Modular construction is revolutionizing the building industry, offering a solution that’s both energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. Did you know that modular buildings can reduce energy consumption by up to 67% during the construction phase and save up to 30% in energy costs for heating and cooling once completed? These impressive figures are just the beginning—modular construction not only cuts down on material waste by up to 90% compared to traditional methods but also reduces carbon emissions by 10-20%.
However, while the energy efficiency benefits of modular buildings are clear, achieving optimal energy performance is not without its challenges. From transportation logistics to the need for standardized designs, the path to fully realizing these benefits is complex.
In this article, we’ll explore how modular buildings achieve their remarkable energy efficiency, backed by data and real-world case studies. We’ll also highlight the key obstacles that still need to be overcome in order to maximize the energy-saving potential of modular construction. By the end, you’ll have a deep understanding of why modular buildings are leading the charge in sustainable architecture and the hurdles that need to be tackled for even greater success.
Energy Efficiency Benefits of Modular Buildings

Modular buildings are increasingly recognized for their energy efficiency, offering numerous advantages over traditional construction methods. Below are the key factors contributing to the energy efficiency of modular buildings:
Controlled Factory Environment
One of the main advantages of modular construction is that it takes place in a controlled factory setting, which allows for precise measurement and assembly. This leads to fewer gaps and better insulation performance when the modules are joined on-site, reducing energy losses. Factory-based manufacturing ensures a higher level of quality control, with more uniform insulation, air-tightness, and precision in fitting windows and doors, which helps minimize energy waste.
Faster Construction Time
Since modular buildings are constructed off-site and only assembled on-site, construction is much faster than traditional on-site building methods. This shorter construction timeline results in less on-site energy consumption, such as heating and cooling, while workers are on-site. Additionally, with concurrent site preparation and module construction, projects are typically completed in nearly half the time, reducing the total carbon footprint of the building process.
Energy-Efficient Materials
Modular buildings often incorporate energy-efficient materials that contribute to overall energy savings. For example, highly insulated panels, Low-E windows, and advanced wall assemblies are used more consistently in modular buildings compared to traditional on-site construction. According to studies, modular buildings can be up to 15% more energy-efficient than conventional buildings, thanks to better insulation and airtightness.
Data-Driven Insights on Energy Efficiency in Modular Buildings
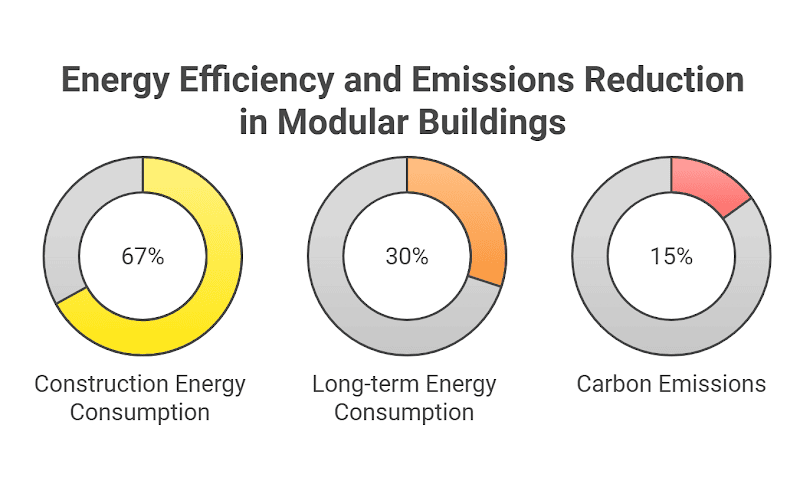
Reduction in Energy Consumption: Research by the Journal of Building Engineering found that modular construction could reduce energy consumption during the building phase by up to 67% when compared to traditional on-site construction. This dramatic reduction is due to the factory environment’s efficiency and the use of advanced, energy-efficient materials. Furthermore, the fact that the modules are built in a controlled environment reduces the likelihood of energy losses during construction.
Energy Savings Over Time: Modular buildings are not only energy-efficient during the construction phase, but they also provide long-term energy savings. A case study on modular homes showed a reduction of 30% in energy consumption for heating and cooling compared to traditional homes. This is due to superior insulation, more efficient HVAC systems, and optimized energy management systems.
Carbon Emissions: According to the National Institute of Building Sciences (NIBS), modular buildings contribute to a 10-20% reduction in carbon emissions compared to traditional buildings. The reduction in emissions comes from several factors: faster construction times, reduced material waste, and better thermal performance.
Sustainable Design Features and Energy-Efficient Technologies
To achieve high energy efficiency, modular buildings integrate various sustainable design features and energy-efficient technologies:
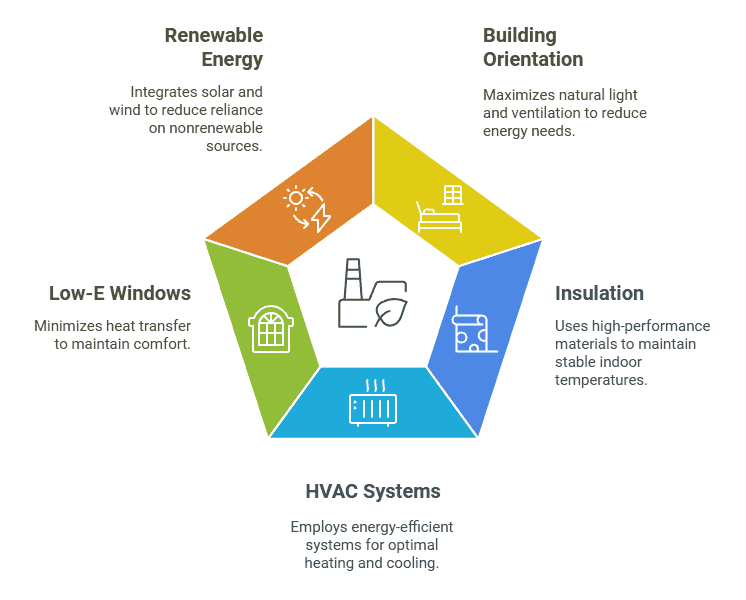
- Building Orientation and Natural Light: Modular buildings are often designed to maximize natural light and ventilation, reducing the need for artificial lighting and air conditioning. Proper orientation of windows, combined with passive solar heating techniques, can significantly lower energy demand.
- High-Performance Insulation: High-R-value insulation materials are commonly used in modular buildings. For instance, Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) and spray foam insulation are standard choices that offer superior thermal performance, keeping indoor temperatures stable with minimal energy input.
- Smart HVAC Systems: Energy-efficient HVAC systems are another key feature in modular buildings. These systems are designed to reduce energy consumption while maintaining comfort, employing technologies such as variable refrigerant flow (VRF) systems, which allow for better control of heating and cooling zones.
- Low-E Windows: Low-emissivity (Low-E) windows are another important element in reducing energy loss. These windows minimize heat transfer, which helps to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature without excessive reliance on heating or cooling systems.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Increasingly, modular buildings are being designed to accommodate renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines. These buildings may be fully or partially off-grid, with excess energy being stored in battery systems or fed back into the grid, thus reducing dependency on nonrenewable energy sources.
Specific Case Studies: Energy Efficiency in Modular Buildings
1. Northgate Modular Housing Project (Canada)
Project Background:
The Northgate project is a modular housing initiative designed for 13 First Nations communities in the Northwest Territories of Canada. The goal was to provide energy-efficient homes that could withstand extreme cold, with temperatures dropping as low as -65°F. This project demonstrated how modular construction could maintain comfort and reduce energy consumption in harsh climates.
Energy Efficiency Measures:
- Thick Insulation: The homes feature triple-layer wall structures with high-performance insulation to minimize heat loss, ensuring warmth even in extreme cold conditions.
- Efficient HVAC Systems: The homes incorporate advanced HVAC systems designed to optimize energy use while maintaining indoor air quality and comfort.
- Low-E Windows: High-performance, low-emissivity (Low-E) windows were used to reduce heat transfer, further minimizing energy loss.
Results:
Energy consumption for these homes was reduced by about 30% compared to traditional construction methods. Modular construction’s precise material management and waste reduction also played a key role in lowering the overall environmental footprint of the project, while the buildings’ rapid assembly was ideal for the harsh climate.
2. The First Nations Modular Housing Project (Canada)
Project Background:
Another notable modular housing project in Canada, this initiative aimed to provide sustainable and energy-efficient homes for several Indigenous communities in remote areas. The project emphasized energy conservation, the use of recycled materials, and the integration of green technologies.
Energy Efficiency Measures:
- Solar Power Systems: All homes were equipped with solar panels to reduce reliance on external power sources, ensuring the homes were more self-sufficient.
- Green Roofs and Rainwater Harvesting: The project incorporated green roofs, enhancing the buildings’ sustainability and reducing stormwater runoff. Additionally, rainwater harvesting systems were integrated to further reduce water consumption.
- Smart Energy Management: The homes featured energy-efficient water heating systems, LED lighting, and smart thermostats, which helped reduce overall energy usage.
Results:
The project achieved a 25% reduction in energy consumption compared to traditional housing. The use of solar panels and rainwater harvesting contributed to making these homes more energy-independent and sustainable, demonstrating the multifaceted benefits of modular construction in creating eco-friendly communities.
3. Bison Modular Home (UK)
Project Background:
The Bison Modular Home project in the UK focuses on creating homes that meet the Passivhaus standard, an advanced building standard aimed at reducing energy consumption to near-zero levels. The project highlights how modular construction can be combined with passive design principles to create homes requiring minimal heating and cooling energy.
Energy Efficiency Measures:
- High-Performance Insulation: The modular homes were built with high-efficiency insulation materials like Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs), which provide exceptional thermal performance.
- Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV): These homes were equipped with HRV systems, which capture heat from outgoing air and use it to pre-heat incoming fresh air, reducing the need for conventional heating systems.
- Low-E Windows: Low-emissivity (Low-E) windows were installed to minimize heat transfer, improving the energy efficiency of the buildings further.
Results:
The Bison Modular Homes achieved up to 20% better energy efficiency than conventional homes. The project successfully met the Passivhaus standard, which is known for its stringent energy performance requirements. This project demonstrated how modular homes can meet or exceed the energy efficiency levels of traditional buildings through the integration of passive design strategies and high-performance building materials.
Challenges to Achieving Energy Efficiency in Modular Buildings
While the energy efficiency of modular buildings is clear, achieving optimal energy performance still presents several challenges:
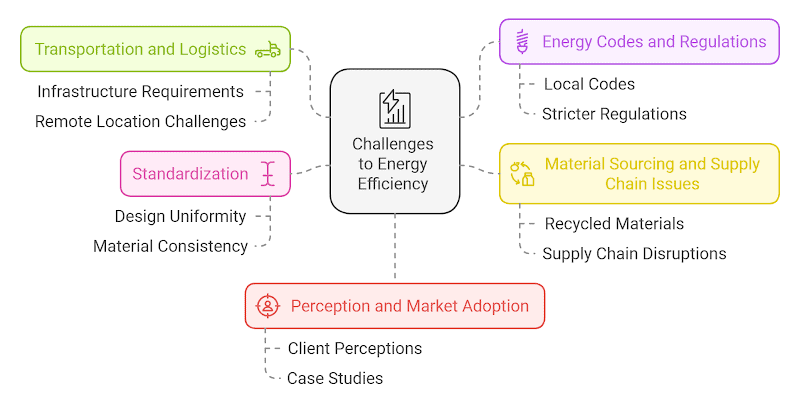
Transportation and Logistics
One of the main obstacles to fully realizing the energy potential of modular buildings is transportation logistics. Large modules require significant transportation infrastructure, and transporting modules to remote or challenging locations can sometimes negate the energy efficiency benefits, especially when multiple trips are required.
Energy Codes and Regulations
Different regions have varying energy efficiency codes and regulations that affect how modular buildings are designed and constructed. Ensuring that modular buildings meet or exceed local energy codes while maintaining cost-effectiveness can be challenging, particularly as these codes become more stringent over time.
Material Sourcing and Supply Chain Issues
While modular buildings often use recycled and eco-friendly materials, consistently sourcing these materials can be challenging. Supply chain disruptions or price fluctuations in sustainable materials may hinder efforts to maintain energy-efficient practices, especially in regions where such materials are not locally available.
Standardization
Another challenge is the need for standardization in design and materials. Modular buildings benefit from a high degree of customization, but standardizing designs and materials across different regions can improve the scalability of energy-efficient solutions. A lack of uniform standards for building components can lead to inefficiencies and make it harder to implement best practices universally.
Perception and Market Adoption
Despite the clear benefits of modular buildings, there is still some reluctance in the market, particularly when it comes to their energy efficiency. Some clients may perceive modular buildings as less durable or customizable than traditional ones. Overcoming these perceptions and demonstrating the energy-saving advantages through real-world case studies is key to broader adoption.
Sustainability Beyond Energy Efficiency
Beyond energy efficiency, modular construction also plays a significant role in overall environmental sustainability:
- Zero Waste: Modular buildings contribute to sustainability by reducing construction waste. According to a report by the Waste & Resources Action Program (WRAP), modular construction can reduce waste by up to 90% compared to traditional building methods. Precision manufacturing ensures that materials are used efficiently, and any excess is often recycled in the factory setting.
- Reduced Site Disturbance: Because much of the construction is done off-site, modular buildings cause less disruption to the construction site. This results in less soil erosion, less damage to the local ecosystem, and a smaller carbon footprint for the project as a whole.
- Recycling and Reuse of Materials: Modular buildings can incorporate a wide range of recycled materials, such as recycled steel and reclaimed wood, reducing the demand for virgin materials and diverting waste from landfills.
Looking Ahead: Future of Energy Efficiency in Modular Construction
The future of modular construction holds great promise for further improvements in energy efficiency. With ongoing advancements in building materials, smart technologies, and sustainable design practices, the next generation of modular buildings will likely push the boundaries of energy performance. Innovations such as adaptive building skins, energy storage solutions, and further integration of renewable energy sources could turn modular buildings into models of sustainability.
As energy codes evolve and demand for green buildings rises, modular construction will increasingly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of energy-efficient, sustainable buildings.
Related Reading:
The History of Modular Construction
5 Latest Trends in Modular Construction in 2024

