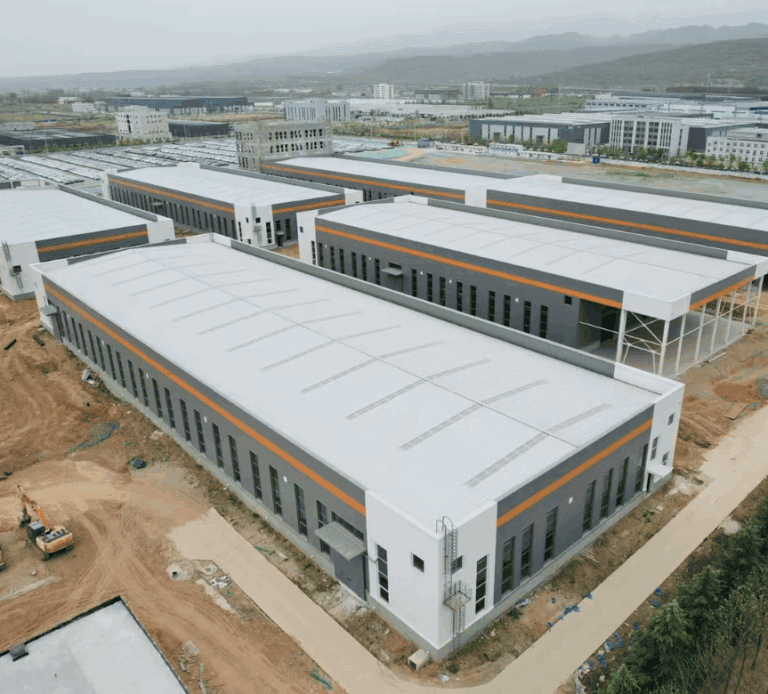
Steel structure components are the parts that make a building stand strong—columns, beams, trusses, floors, roofs, and walls. Each plays a key role in stability, durability, and efficiency.
In this guide, we explain the main steel structure building components, how they work, and why they matter. You will see how the primary framework, floor systems, roof systems, wall systems, and foundations fit together into a complete structure.
At SteelPRO PEB, a certified PEB Structures Manufacturer & Producer, we don’t just describe components—we produce and supply them directly from our factory lines, with international certification and wholesale prices.
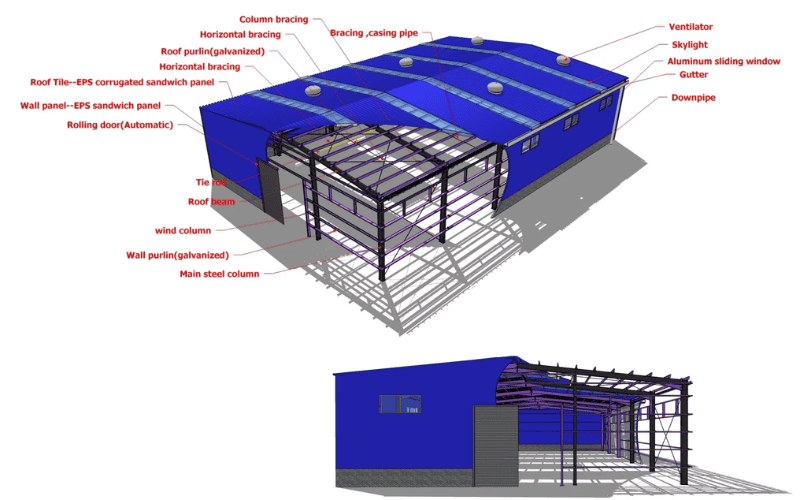
Primary Structural Framework of Steel Structure Buildings
The primary structural framework of steel structure buildings includes steel columns, beams, and trusses. These essential components form the backbone of the building, carrying vertical and horizontal loads, resisting forces such as wind and earthquakes, and ensuring overall stability and durability. In the following sections, we explain each part and its role in a strong and reliable steel building.
Steel Columns
Steel columns are the main vertical members in a steel structure building. They transfer the weight of the roof, floors, and walls down to the foundation. Without columns, a steel building cannot stand. Columns also resist wind and seismic forces, ensuring the structure remains stable and safe.
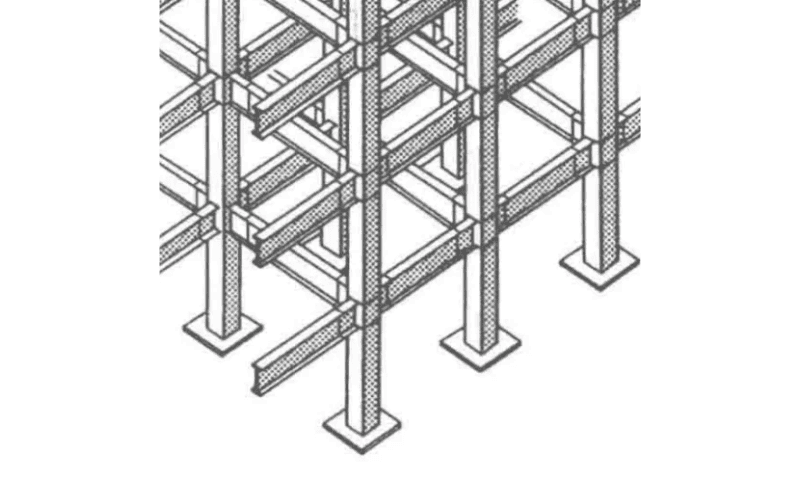
Types of Steel Columns
Steel columns are classified by cross-section shape and by the type of load they carry:
- Cross-Section Shapes
- Circular, square, rectangular, or H-shaped
- Tubular sections (e.g., CHS – Circular Hollow Section) for strength and modern design
- Load Types
- Axially Loaded Columns: load acts along the central axis, ideal for balanced weight
- Eccentrically Loaded Columns: load is off-center, used in complex or asymmetrical designs
Related Reading: 15 Types of Steel Columns: A Guide to Their Uses and Advantages
Connection Methods for Steel Columns
Steel columns are connected to other components using different methods:
- Bolted Connections: quick to assemble on site, suitable for flexible projects
- Welded Connections: stronger and permanent, used in heavy structures
- Base Plates: link columns to foundations and ensure safe load transfer
Steel Beams
Steel beams support the floors and roofs of a steel structure building. They carry loads from slabs, panels, and equipment, and transfer them to the columns. Beams also shape the layout of the building, defining spaces and room divisions. Without beams, a steel building cannot have stable floors or roofs.

Types of Steel Beams
Steel beams can be grouped by cross-section shape and by load-bearing style:
- Cross-Section Shapes
- I-beams
- H-beams
- C-beams (channel beams)
- T-beams
- Box beams (hollow rectangular or square sections)
- Load-Bearing Styles
- Simply Supported Beams: supported at both ends, common for short spans
- Cantilever Beams: fixed at one end, extend outward to create balconies or overhangs
- Continuous Beams: supported at multiple points, suitable for long spans
Related Reading: Steel Structure Beams: Overview, Types, Features and All
Connection Methods for Steel Beams
Steel beams connect to columns or other beams using different methods:
- Bolted Connections: quick installation and adjustment, used in beam-to-column joints
- Welded Connections: permanent and strong, ideal for heavy loads
- Shear Plates and End Plates: provide extra strength, ensure smooth load transfer
Steel Trusses for Large-Span Steel Structures
Steel trusses are lightweight but strong components used to span large distances in steel structure buildings. Their triangular design makes them stable and efficient in carrying loads from the roof or floors to columns and walls. Trusses are especially important in big steel structures such as stadiums, warehouses, and exhibition halls, where wide column-free spaces are needed.
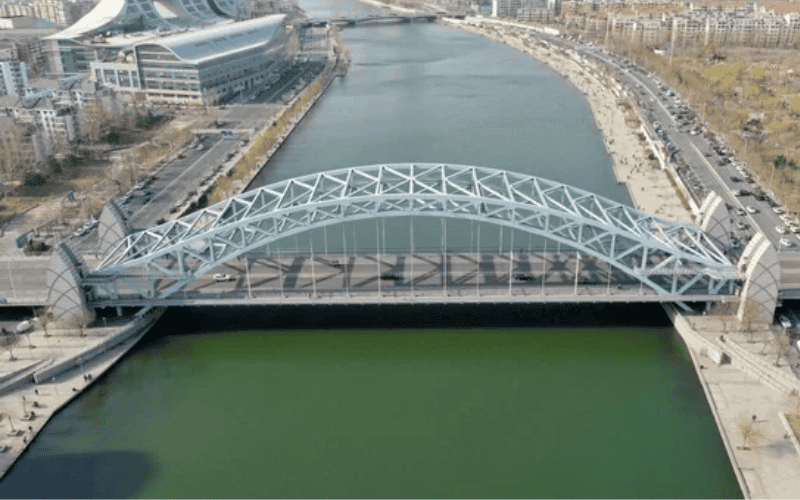

Types of Steel Trusses
Steel trusses come in different designs for different building needs:
- Planar Trusses: flat, triangle-based, common in roofs and bridges
- Space Trusses: 3D designs for heavy loads, used in arenas and exhibition centers
- Single-Layer Trusses: for smaller spans, typical in warehouses
- Double-Layer Trusses: for long spans and heavy roofs, used in industrial projects
- Vierendeel Trusses: no diagonals, flexible for architectural design
- Composite Trusses: combine steel and concrete for seismic resistance
Related Reading: Steel Truss Systems: Types, Design Principles, and Our Expertise
Connection Methods for Steel Trusses
Steel trusses are assembled with different connection methods:
- Bolted Connections: easy to assemble and disassemble on site
- Welded Connections: permanent and rigid, used in heavy-duty structures
- Gusset Plates: reinforce joints, distribute loads safely
Floor Systems in Steel Structure Buildings
The floor systems of steel structure buildings provide stable support for loads and people. They connect with the main framework and help the building resist forces over time. Common floor systems include steel decking for lighter loads and composite slabs for heavier loads. Together, they create durable, efficient, and safe flooring solutions.
Related Reading: Steel Floor Systems: Types, Advantages, and Applications
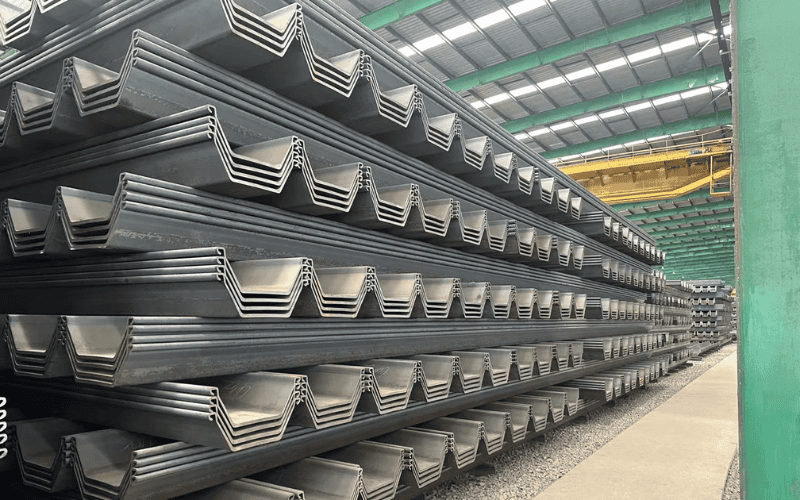
Decking (Profiled Steel Sheets)
Steel decking serves as the base for concrete slabs. It gives temporary support during construction and becomes a permanent part of the floor once the concrete sets.
Key features of steel decking:
- Lightweight but strong: reduces floor weight without losing strength
- Fast installation: easy to place and remains as permanent formwork
- Versatile: used for floors, roofs, and sometimes walls

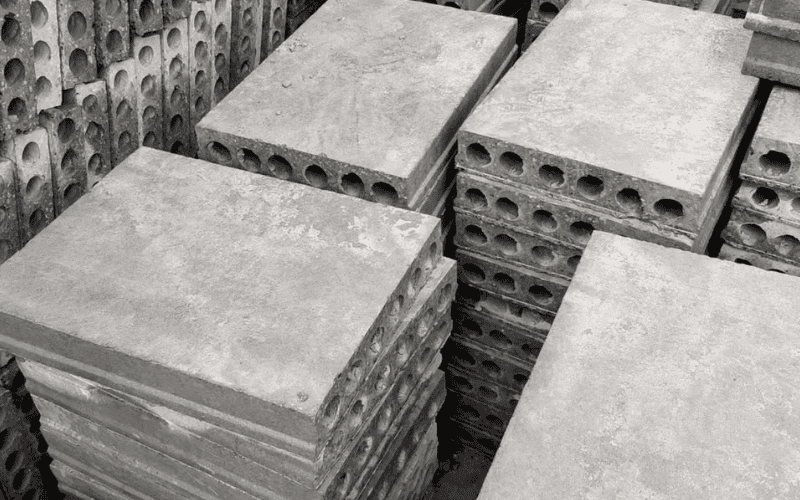
Composite Slabs
Composite slabs are formed by pouring concrete over steel decking. The steel and concrete work together to increase strength and stiffness.
Advantages of composite slabs:
- High strength: handle heavy loads in warehouses and industrial buildings
- Fire resistance: concrete layer adds protection
- Cost efficiency: save time and material compared to traditional slabs

Roof Systems in Steel Structure Buildings
The roof system of a steel structure building protects the interior, supports loads, and ensures long-term durability. It includes roof panels for covering, roof purlins for support, and roof expansion joints for flexibility. Together, they form a safe, insulated, and reliable roof.
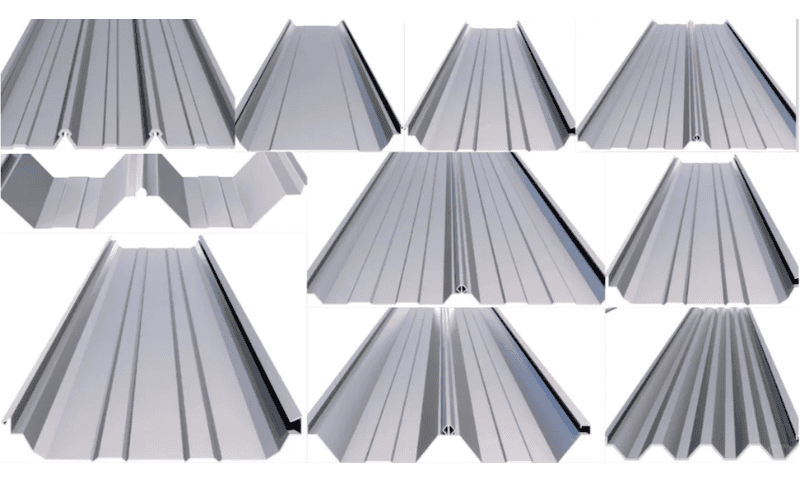
Roof Panels
Roof panels act as the protective shield of a steel building. They keep out rain, block heat, and provide insulation.
- Waterproofing: achieved through panel density and joint design, such as interlocking or standing seams.
- Thermal insulation: often designed as sandwich panels with rock wool or polystyrene foam, reducing heat transfer and energy costs.
- Types of roof panels: profiled steel panels, aluminum-magnesium-manganese alloy panels, color-coated steel panels.
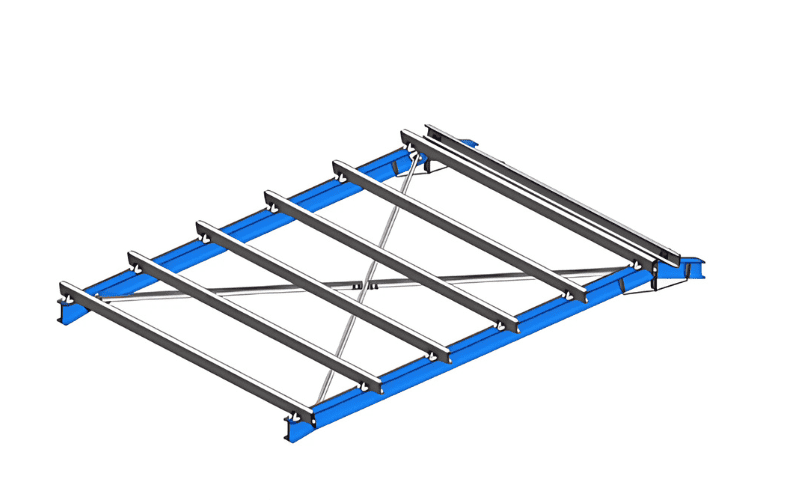
Roof Purlins
Roof purlins support the roof panels and transfer their loads to the beams.
- Benefits: lightweight but strong, distribute loads evenly, prevent local stress points.
- Material: usually made of cold-formed thin-walled steel.
- Shapes: common designs are C-sections and Z-sections.
Roof Expansion Joints
Roof expansion joints allow roof sections to expand and contract with temperature changes, preventing damage.
- Function: avoid cracking, warping, or deformation.
- Design: spacing depends on climate; closer in cold regions, wider in warm regions.
- Construction: use sealants and sliding connections to allow free movement while keeping the roof waterproof.
Wall Systems in Steel Structure Buildings
The wall system of a steel structure building provides enclosure, insulation, and stability. It includes wall panels for protection, wall girts for support, and wall beams for strength in large walls. Together, they form a durable and efficient building envelope.
Wall Panels
Wall panels form the outer skin of a steel building. They protect the inside, keep out wind and rain, and help save energy.
- Thermal insulation: sandwich structure with rock wool or polyurethane foam reduces heat loss and keeps rooms cool.
- Soundproofing: panel material and installation reduce outside noise.
- Waterproofing: sealed joints, waterproof connectors, and coatings block rain and prevent dampness.
- Types of wall panels: metal panels, sandwich composite panels, fiber cement panels.
Wall Girts
Wall girts are horizontal or vertical members fixed to the main frame. They support the wall panels and keep them flat.
Functions of wall girts:
- Provide fixing points for wall panels.
- Transfer loads such as wind pressure, self-weight, and impact forces to the columns and beams.
- Ensure stability and prevent deformation.
Wall Beams
Wall beams add extra strength in tall walls or large-span steel buildings. They work with wall girts to resist loads.
- Function: carry heavy wall panels and wind loads, improve vertical and lateral stability.
- Design considerations: size and material depend on girt spacing and wall load; connections must use reliable welding or bolting for safe load transfer.
Foundation of Steel Structure Buildings
The foundation of a steel structure building transfers loads safely to the ground. It prevents settlement, ensures stability, and keeps the building secure over time. Foundations work together with anchor bolts to connect the entire steel structure to the ground, both in prefabricated and non-prefabricated systems.
Column Foundations
Column foundations support the vertical loads from steel columns and distribute them evenly into the soil.
Functions of column foundations:
- Load transfer: carry the full weight of the building to the ground.
- Stability: prevent tilting, sinking, or shifting of the structure.
- Integration: designed to work with the flexibility of steel structures.
- Applications: used in both prefabricated and non-prefabricated systems.
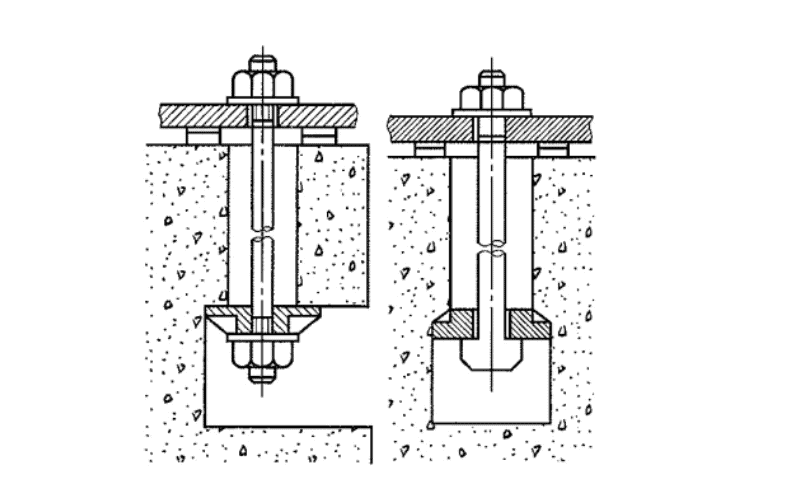
Anchor Bolts
Anchor bolts fix steel columns to the concrete foundation and keep them aligned. They are critical for structural safety.
Key points about anchor bolts:
- Secure connection: hold columns firmly in place, even under wind and seismic forces.
- Precision: must match the base plates of columns, requiring accurate planning and execution.
- Installation: usually embedded in the concrete during pouring, ensuring strong bonding with the foundation.
Steel Structure Parts Names and Their Functions
Users often ask: What are the main parts of a steel structure building?
Below is a list of common steel structure parts names with their basic functions. This quick overview helps you understand how each component works in the whole system.
| Part Name | Function |
| Steel Columns | Main vertical members, transfer loads to the foundation |
| Steel Beams | Horizontal members, support floors and roofs |
| Trusses | Triangular structures for large spans, resist wind and seismic forces |
| Purlins | Support roof panels, distribute loads |
| Wall Girts | Support wall panels, transfer wind loads to columns |
| Roof Panels | Cover the roof, waterproof and insulate |
| Wall Panels | Enclose the building, insulate and protect |
| Bracing | Stabilize the frame, resist lateral forces |
| Anchor Bolts | Fix columns to the foundation |
| Base Plates | Connect columns to foundation securely |
Note:
This list covers the essential components, but designs may vary depending on project requirements.
For complete factory-direct steel structure components, SteelPRO PEB provides certified and customized solutions for warehouses, factories, and industrial projects.
Why Choose SteelPRO PEB for Steel Structure Components
When you buy steel structure components, you don’t need long brochures—you need the right partner. At SteelPRO PEB, a certified PEB Structures Manufacturer & Producer, we don’t just describe beams, columns, or purlins, we make them.
- Direct from factory: 24 production lines, 120,000 tons yearly output, shipped worldwide .
- Certified quality: ISO & CE standards, trusted in over 1,000 projects across 30+ countries.
- Wholesale advantage: no middlemen, faster delivery, lower total cost.
Others sell information. We deliver components—precise, certified, ready to build.
Contact SteelPRO PEB today and get your steel structure components straight from the source.

