steel (COR-TEN A) in harsh environments, along with epoxy or polyurethane coatings to enhance corrosion resistance and ensure durability. If you choose our weathering steel temporary buildings, their lifespan can reach up to 20-25 years.
Design and Structure
Poor design choices can significantly affect the lifespan of temporary buildings. For example, neglecting factors such as load distribution, material durability, and environmental stress can lead to structural issues like cracks or instability. Complex or improperly balanced designs that don’t account for these elements can accelerate wear and reduce the building’s overall lifespan.
We recommend opting for simple, modular designs with steel framing to ensure stability, durability, and easy disassembly. Our design ensures a longer lifespan, often extending beyond the typical 5-year use period of temporary buildings.
Maintenance and Care
Neglecting regular maintenance can drastically reduce the lifespan of temporary buildings. Small issues, like loose bolts or minor rust, can develop into significant problems without timely care, shortening the life of the structure by several years.
Regular Structural Inspections
Check for signs of stress or damage, especially on critical parts like welds and joints. Early detection of cracks or loose bolts can extend the building’s life by 3-5 years.
Material Condition Monitoring
Inspect materials regularly for signs of corrosion, mold, or wear. For metal surfaces, periodic rust removal and re-coating are essential. Neglecting this can lead to material failure within 1-2 years.
Roof and Waterproofing Maintenance
Regular checks for leaks or wear on roofing materials are crucial. Over time, minor leaks can cause significant damage. Seal and repair these issues promptly to prevent deterioration.
Pest Control and Preventative Measures
Inspect for signs of termites or other pests that may damage wooden components. Treat materials to prevent infestations that can compromise structural integrity.
We suggest setting a maintenance schedule, including bi-annual inspections and immediate repairs, to prolong the lifespan of temporary buildings.
Usage Intensity
Excessive load and frequent vibrations can severely shorten the lifespan of temporary buildings. For instance, static loads exceeding the design limit—like stacking 800kg per square meter when the limit is 500kg—can cause floor deformation and support structure failure. For steel buildings, this might result in beam bending or column distortion, cutting the lifespan from 3-5 years to just 1-2 years.
Frequent dynamic loads, like crowds or moving equipment, also contribute to structural fatigue. Over time, even small deformations from constant vibrations can cause material failure.
Ensure load capacities are strictly followed to prevent premature wear and reinforce structures as needed. Also, minimize heavy loads and frequent impacts on critical areas to preserve the building’s longevity.
Why Choose Our Steel Structures for Your Temporary Modular Building Needs
As we’ve explored, the lifespan of Temporary Modular Buildings is influenced by materials, design, and maintenance. Our products, such as the Detachable Container House and Container Home on Wheels, can be customized with high-quality materials like COR-TEN A weathering steel, ensuring exceptional durability and corrosion resistance. Additionally, depending on the geographic environment, we offer the option to add wall coatings that further enhance corrosion resistance.
With modular and flexible designs, our container-based solutions are perfect for a wide range of temporary needs, offering both long-term performance and cost-effectiveness. Choosing our temporary buildings means investing in reliable, easy-to-maintain buildings that stand the test of time.

