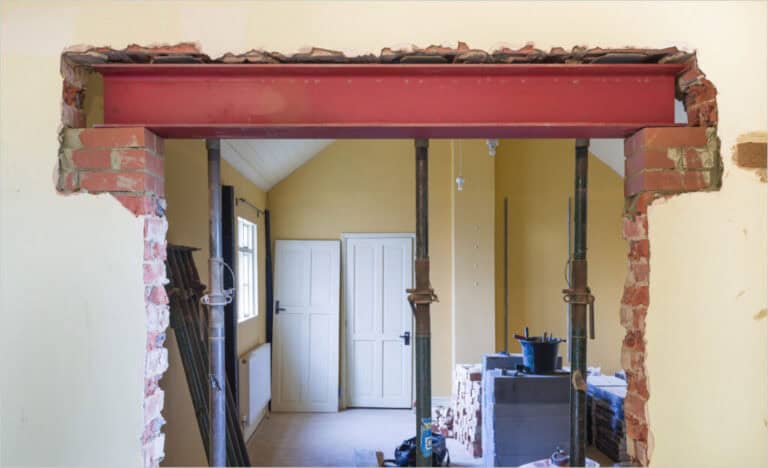
What is a Prefabricated Building?
Prefabricated buildings refer to buildings whose components are manufactured in factories and then transported to the construction site for assembly. This method greatly reduces on-site construction time and ensures high precision and quality control of each component.
The concept of prefabricated buildings has a long history. After World War II, prefabricated buildings were widely used as emergency solutions, especially for the rapid deployment of temporary housing and commercial facilities.
Today, prefabricated buildings have developed into a mature construction method. With years of accumulated expertise, we focus on providing fast and precise prefabricated building solutions that meet modern construction standards and customer needs.
Types of Prefabricated Buildings

1. Classification by material
Steel structure prefabricated buildings
- Features: light weight, high strength, good earthquake resistance, suitable for industrial plants, warehouses, high-rise buildings, etc.
- Examples: steel frame modular buildings, light steel keel houses.
Concrete prefabricated buildings
- Features: strong durability, good fire resistance, commonly used in residential buildings, office buildings, etc.
- Examples: prefabricated concrete wall panels (PC components), composite board structure buildings.
Wood structure prefabricated buildings
- Features: environmental protection, good thermal insulation performance, mostly used in low-rise residential buildings, holiday homes, etc.
- Examples: CLT (cross laminated timber) buildings, wood frame modular houses.
Composite material prefabricated buildings
- Features: combining multiple materials (such as steel + concrete, wood + metal), both lightweight and high strength.
- Examples: SIPs (structural insulation panels) buildings, aluminum-plastic panel houses.
2. Classification by degree of modularity
Modular system
- Features: prefabricated complete rooms or functional units (such as bathroom and kitchen modules) in the factory and spliced on site.
- Applications: apartments, hotels, medical facilities.
Panelized system
- Features: prefabricated walls, floors, roofs and other large panels, assembled on site.
- Applications: residences, schools, temporary offices.
Componentized system
- Features: prefabricated beams, columns, stairs and other independent components, high flexibility.
- Applications: industrial plants, gymnasiums.
3. Classification by construction technology
3D printing prefabricated buildings: walls or overall structures are manufactured by 3D printing technology, which is efficient and environmentally friendly.
Light steel keel structure: cold-bent thin-walled light steel is used as the skeleton, which can be assembled quickly and is suitable for low-rise buildings.
Container building: using waste containers to transform into modular spaces, which is low-cost and movable.
4. Classification by mobility
Fixed prefabricated buildings: permanent structures, such as prefabricated concrete houses.
Movable buildings: wheeled chassis or detachable designs, such as RVs and mobile medical stations.
What are prefabricated components?
Prefabricated buildings are usually composed of multiple prefabricated and assembled components, which are mostly manufactured and processed in the factory and then transported to the site for rapid splicing and assembly. Mainly include:
Wall components: exterior wall panels, interior wall panels, sound insulation panels, usually made of concrete, wood or steel.
Floor components: prefabricated floor slabs and partitions, providing bearing capacity and sound insulation, commonly made of concrete, steel or wood.
Roof components: roof panels, roof beams and trusses, commonly made of steel, concrete or wood.
Columns and beams: prefabricated reinforced concrete or steel columns and beams, supporting the structure of the building.
Stairs and platforms: prefabricated stairs and platforms, usually made of steel or concrete.
Window frames and door frames: prefabricated window frames and door frames, common materials include wood, aluminum alloy, etc.
Pipes and electrical accessories: including water pipes, wire pipes, electrical sockets, etc., pre-installed in the factory and connected on site.
Decorative panels and trims: used to beautify the exterior facade or interior space, commonly made of wood, plastic or metal.
Precast concrete components: such as concrete wall panels, floor slabs and roof slabs, usually used for load bearing and sound insulation.
Prefabricated frames: such as steel or wood frames, used to support and connect other components.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Prefabricated Construction
Why are prefabricated buildings popular?
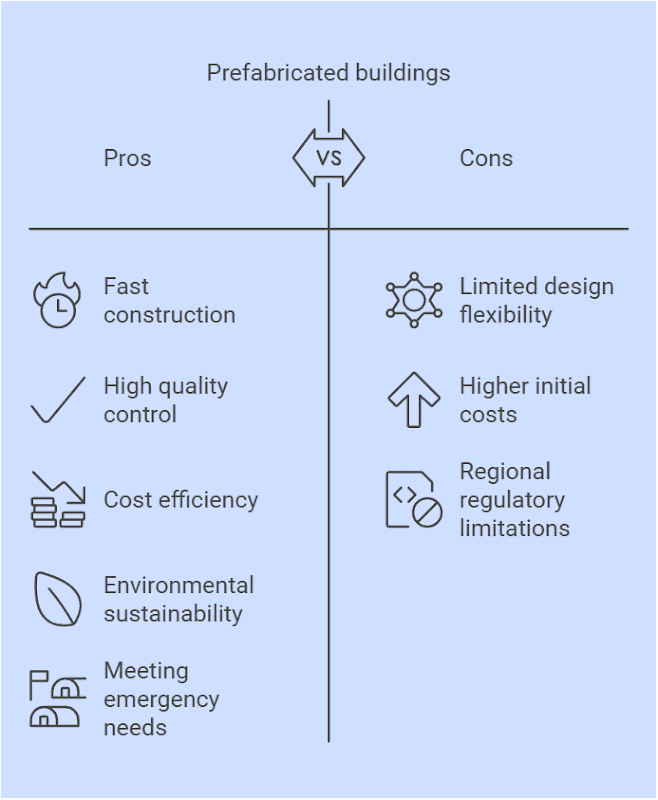
- Fast Construction: A prime benefit of prefabricated structures lies in their rapid construction process. Components are pre-manufactured in factories, with site work focusing on assembly, drastically slicing construction timelines, aiding in adhering to stringent deadlines, and accelerating project completion.
- High Quality Control: We employ modern production lines to guarantee utmost quality and precision for each component. Rigorous quality checks and optimizations are conducted on every part, minimizing onsite construction errors. This ensures our clients enjoy not just swift delivery but also resilient and enduring building quality.
- Cost Efficiency: By utilizing factory production and standardized processes, prefabricated buildings reduce labor costs and material waste, leading to overall project cost savings. More importantly, with faster construction times and higher precision, prefabricated buildings offer higher returns on investment (ROI) in the long term by reducing ongoing maintenance costs.
- Environmental Sustainability: Prefabricated buildings also have significant environmental benefits. Factory-based production reduces waste generated during construction, and many of the materials used in prefabricated buildings are recyclable. We focus on providing sustainable solutions that meet green building standards, ensuring that every project contributes to energy efficiency and reduced carbon emissions.
- Meeting Emergency Needs: Whether in the aftermath of a natural disaster or for temporary housing during a special event, prefabricated buildings can be deployed quickly to provide immediate shelter. With modular and panelized designs, we offer rapid solutions that ensure clients’ needs are met quickly, without compromising on structural stability and comfort.
Related Reading: Advantages of prefabrication
What are the disadvantages of prefabricated buildings?
- Limited Design Flexibility: Although prefabricated buildings can be customized, they offer less design flexibility compared to traditional construction. Particularly in cases of complex architectural requirements or unique designs, prefabricated buildings may be less adaptable. However, we’ve designed our products to strike an optimal balance between standardization and customization, addressing various project needs effectively.
- Higher Initial Costs: The initial cost of prefabricated buildings can be higher, especially in terms of manufacturing and transportation. However, while the upfront investment may be greater, the shorter construction time and reduced errors during the building process lead to significant long-term cost savings.
- Regional Regulatory Limitations: Prefabricated buildings may face regulatory challenges depending on local building codes and standards. Understanding the local regulations is crucial when opting for prefabricated construction. We ensure that all our designs and manufacturing processes comply with regional codes, ensuring smooth project delivery in any location.
Applications of Prefabricated Buildings
| Disaster Relief Housing | Modular Apartments |
| Temporary Housing Solutions | Modular Hotels |
| School Buildings | Prefabricated Warehouses |
| Medical Facilities | Military Barracks |
| Tourist Resorts and Cabins | Agricultural Buildings |
| Emergency Shelters | Religious Structures |
| Modular Offices | Prefabricated Churches |
| Retail and Commercial Spaces | Modular Libraries |
| Sports Facilities | Disaster Recovery Centers |
| Residential Housing | Prefabricated Laboratories |
How are Prefabricated Buildings Manufactured?
Manufacturing Process
The journey starts with the design phase, where we closely collaborate with you to finalize the exact specifications for your building. Once the design is approved, we move to the manufacturing phase, where every component is produced in our state-of-the-art factory. The prefabricated parts, such as walls, floors, and roof panels, are manufactured in controlled environments to ensure the highest quality standards.
After thorough testing, the components are prepared for shipment to the construction site. With modular and panelized parts ready for assembly, the on-site construction phase is rapid and efficient, cutting down project durations and labor expenses.
We take pride in our highly organized manufacturing process, ensuring that your prefabricated building is ready on schedule, with precision and quality that exceed expectations.
What Are Prefabricated Materials?
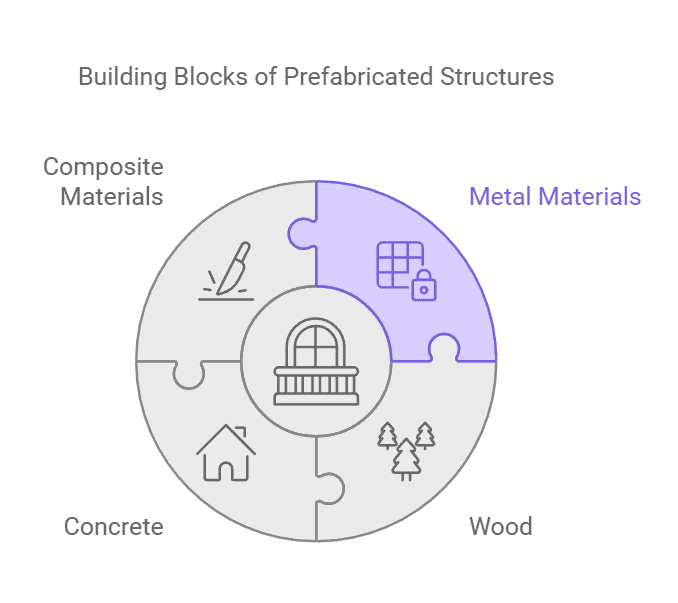
Metal Materials: Metal materials, such as steel and aluminum alloys, offer high strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors, making them ideal for the structural skeleton of the building.
- Light Steel: Provides excellent support with lower weight and is widely used for multi-story buildings.
- Aluminum: Offers great corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various environments.
Wood: Wood has been a traditional material in prefabricated construction, especially for smaller buildings or low-rise structures. It is cost-effective, sustainable, and easy to work with, allowing for quick assembly and customization. Wood is also an eco-friendly material, often sourced from sustainably managed forests.
Concrete: Precast concrete panels are often used for the walls and foundation of prefabricated buildings. Concrete provides excellent strength and durability, making it perfect for large-scale projects and buildings that require robust structural integrity, such as high-rise offices or commercial spaces. Precast concrete also enhances thermal performance, providing better insulation.
Composite Materials: Composite materials like fiberglass and polyurethane foam are frequently used in the external walls, roofing, and insulation of prefabricated buildings. These materials are lightweight, provide excellent insulation, and are resistant to moisture and decay. Their use in prefabricated structures helps improve energy efficiency and reduce long-term maintenance costs.
History of Prefabricated Buildings
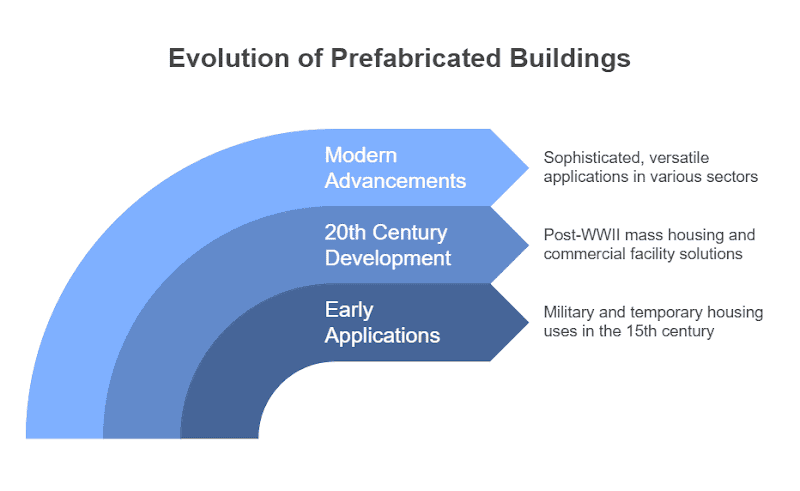
Early Applications
The history of prefabricated buildings dates back to the 15th century, primarily used for military applications and temporary housing during wartime. The method gained popularity over time as it provided a faster, more efficient solution compared to traditional building methods. Prefabricated structures were often used for emergency shelters, disaster recovery, and temporary accommodation.
Rapid Development in the 20th Century
Following World War II, there was an explosion in the demand for quick and efficient housing solutions, leading to widespread adoption of prefabricated construction. In the post-war years, prefabricated buildings became a go-to solution for mass housing and commercial facilities, especially in regions where rebuilding efforts were urgently needed.
Modern Advancements
Due to advancements in materials science and manufacturing tech, prefabricated buildings have transformed into sophisticated and adaptable solutions for modern construction. Nowadays, they cater to various applications, encompassing residential homes, office buildings, schools, hospitals, and public infrastructures. As technology further progresses, prefabricated construction’s potential grows, presenting clients with more efficient, customizable, and eco-friendly building alternatives.
What is the Difference between Precast and Prefabricated Buildings?
Prefabricated Buildings
These buildings include a combination of different materials (wood, steel, composite materials, etc.) and structural types to suit various building needs. Prefabricated buildings are versatile, offering a wide range of options for both low-rise and high-rise structures.
Precast Concrete Buildings
Precast concrete buildings focus primarily on using precast concrete components, which are ideal for large, durable, and high-strength applications. These buildings are commonly utilized for projects where the structure must withstand substantial loads, including high-rise buildings and large-scale infrastructure developments.
Key Differences
- Flexibility: Prefabricated buildings offer greater flexibility in design, suitable for a variety of projects. Whether it’s for residential, commercial, or temporary structures, prefabricated buildings can be tailored to different functional requirements.
- Structural Stability: Precast concrete buildings offer superior structural stability and load-bearing capacity, rendering them perfect for large-scale, heavy-duty constructions. However, this also limits their flexibility for smaller-scale or more varied projects.
PEB (Pre-Engineered Buildings) vs. Prefabricated Buildings:
- PEB (Pre-Engineered Buildings):
- Constructed using steel frames, designed and manufactured to meet specific requirements.
- Typically used for industrial, commercial, and large-scale buildings.
- Components are pre-engineered and fabricated in a factory and then assembled on-site.
- Strong, durable, and ideal for buildings with large spans and open spaces.
- Prefabricated Buildings:
- Can be made from various materials such as steel, wood, or concrete, depending on the design.
- Involves the construction of components like walls, floors, and roofs off-site, which are then assembled on-site.
- Suitable for a wide range of applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
- Often more flexible in terms of design and materials compared to PEB.
Key Difference: PEBs are primarily steel-based and engineered for specific commercial and industrial uses, while prefabricated buildings can utilize multiple materials and are more versatile in terms of design and application.
Modular vs. Prefabricated:
- Modular construction:
- Constructed in sections or modules off-site.
- Can be easily expanded or reconfigured.
- Typically built to be relocatable.
- Prefabricated Buildings:
- Built with pre-made components (walls, roofs, etc.) that are assembled on-site.
- Generally not designed to be moved once built.
- Suitable for permanent structures.
Key Difference: Modular buildings are designed for flexibility and mobility, while prefabricated buildings are often more permanent and static in nature.
Are Prefabricated Buildings Expensive?
No, prefabricated buildings can save a lot of money in the long run because construction is faster, labor costs are lower, and there is less material waste.
We are a Prefabricated Steel Building Supplier
SteelPRO PEB specializes in manufacturing a wide range of prefabricated buildings, from warehouses and factories to residential units, barns and modular buildings, we provide high-quality steel structures that are built to last.
Our steel buildings are cost-effective and durable. Whether you seek a customized solution or a standard design, we possess the expertise to deliver precisely what you require. Thanks to our efficient manufacturing and punctual delivery, your project will remain on schedule.
If you are looking to streamline your next building project with prefabricated steel structures, contact us today. Let us build your future together with SteelPRO PEB.

