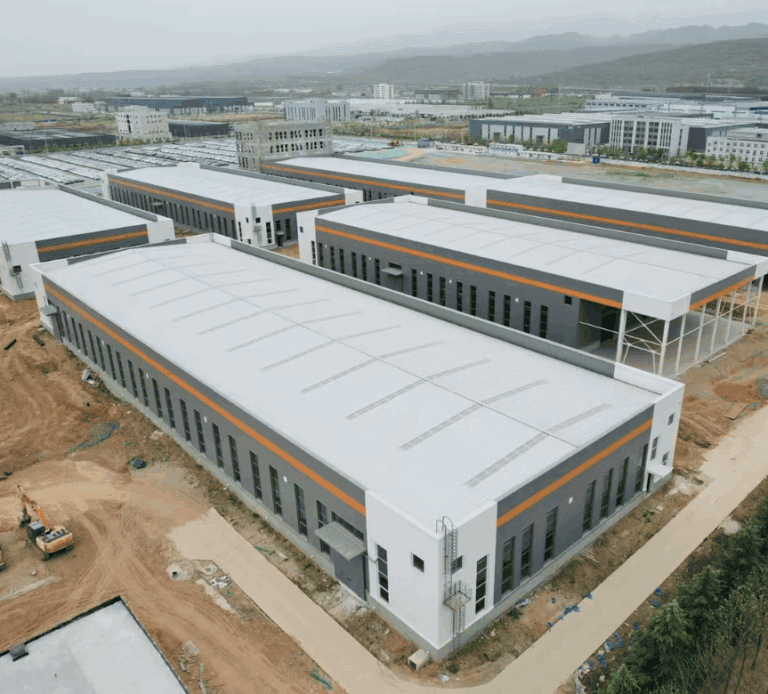
Ever found yourself frustrated by unexpected repairs, design uncertainties, or just trying to figure out how all the pieces of a steel workshop building come together? You’re not alone. Whether you’re managing a facility, planning a project, or simply curious about how these structures work, understanding the components is key. In this guide, we’ll break down every essential part—how they function, why they matter, and how they all fit into the bigger picture. Let’s get started!
Roof System: The First Line of Defense
A well-designed roof isn’t just about shelter—it’s about efficiency and longevity.
Key Roof Systems Components Explained
| Component | Material/Design | Function |
| Roof Steel Beam | Wide-flange beams (e.g., W12x30) | Primary load-bearing support for roof structure |
| Roof Trusses | Pre-engineered triangular frames (ASTM A36 steel) | Distribute loads across long spans |
| Roof Sheet | Corrugated Galvalume® (0.7mm) or insulated panels | Weatherproofing, thermal efficiency |
| Roof Purlins | C/Z-shaped cold-formed steel (12–16 gauge) | Secondary support for roof sheets |
| Roof Support Column | HSS (Hollow Structural Section) columns | Vertical support for beams/trusses |
| Bracing & Tie Rods | Steel rods (¾” diameter) or angle braces | Prevent lateral movement, stabilize structure |
| Knee Brace | Diagonal steel plates (½” thick) | Reinforce beam-to-column connections |
| Purlin Bracket | Galvanized steel brackets (3/16” gauge) | Secure purlins to primary beams |
Critical Steel Workshop Building Design Details You Can’t Ignore
1. Roof Paneling
- Outer Layer: Corrugated steel sheets (0.5–1.2 mm thickness) or insulated sandwich panels (EPS/PU core) dominate industrial roofs. For natural light, polycarbonate (PC) panels (up to 90% light transmission) are embedded every 20–30 ft.
- Inner Layer: Vapor barriers and 6-inch-thick fiberglass insulation (R-19 value) prevent condensation in cold climates.
- Fasteners: Self-drilling screws with EPDM washers ensure waterproofing even in hurricane-prone areas like Florida.
2. Purlin Network
- C/Z-Purlins: Cold-formed C-shaped purlins (12–16 gauge) handle spans up to 30 ft, while Z-purlins optimize load distribution for wider buildings.
3. Drainage Solutions
- Gutters & Downspouts: Galvanized steel gutters (6–8-inch width) paired with PVC downspouts reduce ice buildup in snowy regions. A 1:500 slope ensures rapid runoff.
4. Ventilation & Lighting
- Turbine Vents: These zero-energy devices move 800–1,200 CFM of air, cutting cooling costs by 20% in Texas warehouses.
- Smoke Vents: Motorized units (72” x 96”) meet NFPA 204 compliance for fire safety.
Pro Tip: Our pre-coated PVDF steel panels resist UV fading for 30+ years—perfect for Arizona’s harsh sun.
Wall System: Balancing Strength and Flexibility
Walls do more than enclose space—they adapt to your operational needs.
Essential Wall Components in Steel Workshop Buildings
From skeleton to skin, here’s what builds a high-performance wall:
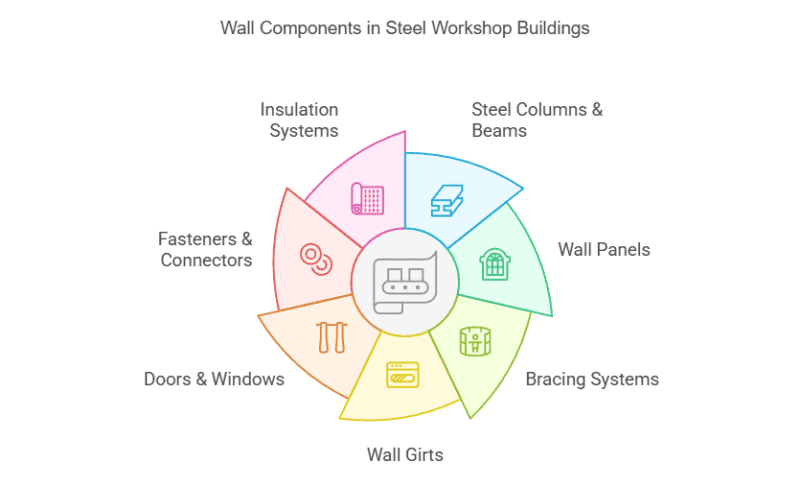
1. Steel Columns & Beams
- Vertical Columns:
- HSS (Hollow Structural Sections): Rectangular or circular tubes (e.g., 8x8x½”) anchor walls to foundations.
- Wide-Flange Columns: Heavy-duty options (e.g., W10x49) for multi-story workshops.
- Function: Transmit roof/wind loads to the foundation.
- Horizontal Beams:
- Spandrel Beams: Connect columns at wall tops, supporting roof systems (e.g., W8x31).
- Lintel Beams: Reinforce door/window openings (e.g., C10x15 channels).
- Function: Resist lateral forces and distribute weight.
2. Wall Panels
- Exterior Cladding:
- Corrugated Steel: 24–26 gauge ribbed panels (AZ55 galvanized) for durability.
- Insulated Sandwich Panels: 4–6” thick PU/EPS cores for thermal efficiency.
- Function: Weatherproofing and structural rigidity.
- Interior Liners:
- Vapor Barriers: 6-mil polyethylene sheets block moisture ingress.
- Acoustic Panels: Perforated steel with fiberglass backing (STC-40+).
- Function: Climate control and noise reduction.
3. Bracing Systems
- Diagonal Rod Bracing: 1”–2” steel rods in X or K configurations.
- Shear Walls: Steel sheet panels welded to columns.
- Function: Prevent racking under wind/earthquake loads.
4. Wall Girts
- Horizontal Girts: C/Z-shaped cold-formed steel (6”–8” depth), spaced 4–6 ft vertically.
- Vertical Girts: Used with horizontal variants for heavy cladding.
- Function: Support wall panels and transfer loads to columns.
5. Doors & Windows
| Type | Purpose | Avoid in Workshops |
| Overhead Sectional Doors | High-traffic loading bays (16’x14’ steel) | Wooden Doors – Prone to rot/impact damage |
| Roll-Up Doors | Compact spaces (aluminum/steel slats) | Single-Pane Windows – Poor insulation |
| High-Speed Doors | Temperature-controlled zones (PVC strips) | Fixed Non-Opening Windows – No ventilation |
| Tilt-Up Windows | Ventilation (aluminum frames) | Decorative Glass – Fragile, safety risk |
6. Fasteners & Connectors
- Self-Drilling Screws: #14–#16 with EPDM washers for panel-to-girt attachment.
- High-Strength Anchor Bolts: Used to secure columns to the foundation, ensuring stability against lateral forces.
- Structural Rivets: Provide additional fastening strength in high-vibration areas, reducing the risk of loosening over time.
- Bolted Connections: A325 bolts for column-to-beam joints.
- Welded Connections: Applied in critical joints for enhanced load-bearing capacity, often used in beam-to-column connections.
- Function: Ensure structural integrity and airtightness.
These steel connections in steel structure buildings play a crucial role in ensuring both structural integrity and airtightness, preventing leaks and maintaining stability under various loads.
7. Insulation Systems
- Batt Insulation: Fiberglass (R-13) or mineral wool (R-15) installed between girts for effective thermal resistance.
- Rigid Board Insulation: XPS/PIR boards (R-5 per inch), ideal for high-humidity areas to prevent moisture buildup.
- Spray Foam Insulation: Expanding polyurethane foam that seals gaps and enhances thermal efficiency while adding structural rigidity.
- Reflective Foil Insulation: Aluminum-backed insulation that helps reduce heat transfer in warmer climates, improving energy efficiency.
- Insulated Metal Panels (IMP): Factory-made sandwich panels with foam cores, providing both insulation and structural strength.
These steel structure insulation solutions help minimize thermal bridging and energy loss, ensuring a more comfortable and cost-efficient workshop environment.
Steel Workshop Building Wall Design: Smart Choices for Real-World Demands
Now, let’s translate components into solutions.
1. Impact-Resistant Cladding
- Problem: Forklifts denting walls in cramped factories.
- Fix: 22-gauge ribbed steel panels (tested to withstand 10,000+ impacts) at lower 8 ft heights.
2. Windproof Framing
- Problem: Coastal South Carolina’s 150 mph hurricanes.
- Fix: Double rows of 8” C-girts with ⅜” bolts every 12”—survived Hurricane Matthew (2016).
3. Thermal Breaks
- Problem: Condensation in Minnesota cold storage (-20°F).
- Fix: Thermal spacer blocks between steel framing and panels eliminate cold bridging.
Why This Works for Metal Workshop Buildings:
- Speed: Pre-insulated wall panels (4’x40’) slashed install time by 50% at a Nebraska tractor plant.
- Flexibility: Swap standard panels for acoustic liners (STC-50) near airports—no structural changes needed.
Pro Tip: Our BIM-driven prefab walls embed door/window openings with ⅛” precision—no onsite cutting. Result? 40% faster installs in Chicago logistics hubs.
Steel Workshop Structural System: The Backbone of Reliability
A steel workshop’s strength lies in its interconnected components. Let’s dissect these critical elements, combining clarity with depth.
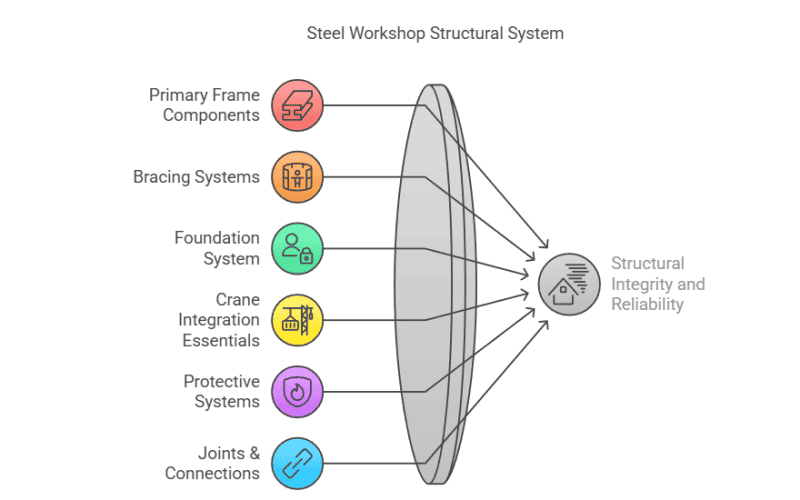
1. Primary Frame Components
The primary frame bears the building’s weight and resists environmental forces. Key elements include:
- Main Columns:
Vertical members like wide-flange beams (W14x68) or hollow structural sections (HSS 12x12x½”) transfer roof and crane loads to foundations. - Roof Beams:
Horizontal members (e.g., W24x55 beams) span between columns, resisting gravity loads (snow, equipment) and lateral forces (wind, seismic). - Crane Runway Beams:
Heavy welded plate girders (up to 36″ deep) support overhead cranes. Their flanges withstand wheel loads from Class D cranes (up to 100 tons). - Gable End Frames:
Rigid frames at building ends, engineered to handle wind pressures without diagonal bracing, maximizing interior space.
2. Bracing Systems
Custom features turn a standard building into a productivity powerhouse.
3. Foundation System
A stable foundation ensures longevity. Key components:
- Spread Footings:
Reinforced concrete pads (8x8x2 ft) distribute column loads to soil. - Grade Beams:
Connect footings to prevent differential settlement in expansive soils. - Anchor Rods:
High-strength threaded rods (ASTM F1554 Grade 55) embed columns into concrete, resisting uplift.
4. Crane Integration Essentials
| Component | Function |
| Runway Rails | Guide crane movement (ASTM A36 steel). |
| Bumpers | Absorb impact at track ends (rubber-steel hybrid). |
| Festoon Systems | Deliver power to mobile cranes via overhead cables. |
5. Protective Systems
- Galvanizing: Zinc coating (3.9 oz/sq ft) prevents rust in coastal climates.
- Intumescent Paint: Expands under heat, insulating steel at 200°C+ for fire resistance.
6. Joints & Connections
- Moment Connections: Full-penetration welds allowing controlled rotation during earthquakes.
- Shear Tabs: Bolt-on plates transferring vertical loads while permitting thermal expansion.
Conclusion: Why Partner with Us?
Steel workshops thrive on precision—85% of post-construction issues stem from poor detailing. Here’s how we deliver better:
- Speed: Pre-cut, pre-drilled components slash build time (e.g., a 50,000 sq ft warehouse erected in 12 weeks).
- Smart Maintenance: Our IoT-enabled bolt sensors alert you to loosening before failures occur.
- Customization: From 200-ft clearspans to explosion-resistant panels, we engineer solutions, not just buildings.
Whether you’re battling snow loads in Minnesota or salt spray in Florida, every component matters. For those seeking efficient, durable, and adaptable structures, our Light Steel Structure Workshop offers a proven solution. Ready to build smarter? Let’s talk steel.

