When it comes to earthquake resilience, not all buildings are created equal. Steel structures stand out for their superior seismic resistance, offering a level of flexibility, strength, and reliability that other materials just can’t match. Whether you’re in an earthquake-prone region or not, choosing the right design can make all the difference in protecting both the structure and its occupants.
In this article, we’ll explore why seismic-resistant steel structures are a game-changer and how they compare to other building types. From homes to industrial facilities, steel’s unique qualities are reshaping earthquake-resistant architecture.
Why are Steel Structures Good at Resisting Earthquakes?
Steel structures are known for their exceptional ability to withstand seismic forces, making them an ideal choice for earthquake-prone areas. Here’s why they stand out.
High Toughness and Flexibility
Steel’s toughness allows structures to handle significant movement during an earthquake without breaking. It absorbs and spreads out seismic energy, allowing the building to sway without damage.
Strength and Light Weight
Steel is both strong and lightweight, enabling it to bear heavy loads while keeping the building’s weight low. This reduces shaking during an earthquake and enhances seismic resistance.
Outstanding Ductility
Ductility is all about how much a material can stretch or bend without snapping. Steel structures are perfect for this! Unlike brittle materials, they can absorb seismic energy by stretching, compressing, or twisting, which helps prevent sudden breaks or failures. This makes them much safer in an earthquake.
Flexible Connection Points
Steel uses flexible connections through welding or high-strength bolts, allowing the frame to move slightly during an earthquake without losing stability. These connections ensure the structure remains intact even during strong shaking.
Quick Response and Easy Repair
Steel structures react quickly to seismic forces and are less likely to suffer permanent damage. Repairs are quick and easy if something goes wrong, saving you both time and money.
Predictable Performance
We can predict steel structures’ behavior during an earthquake while providing sketches, allowing us to optimize the design and ensure safe performance when it matters most.
Structural System Advantages
- Frame Structure System: Steel frames absorb seismic energy through joint movement, maintaining stability and giving people time to evacuate.
- Support Systems: Special braces, like energy-dissipating supports, absorb extra seismic energy, boosting the building’s strength.
Material Properties
Steel’s toughness and ductility mean it can handle the movement and shaking from earthquakes without breaking. That’s why steel buildings offer reliable seismic resistance—no matter the shake or sway.
A Little Extra: Steel structures are not just about the material—they’re designed to adapt. With flexible joints, support systems, and energy-dissipating features, steel buildings are specifically built to handle earthquakes. Safe, reliable, and ready for action.
Seismic Comparison Between Steel Structures And Other Types Of Buildings
| Seismic Performance | Steel Structure | Wooden Structure | Reinforced Concrete | Brick-Masonry |
| Deformation Ability | Excellent, absorbs seismic energy | Poor, brittle failure | Moderate, rigid | Poor, prone to cracking |
| Structural Stability | Flexible and stable | Weak stability | Strong, but rigid | Poor, prone to damage |
| Design Flexibility | High, adaptable | Low, weak seismic resistance | Limited flexibility | Low, weak seismic resistance |
| Seismic Systems | Frames, shear walls, supports | No effective seismic systems | Shear walls, frames | Relies mainly on walls |
Wooden structures can be brittle, concrete tends to be rigid, and brick masonry is the weakest when it comes to earthquakes. On the other hand, steel structures provide the best seismic resistance, offering great flexibility and stability. That’s why steel structures are the go-to choice for earthquake-prone areas.
Types of Seismic Steel Structures
Steel structures are designed to withstand seismic forces, and different seismic-resistant designs offer unique advantages. Here are some of the most common ones:
X-Bracing
Features: Steel cross braces form an X-shape, dispersing seismic forces effectively to the ground, reducing impact on the building. Adding shear walls can further strengthen the structure’s rigidity.
Application: We use this system in medium to high-rise buildings, industrial plants, and large storage facilities that require extra seismic protection.
K-Bracing (Double Diagonal Bracing)
Features: K-bracing adds diagonal braces that form a “K” shape, creating a symmetrical support system. This helps resist horizontal seismic forces and minimizes lateral displacement.
Application: We incorporate this method in commercial buildings and low-rise structures where moderate seismic resistance is needed.
Chevron Bracing
Features: Chevron bracing creates a “V” or inverted “V” shape, typically placed on either side of the frame. This design provides strong rigidity and effectively distributes seismic forces.
Application: This design is ideal for mid-to-high-rise buildings and industrial facilities where high seismic resistance is a must.
Diagonal Bracing
Features: Diagonal braces help resist lateral forces by forming a more flexible layout compared to X-bracing. These braces absorb seismic energy via diagonal tension.
Application: We apply this system in large warehouses and bridges to prevent lateral movement during seismic events.
Horizontal Bracing
Features: Horizontal braces enhance the frame’s resistance to seismic forces by reducing lateral displacement during earthquakes.
Application: We use this in large steel structures to enhance overall seismic resistance and minimize potential damage during an earthquake.
Frame-Shear Wall System
Features: This system combines a steel frame with reinforced concrete or steel shear walls to strengthen earthquake resistance. The shear walls provide additional lateral force resistance, while the steel frame ensures flexibility.
Application: This system is used in high-rise buildings and large structures that require high seismic protection.
Moment-Resisting Frames
Features: Moment-resisting frames use strong connections at the joints, allowing the frame to bend and absorb seismic energy. Unlike traditional braced systems, these frames rely on rigid beam-column connections for seismic resistance.
Application: We implement moment-resisting frames in high-rise buildings and structures where open, unobstructed floor plans are essential, and bracing isn’t desirable.
Full Steel Frame
Features: Entirely made of steel, the frame uses high-strength connections to improve seismic stability and ensure performance during an earthquake.
Application: Used in large commercial buildings and industrial facilities where maximum seismic safety is essential.
Additional Considerations
Steel structures already have great toughness and strength, but they become even more earthquake-resistant when combined with technologies like base isolators and moment-resisting frames. Base isolators reduce the transmission of seismic waves to the building by decoupling it from ground motion, while moment-resisting frames absorb and dissipate seismic energy, ensuring the structure stays stable during strong tremors.
For earthquake-prone regions, we can incorporate these advanced technologies and devices to further enhance the seismic performance of the building, ensuring greater safety, stability, and minimal damage.
What Is the Most Earthquake-Resistant Building Material?
Steel frames, particularly those made from high-strength steel, are the most earthquake-resistant due to their flexibility, durability, and ability to absorb and dissipate seismic energy.
Earthquake Resilience: It’s More Than Just the Structure
Steel structures are strong against earthquakes, but that doesn’t guarantee complete safety. The right planning and preparation are key to ensure your building’s resilience. Here’s what you need to consider.
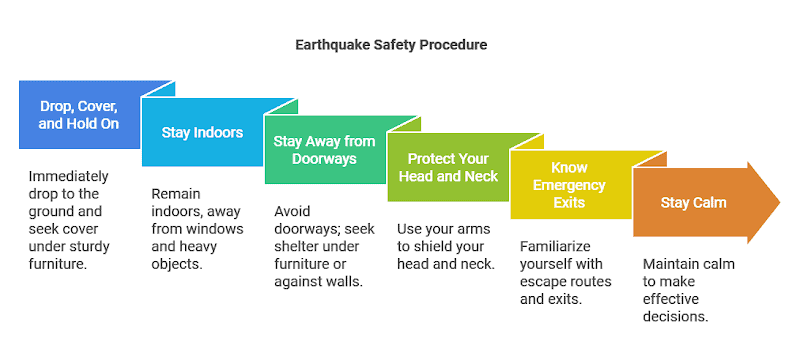
1. Earthquake Escape Skills
Having a steel structure is important, but knowing how to get out safely during an earthquake is just as crucial. Plan and practice escape routes to ensure everyone can exit quickly when needed.
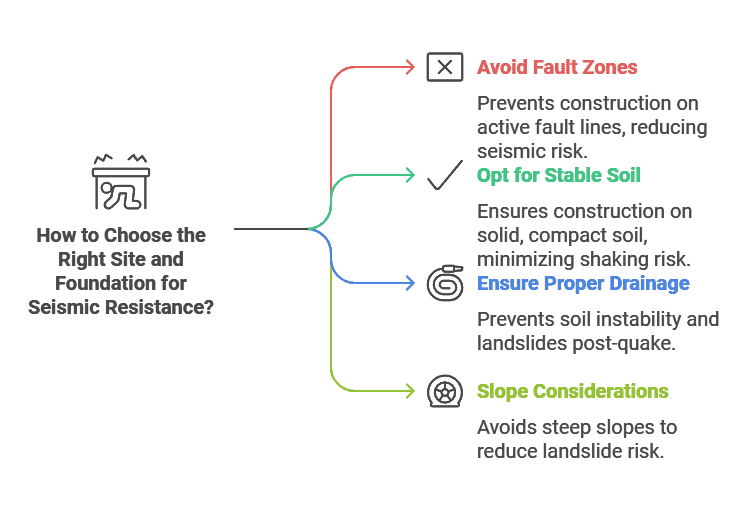
2. Choose the Right Site and Foundation
The location and foundation play a huge role in seismic resistance. A solid, stable site is essential. If you’re in a risk zone, reinforce the foundation to avoid potential issues.
3. Layout Matters
The layout of a building plays a big role in how it responds to earthquakes. Here’s how to get it right:
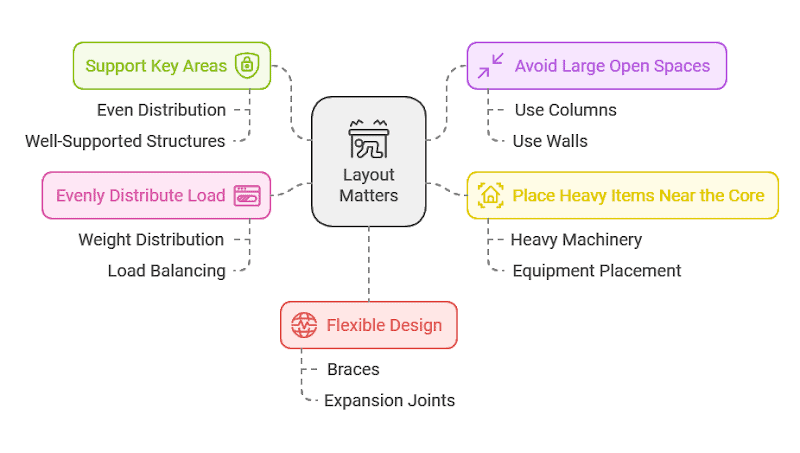
It’s about more than just the materials—thoughtful planning makes all the difference in ensuring a building is truly earthquake-resilient.
Professional Seismic Steel Structure Manufacturer
Whether you’re building for residential, agricultural, commercial, industrial, or simply for storage purposes, choosing us means choosing safety and reliability—even if you’re not in an earthquake-prone area. We can still incorporate earthquake-resistant steel construction methods into your design to ensure peace of mind, providing you with extra security and confidence.
Your safety is our priority, and we’re here to make sure your structure stands strong, no matter the circumstances. Let us help you build a safe and durable future!

