A solar greenhouse isn’t just a structure—it’s a way to grow more efficiently by using the sun as your main energy source. With the right design, it can help maintain a stable environment for crops, even in colder or off-grid locations.
If you’re exploring options for year-round growing, cutting energy costs, or building in remote areas, this approach is worth a closer look.
In this article, we’ll walk through what a solar greenhouse is, what it’s commonly used for, how it works, and how to know if it’s the right fit for your project.
What to Expect in This Blog:
What Exactly Is a Solar Greenhouse?
A solar greenhouse is a type of greenhouse designed to make the most of the sun’s energy. Unlike traditional greenhouses that may rely heavily on electricity or gas for heating, a solar greenhouse is built to collect, store, and efficiently use solar energy—either passively, actively, or both.
You might hear the term used in different ways, so let’s break it down clearly:
- Passive solar greenhouses use smart design features—like south-facing orientation, insulated north walls, and thermal mass (such as water barrels or concrete floors)—to trap and retain heat during the day and release it at night.
- Active solar greenhouses go a step further by integrating solar panels. These panels can power fans, pumps, lights, or other systems, making the greenhouse more energy-independent.
The goal is simple: to create a stable growing environment, especially in cold seasons or remote areas, without relying too much on fossil fuels or the grid.
If you’re thinking about growing crops year-round, cutting energy costs, or building in areas with limited electricity, this kind of structure could be exactly what you need.

Related Reading:
What is a Solar Greenhouse? Do You Really Know?
Why Would You Use a Solar Greenhouse Instead of a Traditional One?
If you’re already familiar with regular greenhouses, you might wonder: why switch to a solar greenhouse? The answer comes down to one thing—control without the cost.
A solar greenhouse gives you better temperature stability, longer growing seasons, and lower operating costs. That can make a big difference, especially if:
- You’re farming in cold climates where heating is expensive
- You’re in a remote area with no stable power supply
- You want to grow year-round, without relying on fossil fuels
- You’re trying to reduce your carbon footprint or meet sustainability goals
Traditional greenhouses often depend on electric or gas-powered systems to maintain a stable environment. But those energy costs add up fast—and they’re not always reliable.
With a solar greenhouse, you use the sun itself as the primary energy source. That means:
- Lower utility bills
- More predictable conditions for your crops
- Better performance in off-grid or high-altitude regions
It’s also ideal for government-backed agriculture projects, NGO-led rural development, or any farm looking to modernize without taking on massive energy infrastructure.
So if you’re looking for a smarter, cleaner, and more cost-effective way to grow—solar greenhouse design is worth serious consideration.
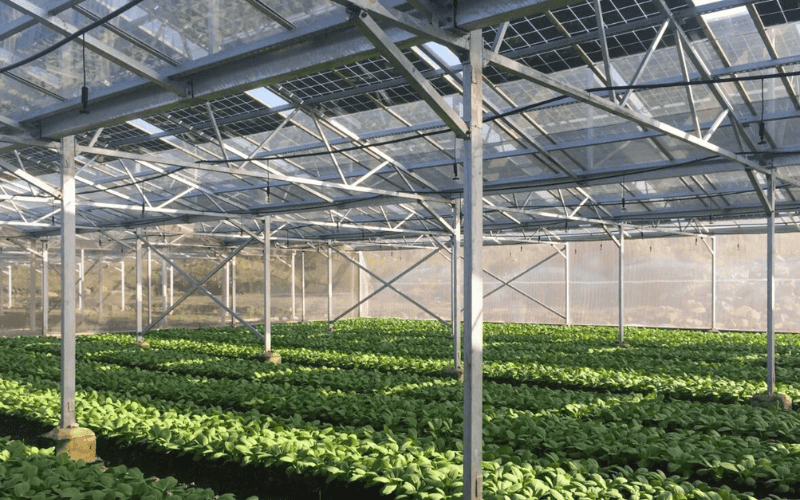
What Can You Grow in a Solar Greenhouse?
The short answer? Almost anything you can grow in a traditional greenhouse—and often more.
Because solar greenhouses offer better temperature control and energy efficiency, they’re especially good for crops that need consistent warmth or longer seasons. Here are some of the most common applications:
- Vegetables and fruits
Tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, leafy greens, strawberries, and more—solar greenhouses allow year-round production, even in cold climates. - Flowers and ornamentals
Ideal for nurseries or floriculture businesses that need stable growing conditions to meet seasonal market demand. - Herbs and medicinal plants
From basil and mint to ginseng and aloe vera, solar greenhouses help boost both yield and quality. - Seedlings and plant nurseries
Early-stage growth requires protection and precise temperature—solar setups are perfect for this. - Aquaponics and hydroponics
Many growers integrate solar greenhouses with water-based systems, creating highly efficient, closed-loop environments.
You can scale up or down depending on your needs—from small hobby setups to full commercial production. The key is that a solar greenhouse gives you more flexibility and control over your crops, with much less energy input.
How Does a Solar Greenhouse Work in Practice?
So how does a solar greenhouse actually work day to day? It’s not magic—just smart design and efficient use of natural energy, supported by a well-built structure.
Passive Solar Design: Structure That Works With the Sun
Everything starts with how the greenhouse is built. Passive solar greenhouses use structural features to capture heat during the day and hold onto it at night—with no electricity involved.
Key design elements include:
- South-facing orientation to absorb maximum sunlight
- Insulated north wall, often built with sandwich panels, to block cold air and reduce nighttime heat loss
- Thermal mass, like concrete floors or water barrels, to store daytime heat and release it slowly overnight
- Double-glazed or polycarbonate roofing that balances light transmission and insulation
- Roof pitch and overhangs designed to manage solar gain throughout the seasons
The structure isn’t just a shell—it’s part of the system. Every element plays a role in stabilizing temperature and lowering energy needs.
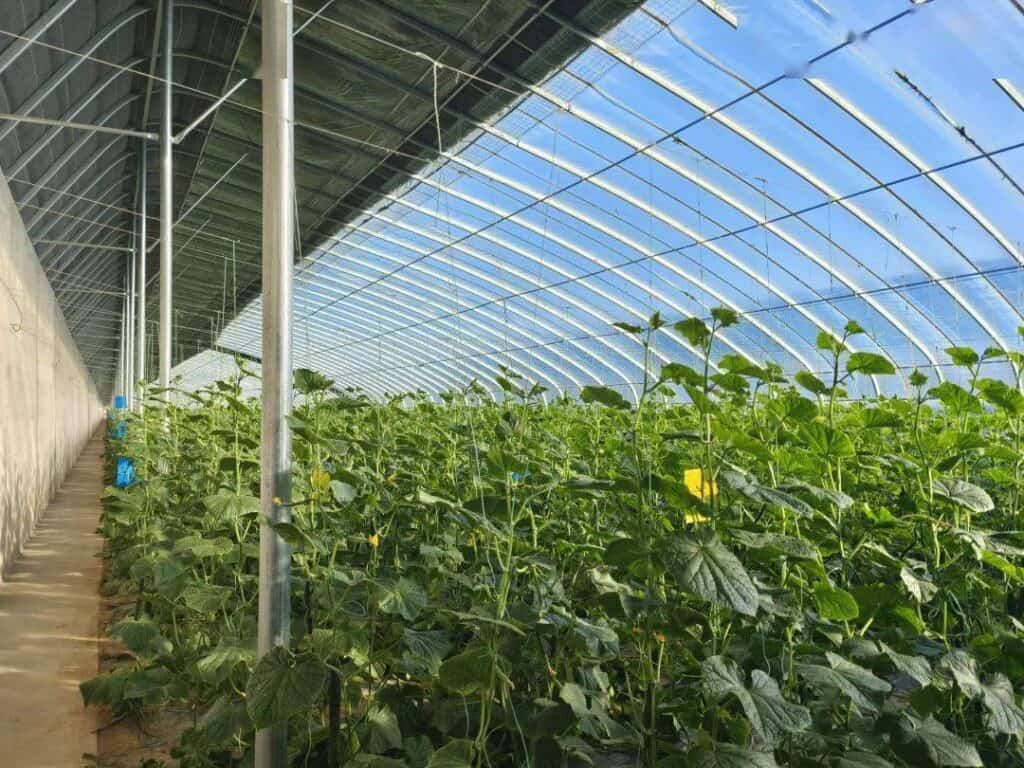

Active Solar Systems: Adding Smart Energy Where Needed
Some growers also integrate active solar components—like PV panels on the roof or integrated solar structures. These systems can power:
- Fans and ventilation
- LED grow lights
- Irrigation and climate control
- Battery storage for off-grid backup
This gives you greater control over the environment, especially in extreme climates or remote locations.
The steel frame and roof system need to support not only the greenhouse enclosure but also any added solar loads—which is why structural planning matters.
Adaptable for Real Conditions
Whether you’re in a hot valley or a snowy mountain area, solar greenhouses can be tailored to fit. Structure, materials, and solar systems can all be adjusted to local needs.
For example:
- In cold climates: thicker insulation, higher thermal mass, and a reinforced frame to handle snow
- In hot zones: better ventilation, shading elements, and light-diffusing roof materials
- For off-grid sites: steel framing that supports both the greenhouse and a solar energy system above
With the right design, structure, and solar integration, you get a greenhouse that performs year-round—with far less energy and far fewer surprises.
Where Are Solar Greenhouses Most Commonly Used?
One of the best things about solar greenhouses is how flexible they are. You’ll find them in all kinds of places—but usually for one key reason: the need for energy-efficient, off-grid, or year-round growing.
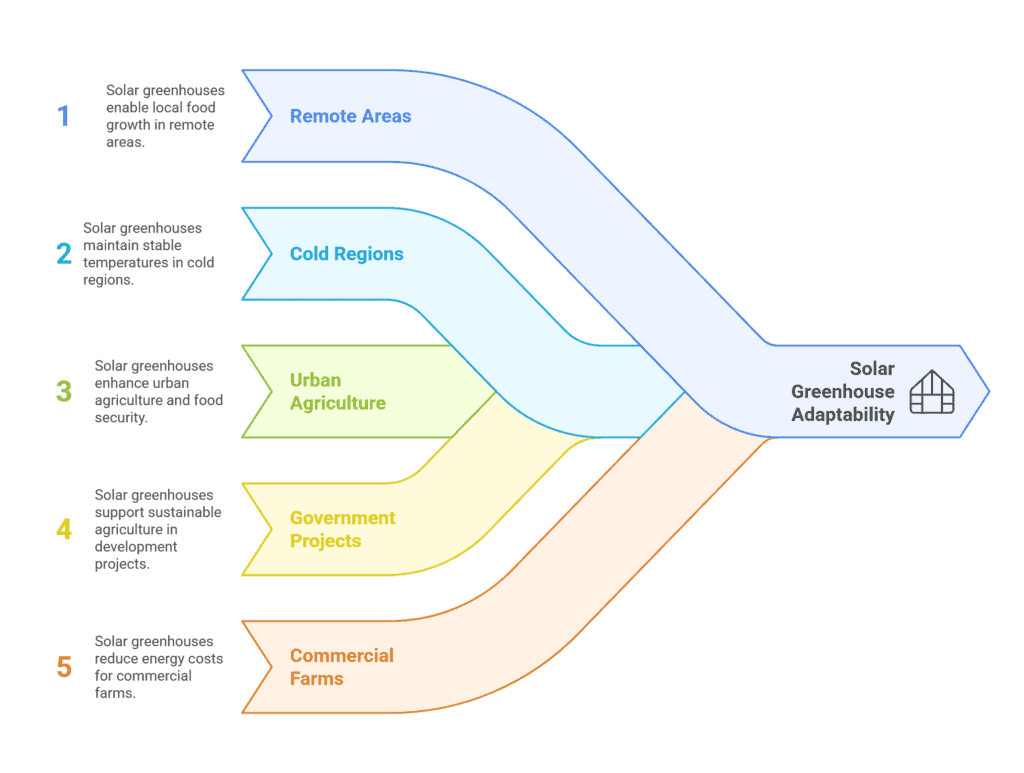
Let’s look at where they work best—and why.
Remote and Off-Grid Areas
In regions without stable electricity—mountain villages, desert farms, or island communities—a solar greenhouse can be a game changer. It lets you grow food locally without relying on diesel generators or long power lines. With the right structure and solar integration, it can stay warm even in cold nights, fully off-grid.
Cold or High-Altitude Regions
Traditional greenhouses often struggle with heat loss in cold zones. But a solar greenhouse, designed with passive heat storage and proper insulation, keeps temperatures stable through the night and across seasons. Places like northern China, Canada, or the Himalayas have adopted solar greenhouses for exactly this reason.
Urban and Rooftop Agriculture
In cities, space is limited and energy is expensive. Solar greenhouses are now used on rooftops, in community gardens, and in educational centers—where clean energy and food security go hand in hand. Lightweight steel or aluminum structures combined with solar panels make this both feasible and efficient.
Government and NGO Projects
Across Africa, Southeast Asia, and Central America, solar greenhouses are part of agricultural development and food security programs. They offer a practical way to grow food sustainably, with less water, less power, and more local control.
Commercial Smart Farms
Large-scale greenhouse operations are now looking to solar to cut long-term energy costs and meet carbon reduction targets. By pairing greenhouse design with solar structures, these farms boost both sustainability and resilience.
If you’re thinking, “Could this work in my area?”—chances are, the answer is yes. With the right structural design and energy setup, a solar greenhouse can adapt to almost any environment.
Is a Solar Greenhouse Right for Your Project?
At this point, you might be asking: Can this work for my location, my crops, or my budget?
The good news is—solar greenhouses are highly adaptable, but they’re not one-size-fits-all. A few key factors can help you decide if it’s the right fit:
Your Climate
If you deal with long winters, sharp temperature swings, or unreliable energy access, a solar greenhouse can stabilize conditions and reduce your heating needs.
Your Energy Goals
Looking to go off-grid, lower your power bills, or meet sustainability targets? Solar integration makes that possible—and often cost-effective in the long term.
Your Crop Types
Whether you grow vegetables, herbs, flowers, or run a nursery, solar greenhouses can be designed around your crops’ light and temperature needs.
Your Available Space and Structure
From small-scale setups to commercial steel-frame systems with solar roofing, the structure can be tailored to fit your land, roof, or site conditions.
Your Long-Term Plans
Solar greenhouses are ideal if you’re thinking about future-proofing your farm, expanding production, or investing in low-maintenance infrastructure.
No two projects are the same. But with the right design—from structure to solar system—a solar greenhouse can become a smart, reliable part of your agricultural future.
If you’re not sure where to start, we’re here to help. We can advise on structural options, solar integration, and what works best in your region or industry. Just reach out—we’ll help you explore what’s possible.
Final Thoughts
A solar greenhouse isn’t just a structure—it’s a smarter way to grow.
In a world facing rising energy costs, climate uncertainty, and growing food demand, solar greenhouses offer something rare: control, efficiency, and independence, all in one solution. Whether you’re farming in a remote village or scaling up a modern agri-business, this approach lets you grow more—with less.
And the best part? It’s not future tech. It’s ready now—adaptable, proven, and increasingly accessible through better design and structural innovation.
If you’re planning your next agricultural step, this might just be the opportunity to build not only smarter—but cleaner and more resilient from the ground up.

