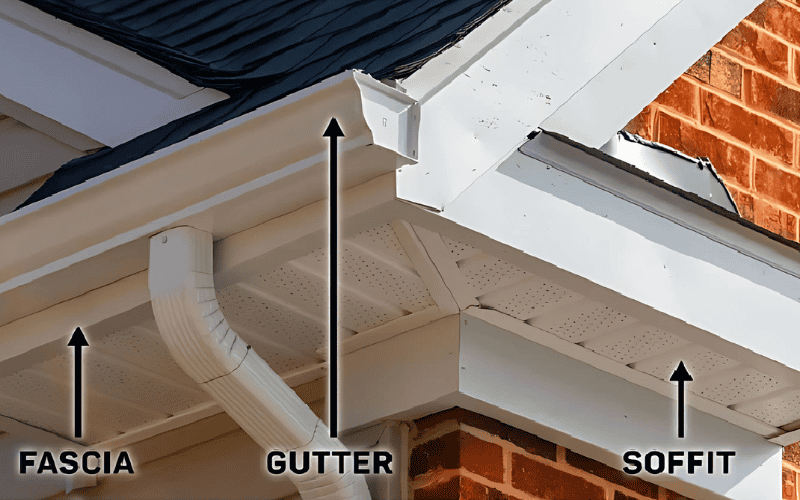
Have you ever noticed that when it rains heavily, the rainwater always flows precisely into the gutter, while the inside of the eaves can stay dry? This is thanks to the “roof partner” Fascia (fascia board) and Soffit (soffit).
One stands vertically on the outside of the eaves, holding up the gutter and blocking wind and rain; the other is hidden horizontally at the bottom of the eaves, balancing ventilation and protection. Despite being frequently misconstrued as “ordinary boards,” they serve as the primary barrier against leaks and moisture. We will take you to explore these two key components and their differences.
What is Fascia?
Fascia is a key part of the roof structure. It is usually a horizontal sheet located at the outer edge of the roof and installed along the edge or eaves of the roof. It is the connecting part between the roof and the wall, playing a dual role of decorative and protective.
Material of fascia:
- Wood: Traditional fascia board, providing sturdy support and a natural appearance.
- Aluminum alloy: It is corrosion-resistant and easy to maintain, making it suitable for long-term use.
- PVC: Waterproof, corrosion-resistant, lightweight and easy to clean.
- Metal: Such as steel or stainless steel, provides additional strength and durability, often used in modern buildings.
The design and material selection of the fascia will directly affect the durability and appearance of the roof system, and regular maintenance is required to maintain its structural integrity.
What is Soffit?
Soffit is the horizontal part located below the roof structure, between the eaves and the exterior wall, and usually covers the area below the eaves. Its main function is to provide ventilation for the roof, keep air flowing between the roof and the interior of the house, and also play an aesthetic role.
Materials of Soffit:
- Wood: A traditional material that can provide a natural appearance, but requires regular maintenance to prevent corrosion.
- Aluminum alloy: corrosion-resistant, lightweight and easy to maintain, widely used in modern buildings.
- PVC: waterproof and corrosion-resistant, suitable for humid or rainy environments, relatively simple to clean and maintain.
- Fiber cement: suitable for buildings that require extra strength or in high humidity areas.
- Soffit design:
Soffit is usually designed with a vent structure to help air flow. Some soffit is also designed with breathable grids or holes to promote effective ventilation of the roof space. In addition, the appearance of soffit is often matched with fascia to form a unified roof edge design.
In general, the function of soffit is not limited to exterior decoration, it plays a vital role in the ventilation and protection of the roof system.
Difference between Fascia and Soffit
| Comparison | Fascia | Soffit |
| Position | Located at the outer edge of the roof, above the eaves | Located below the eaves, connected to the exterior wall |
| Primary Function | Supports the gutters, protects the roof structure | Provides roof ventilation, prevents moisture buildup, covers the overhanging part of the roof, and enhances roof structural health |
| Visual Priority | Visible on the exterior, affects aesthetics | Typically hidden, focuses more on functionality |
| Ventilation Role | Usually does not provide direct ventilation, more focused on support | Has important ventilation function, often perforated to promote air circulation |
| Material Selection | Focused on load-bearing and weather resistance | Focused on moisture resistance and breathability |
Why are they so important to buildings?
Fascia and soffit not only bolster the building’s functionality but also play a pivotal role in its aesthetics, durability, and safety.
The core role of fascia
Protect roof rafters from rain erosion: Fascia, as the outer edge of the roof, can effectively protect roof rafters (or beams) from rain, snow, etc. For steel-structured buildings, rust-proofing of fascia is particularly important, which can extend the service life of the structure and prevent corrosion of metal parts.
Provide a mounting base for gutters: Fascia provides a stable mounting base for roof gutters to ensure the normal operation of the drainage system. A stable drainage system can prevent water accumulation on the roof and reduce the damage to the building structure caused by water leakage.
Improve the integrity of the building’s appearance: The design of fascia not only serves practical purposes but also enhances the overall aesthetic appeal of the building. For fascias made of metal, the color, texture or pattern can be customized according to the needs of the building design, making the appearance more coordinated and modern.
The core role of soffit
Ventilation function: Soffit is usually designed with a perforated structure that can help regulate the difference in air pressure between the inside and outside of the roof. Through effective ventilation, soffit helps avoid the accumulation of moisture and mold, and protects the healthy environment of the roof and the interior of the building.
Sheltering structure: Soffit covers the roof overhang, hiding the beams, pipes and other structural components inside the roof, keeping the facade neat and beautiful, and preventing the exposed roof structure from affecting the visual effect of the building.
Fire and insect resistance: Metal soffit is not only moisture-proof and breathable, but also provides additional fire and insect resistance. Metal soffit is more durable and suitable for buildings that require higher safety standards and weather resistance.
Maintenance of Fascia & Soffit
Daily maintenance of metal fascia/soffit
Regularly clean the fallen leaves and silt in the gutter (recommended once a quarter) to prevent water from seeping in from the joints and causing rust on the metal sheet. If the anti-rust coating on the surface of the fascia is found to be peeling or scratched, it needs to be polished in time and repainted with the same color paint to prevent oxidation from spreading.
For the soffit, you can use a soft brush to remove the spider webs or dust in the ventilation holes (avoid high-pressure water guns to prevent water pressure from destroying the hole structure) to ensure air circulation efficiency.
Periodic inspection and repair
Before and after the rainy season every year, it is recommended to check whether the connection between the fascia and the gutter is firm, and whether the soffit is deformed or loose.
If the edge of the metal sheet is found to be lifted, the joint glue is cracked, or the hole is blocked by more than 30%, it needs to be repaired immediately-minor rust spots can be polished with sandpaper and repainted, and severe deformation requires partial replacement.
When cleaning, utilize a neutral detergent and a soft cloth to wipe the surface, to prevent acidic solvents from corroding the metal layer.
Extending life from the source: scientific materials and installation
Choosing aluminum-zinc steel sheets with self-repairing coatings (such as AMM coatings) can significantly reduce maintenance frequency.
During installation, ensure that the Soffit retains a tilt angle of at least 5° to prevent water accumulation; stainless steel rivets must be used at the fixing points between the Fascia and the roof structure and filled with waterproof sealant.
If the building is located in a high humidity or coastal area, it is preferred to use metal Soffit with a fully welded process to reduce the risk of corrosion at the joints.
Do the fascia and soffit have to be installed at the same time?
No, they don’t necessarily have to be installed at the same time, but they are often installed together because they work together to support the roof structure. The fascia provides support and protection for the edge of the roof, while the soffit helps ventilate and prevent moisture buildup. While you can install one or the other, installing both together allows for better roof protection and structural health.
How do you tell if your fascia or soffit needs to be replaced?
Situations that call for replacing your fascia or soffit include:
- Corrosion or rust: Metal fascias or soffit are severely rusted or corroded, affecting their function.
- Cracks or deformation: If the fascia is cracked or the soffit is deformed, it may affect the support and ventilation function of the roof.
- Water accumulation or mold: If the drainage system is blocked or the soffit is poorly ventilated, it may cause moisture accumulation and mold growth, affecting indoor air quality.
- Fascia damage: When the fascia is severely damaged, peeling, or faded, it is also necessary to consider replacement.
Can you install a soffit without fascia?
Technically, it is possible to install a soffit without a fascia, but it is not recommended. The fascia provides the necessary support for the soffits and gutters, helping to stabilize the entire roof structure. Without the fascia, the soffits may lack stability and the gutter system may not function properly.
Conclusion
Fascia and soffits are crucial components of any roof system, playing a vital role in both the structural integrity and aesthetic appeal of a building. Faces provide support for gutters and protect the roof from water damage, while soffits facilitate ventilation and protect the underlying roof structure from environmental elements.
Whether you are maintaining an existing roof or considering a new installation, it is critical to understand the functions and maintenance needs of fascias and soffits. By selecting durable materials and carrying out regular maintenance, you can guarantee that your roof system will remain robust, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing for many years.

