Steel Structure Fabrication is the key to transforming steel into reliable building structures. This article provides a thorough insight into the steel structure fabrication process, encompassing design optimization through to factory production. Whether you are a practitioner in the engineering field or a reader interested in steel structure fabrication, you can gain practical knowledge and insights from it.
Next, let’s explore each key step of steel structure fabrication in depth!
Preparation for Steel Structure Fabrication: Design and Material Selection
The first step in steel structure fabrication is design and material selection, which sets the foundation for the entire process. Design determines the structure’s performance and appearance, while material selection impacts its strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Design: From Concept to Detailed Plans
Steel structure design is a systematic process that considers building functionality, load requirements, and cost. Key steps include:
Conceptual Design: Define the structural layout (e.g., portal frames for industrial plants, frame-braced systems for high-rises) and select component types (e.g., H-beams, box sections).
Detailed Design: Perform load analysis, optimize component cross-sections using software (e.g., SAP2000, Tekla), and create detailed construction drawings.
Design Verification: Validate strength and stability through structural analysis and ensure compliance with standards like GB 50017 (China) or EN 1993 (Europe).
Material Selection: Choosing the Right Steel and Connections
Material selection directly affects performance and cost. Key considerations include:
Steel Types: Carbon steel (e.g., Q235, ASTM A36) for general use, high-strength steel (e.g., Q460) for heavy loads, weathering steel (e.g., Corten) for outdoor use, and stainless steel for special applications.
Connection Methods: Welding for rigid joints, bolting for adjustable connections, and riveting for specific cases.
Cost Control and Optimization
Optimizing design and material selection helps control costs:
- Use software to reduce material usage.
- Standardize components and connections to simplify fabrication.
- Plan material usage efficiently to minimize waste.
Related Reading: Steel Structure Design
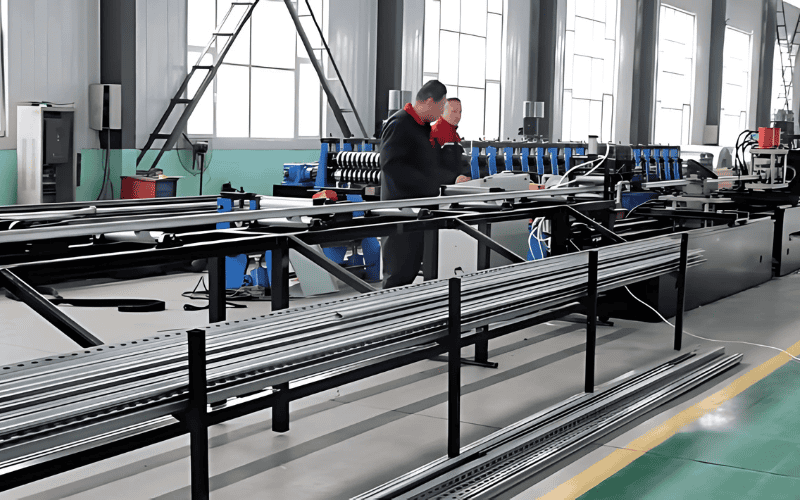

Steel Structure Fabrication Process
The fabrication of steel structures is a meticulous process that transforms raw materials into precise, high-quality components. Below, we outline the key steps involved in steel structure fabrication, ensuring accuracy, durability, and efficiency at every stage.
1. Lofting and Cutting
Lofting
Lofting involves creating templates and marking rods based on design drawings to ensure accurate dimensions. Using 1:1 scale geometric drawings, templates and rods are made from steel plates. These serve as references for cutting, bending, and drilling.
Key Points:
- Ensure all markings are clear and include component numbers, drawing references, and hole sizes.
- Preserve templates and rods for future reference until project completion.
Cutting
Common cutting techniques include:
- Shearing: For straight cuts on plates and sections.
- Sawing: For precise cuts on beams and profiles.
- Flame Cutting: Uses oxygen and fuel gas to cut thick steel plates.
- Plasma Cutting: Ideal for cutting stainless steel, aluminum, and other alloys.
Quality Control: Ensure cuts are clean, free from burrs, and within specified tolerances.
2. Assembly and Welding
Assembly
Assemble cut parts into components according to design specifications.
Key Points:
- Ensure contact surfaces are clean and free from debris.
- Use tools like square rulers to maintain alignment and precision.
- Temporarily fix parts using bolts or small welds before final welding.
Welding
Methods:
- Manual Arc Welding (MMA): For tack welding and small-scale operations.
- Gas Metal Arc Welding (MAG): For continuous welding, using a shielding gas (e.g., argon-CO2 mix).
- Submerged Arc Welding (SAW): For long, automated welds, ideal for heavy sections.
Quality Control: Conduct non-destructive testing (NDT), such as ultrasonic testing, to inspect welds for any defects including cracks or porosity.
Related Reading: Steel Structure Welding Technology
3. Straightening and Drilling
Straightening
Purpose: Correct deformations caused by cutting, welding, or transportation.
Methods:
- Mechanical Straightening: Using presses or rollers.
- Flame Straightening: Applying controlled heat to specific areas to reshape the steel.
Key Points: Ensure components meet dimensional tolerances before proceeding to the next step.
Drilling
Purpose: Create holes for bolted connections.
Methods:
- Drilling: Using drill presses for precise hole placement.
- Punching: For thinner materials, though less common due to potential edge deformation.
Quality Control: Ensure hole sizes and positions align with design specifications.
4. Rust Removal and Painting
Rust Removal
Method: Shot blasting is a common method employed to clean steel surfaces by removing rust, scale, and contaminants.
Key Points:
- Ensure the surface is clean and roughened to improve paint adhesion.
- Remove residual dust and debris after blasting.
Painting
Process:
- Apply a primer coat immediately after rust removal to prevent re-rusting.
- Apply intermediate and top coats subsequently to attain the desired thickness and final finish.
Quality Control: Ensure even application, with no runs, sags, or missed spots.
5. Marking and Packaging
Marking
Purpose: Label components with unique identifiers (e.g., part numbers, drawing references) for easy identification during installation.
Key Points: Use durable markings that remain visible throughout transportation and installation.
Packaging
Purpose: Protect components from damage during transportation and storage.
Methods:
- Use protective coverings (e.g., plastic wraps, wooden crates) for sensitive areas.
- Secure components to prevent movement during transit.
Quality Control: Inspect components before packaging to ensure they meet quality standards.
Summary
The steel structure fabrication process is a carefully orchestrated sequence of steps, each critical to ensuring the final product’s quality, durability, and performance. From lofting and cutting to assembly, welding, and final finishing, every stage requires precision, expertise, and rigorous quality control. By strictly following these processes, we ensure that our steel structures meet the highest standards of safety and reliability.
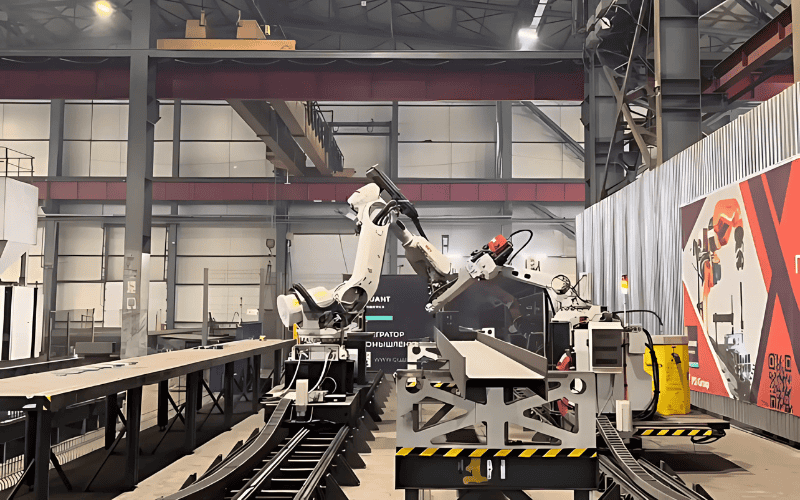
Steel Structure Fabrication Tips
- Precise Design: Start with detailed, accurate designs. This ensures smooth fabrication and reduces errors.
- Quality Materials: Use high-quality steel suited to your project’s needs. Material strength and durability are key.
- Accurate Cutting: Ensure precise cutting of steel components to avoid costly rework.
- Welding Quality: Focus on clean, consistent welding to maintain structural integrity.
- Proper Coating: Apply protective coatings to prevent corrosion and extend lifespan.
- Efficient Assembly: Optimize the sequence of assembly to save time and reduce material waste.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct thorough quality checks at each stage of fabrication to catch issues early.
Quality Inspection in Steel Structure Fabrication
Quality inspection is critical throughout the steel structure fabrication process, as it directly impacts the safety, durability, and performance of the final structure. Here are key aspects to focus on:
Material Inspection: Ensure all raw materials meet industry standards. Inspect for any imperfections, including cracks, rust, or deformation, prior to using them in the fabrication process.
Dimensional Accuracy: Confirm that all components conform to the dimensions outlined in the design specifications. This helps prevent issues during assembly and ensures structural integrity.
Welding Quality: Inspect welds for strength and uniformity. Proper welding techniques should be used, and post-weld inspections should be conducted to check for cracks, porosity, or incomplete fusion.
Surface Finish: Examine the surface finish for defects like rust, corrosion, or scratches. Surface treatment methods, like galvanizing or painting, should be applied to safeguard against environmental degradation.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Use techniques like ultrasonic testing or X-ray inspection to identify internal flaws that aren’t visible to the naked eye.
Assembly and Fit-Up: Inspect the assembly process to confirm that the components fit together as per the intended design. Misalignment can lead to structural weaknesses or additional stress on the system.
Prior to departure from our factory, we guarantee that each steel structure undergoes a comprehensive quality inspection. Our team checks all aspects of the fabrication process, from material quality to precise dimensions and weld integrity. This ensures that every component meets industry standards and is ready for safe and reliable use in your project.
Challenges and solutions in steel structure fabrication
In steel structure fabrication, we respond to various challenges through scientific deformation control, reasonable material selection and application of environmental protection technology.
Deformation control
Challenge: During cutting, welding and drilling, steel is prone to deformation, which affects the accuracy and installation quality of components.
Our solution:
- Welding deformation control: Reduce deformation by optimizing welding sequence, controlling heat input and using clamps. Use mechanical or flame correction when necessary.
- Cutting and drilling accuracy control: Use high-precision CNC equipment to ensure the accuracy of cutting and drilling, and regularly maintain the equipment to avoid errors.
Material selection
Challenge: Different projects have different performance requirements for steel. Improper selection may lead to insufficient structural strength or excessive cost.
Our solution:
We recommend the most suitable steel according to your project needs to ensure a balance between performance and economy.
- Carbon steel (such as Q235, Q355): Suitable for most building structures.
- High-strength steel (such as Q460): Suitable for large spans or heavy-loaded structures.
- Weathering steel (such as Corten steel): suitable for outdoor or corrosive environments.
- Stainless steel: used in special occasions, such as chemical equipment.
Environmental protection and sustainability
Challenge: With the improvement of environmental protection requirements, steel structure manufacturing needs to reduce the impact on the environment while meeting the needs of sustainable development.
Our solution:
- Environmentally friendly coatings: Use low-VOC coatings to reduce pollution to the environment.
- Recyclability: Steel is 100% recyclable. We reduce waste and support sustainable development by optimizing design and manufacturing processes.
Are you ready to enhance your project with unparalleled precision and quality? Our advanced steel structure fabrication process ensures that every stage, from design to final inspection, is executed with the highest standards.
With state-of-the-art technology and a team of skilled experts, we deliver steel structures that are not only reliable but built to last. Reach out to us today to learn how our outstanding fabrication process can seamlessly and efficiently bring your vision to life.

