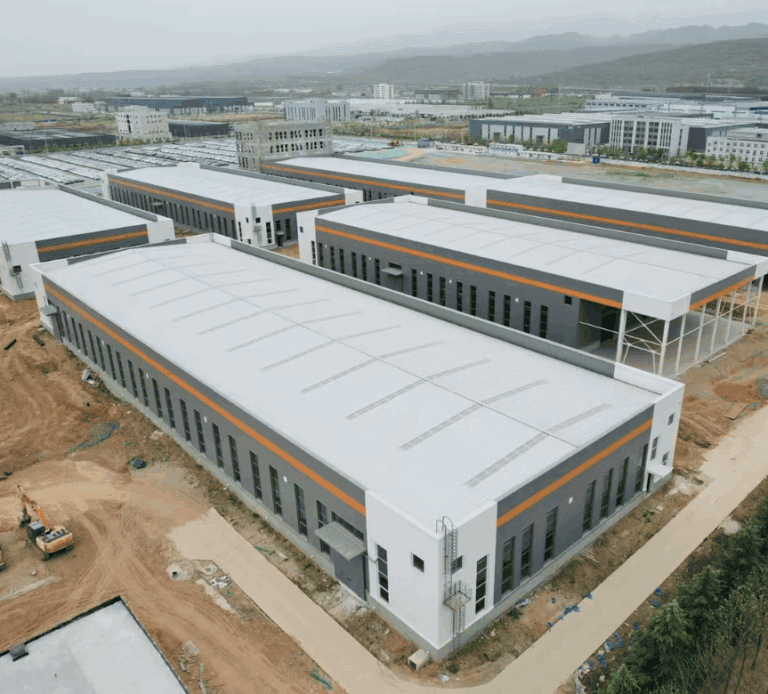
With various types of steel roofs to choose from, each offering different benefits, making the right choice can be overwhelming. However, by carefully considering factors such as climate and functional needs, you can make an informed decision that meets both practical and design goals. We will walk you through the various aspects of steel roofing to help you choose the steel roofing solution that best suits your specific project needs.
What is a Steel Structure Roof?
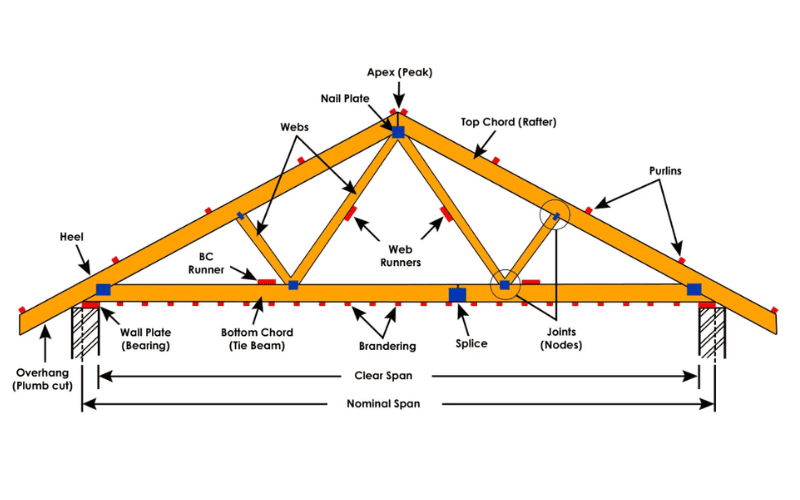
A steel structure roof is a roof system built with steel as the main material. It has the characteristics of high strength, light weight and large span, and is suitable for industrial, commercial and residential buildings. The steel roof is composed of roof panels, roof frame, connectors, waterproof layer, thermal insulation layer and drainage system, which together ensure the strength, waterproofness, thermal insulation and drainage function of the roof.
Commonsteel structure roofs materials
- Galvanized Steel: Coated with zinc to prevent rust; cost-effective and durable.
- Galvalume Steel: Coated with aluminum-zinc alloy for enhanced corrosion resistance.
- Weathering Steel: Forms a protective rust layer; low maintenance.
- Stainless Steel: High corrosion resistance; durable and long-lasting.
- Color-Coated Steel: Painted surface for aesthetics and added protection.
- Aluminum-Zinc Alloy Steel: Superior corrosion resistance; ideal for harsh environments.
Main Types of Metal Roofs
1. Rigid Frame Roof
Features: A rigid frame composed of steel beams and steel columns, with strong bearing capacity and high stability. Common connection methods are welding or bolting.
Applicable scenarios: Suitable for large-span buildings such as industrial plants, warehouses, and large commercial buildings.
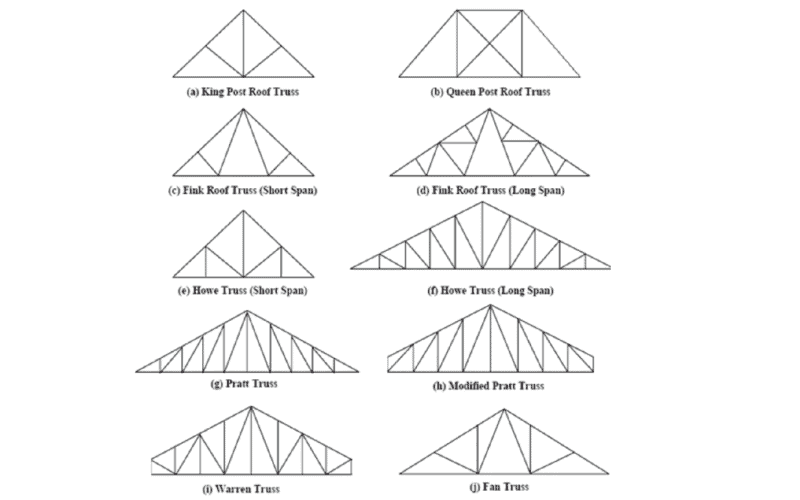
2. Roof Truss
Features: Roof truss is connected by a series of triangular steel components (trusses), which can effectively share the load, has a light structure, and is suitable for large-span applications.
Applicable scenarios: Commonly used in stadiums, exhibition halls, large warehouses, etc., which require large spaces and do not want to use internal pillars.
3. Space Frame Roof
Features: It is composed of multiple steel pipes or steel beams staggered to form a mesh structure, which can support large spans and adapt to complex roof shapes, and has high strength and stability.
Applicable scenarios: Suitable for large-span, special-shaped buildings, such as airport terminals, shopping malls, large stadiums, etc.
4. Arch Roof
Features: It adopts an arched structure, and the load is shared by arched beams or arched steel frames. It can effectively resist compression and has strong wind and earthquake resistance.
Applicable scenarios: It is often used in large buildings such as stadiums, industrial plants, warehouses, etc., especially in places that require elegant appearance and bearing capacity.
5. Suspension Roof
Features: The roof is suspended by steel cables or steel chains to form a curved roof structure that can provide support for large spans.
Applicable scenarios: It is suitable for buildings such as bridges, exhibition halls, and stadiums that need to span a large space and have a unique appearance.
6. Pitched Steel Roof
Features: The roof has a certain slope and is composed of steel beams and steel roof panels. Drainage is usually considered in the design.
Applicable scenarios: It is widely used in industrial plants, warehouses, agricultural buildings, etc., especially in areas with strong drainage needs.
7. Pre-engineered Steel Roof
Features: The roof is composed of factory-prefabricated steel plates and structural components, assembled on site, with simple structure and fast installation.
Applicable scenarios: Suitable for projects that require standardized and fast construction, such as standard factories, warehouses, etc.
How to Choose a Steel Roof Based on Climate and Functional Requirements?
The impact of climate factors on the selection of steel roofs
a. Cold climate
Snow-proof design: In cold areas, the load-bearing capacity of the roof needs to be considered, especially the weight of snow. Choose a steel roof structure that is designed to resist the pressure of snow, such as increasing the slope, using reinforced steel beams, or choosing thicker steel plates.
Insulation layer: It is necessary to choose materials with good thermal insulation properties to avoid heat loss in the house. Usually, a double-layer roof or an insulation layer can be added to the roof.
Anti-freeze cracking design: To choose steel that is resistant to low temperatures and frost heave, you can choose galvanized or coated steel plates to prevent the steel from cracking due to climate change.
b. High temperature climate
Reflective coating: In high temperature areas, choosing a steel roof coating with heat reflective properties (such as reflective coating or light-colored coating) can effectively reduce heat absorption and reduce the temperature in the house.
Ventilation design: The steel roof should have a good ventilation design, and vents, roof exhaust vents and other means can be used to reduce heat accumulation in the house.
Heat-resistant steel: In high-temperature environments, it is crucial to choose steel that is resistant to high temperatures. Coated steel or special coated steel can improve the stability and durability of steel roofs in high temperatures.
c. Wet or rainy climates
Anti-corrosion coating: In humid environments, it is critical to choose steel roofing materials that are highly resistant to corrosion. You can choose stainless steel, galvanized steel, or steel with special anti-corrosion coatings to prevent rust.
Drainage design: In rainy areas, ensure that the roof has sufficient slope and an efficient drainage system to avoid water accumulation. It is crucial to choose a steel roof design with good drainage performance.
Waterproof membrane or sealing layer: Use a waterproof membrane or sealing layer to further improve the waterproof effect and prevent rainwater from penetrating.
d. Tropical or heavy rain areas
Wind-resistant design: If the roof is in an area susceptible to extreme climates such as typhoons and tropical storms, the roof design needs to strengthen wind resistance. Choose a steel roof system with a high-strength structure (such as reinforced steel beams and connection points) to ensure that it can withstand strong winds and heavy rains.
Weather-resistant materials: Use materials that are resistant to oxidation and humid climates, such as special coated steel sheets or hot-dip galvanized steel sheets, to cope with extreme moisture and stormy weather.
2. The impact of functional requirements on the selection of steel roofs
a. Commercial buildings (such as shopping malls, office buildings)
Aesthetics and functionality balance: When choosing a steel roof, you need to consider both aesthetics and functionality. You can choose decorative coatings or adopt more modern steel roof designs (such as transparent roofs, roof gardens, etc.) while ensuring structural safety.
Insulation and sound insulation design: In a commercial environment, insulation and sound insulation are particularly important. Choose a steel roof with good sound insulation performance and add sound insulation materials to the roof design.
b. Industrial warehouses or factories
Long-span design: For large warehouses or factories, steel roofs usually need to be designed as long-span structures to ensure sufficient internal space. Choosing a rigid steel frame roof system suitable for large spans (such as portal steel frames, steel trusses, etc.) can improve space utilization efficiency.
Strength and durability: Considering factors such as heavy stacking and mechanical vibration, the roof needs to have higher strength and earthquake resistance. It is crucial to choose high-strength steel and earthquake-resistant design at this time.
Heat resistance and ventilation: If it is a high-temperature workshop (such as metallurgy, chemical plants, etc.), the steel roof needs to have high temperature resistance and a good ventilation system.
c. Agricultural facilities (such as greenhouses, farms)
Light transmittance: For agricultural buildings such as greenhouses, steel roofs should have good light transmittance so that plants can get enough sunlight. Transparent or translucent materials (such as polycarbonate or clear coated steel plates) can be used.
Anti-corrosion and thermal insulation: The agricultural environment is humid and the temperature difference is large, so the steel roof needs to have strong anti-corrosion and good thermal insulation in cold seasons.
d. Residential buildings
Beauty and thermal insulation: In residential buildings, the beauty and living comfort of the steel roof are very important. Choose a steel roof system with good appearance and combine it with an efficient thermal insulation design to ensure the comfort of the living environment.
Low maintenance requirements: Residential roofs generally require less frequent maintenance, so you can choose corrosion-resistant and weather-resistant materials to reduce the long-term maintenance costs of the roof.
How Long Does a Metal Roof Last?
Steel structure roofs can usually be used for more than 50 years, or even longer. Its durability far exceeds that of many traditional materials. Want the roof to accompany you for a longer time? Just do the following:
Regular inspection: It is recommended that you check the roof at least once a year to see if there is any corrosion, deformation or loose connections. Just like our annual physical examination, early detection and early solution of problems can prevent small problems from becoming big troubles.
Cleaning and maintenance: Leaves, dust or other debris may accumulate on the roof, especially near the drain. Regularly clean these debris to maintain an unobstructed drainage system. This not only prevents water accumulation but also avoids prolonged moisture exposure on the roof.
Anti-corrosion treatment: The anti-corrosion coating of the steel structure roof is its “umbrella”. Regularly check whether the coating is damaged or peeling, and repair it in time. Just like waxing a car, maintaining the integrity of the coating will make the roof more durable.
Joint inspection: The joints and connection points of the roof are prone to problems. Regularly inspect these parts to ensure they are properly sealed, preventing rainwater infiltration. Ignoring even a small leak can escalate into larger issues.
Contact US Now!
We offer comprehensive technical support and professional guidance to assist you in maintaining your steel structure roof effectively. From choosing the right anti-corrosion coating to detailed steps for regular inspections, our team will answer your questions via phone, email or video, and provide detailed maintenance manuals.
In addition, our products are strictly quality tested to ensure that you receive durable and high-performance materials. No matter what problems you encounter, we will do our best to provide you with solutions to keep your steel structure roof in the best condition for a long time!

