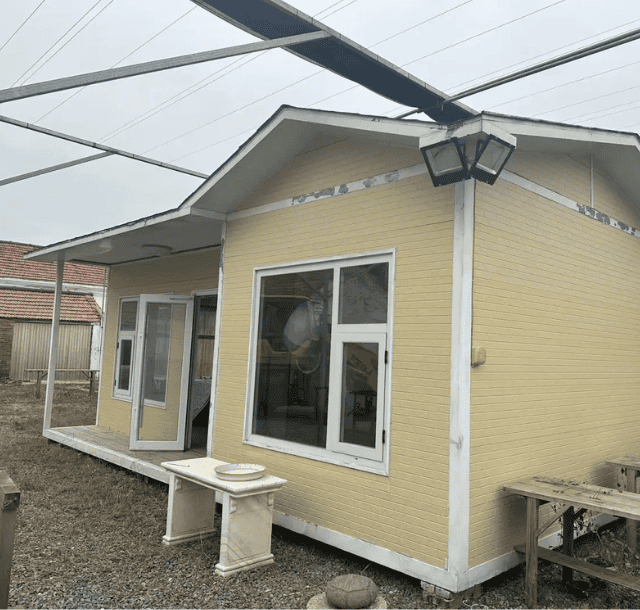
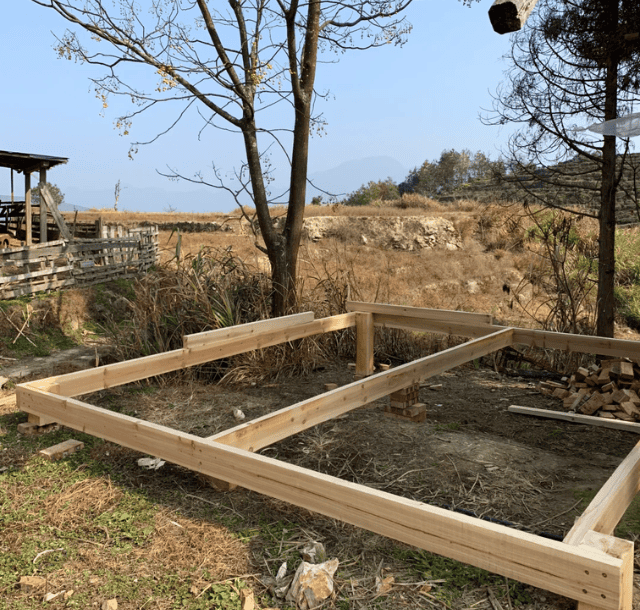
With housing prices soaring, modular homes, a technology that “builds houses like assembling Lego blocks,” are providing cost-effective housing solutions for more than 2 million families around the world (2023 data from the American Modular Building Association).
Today, we’ll take a deep dive into modular homes and learn why they are considered the best choice for future affordable housing. From the construction process to the pros and cons, to how to finance the purchase of modular homes, this article will give you a comprehensive understanding of this emerging housing model. Whether you’re a first-time homebuyer or someone who’s skeptical about traditional housing methods, modular homes may be an ideal option worth considering.
What is a modular home?
A modular home is made up of multiple modules that are prefabricated in a factory and transported to the construction site and quickly assembled into a complete home.
In contrast to traditional construction techniques, a modular home has each of its parts constructed in a factory, guaranteeing quality, precision, and a faster build time. This method is not only efficient and environmentally friendly, but can also be customized according to individual needs, making it an ideal choice for modern affordable homes.
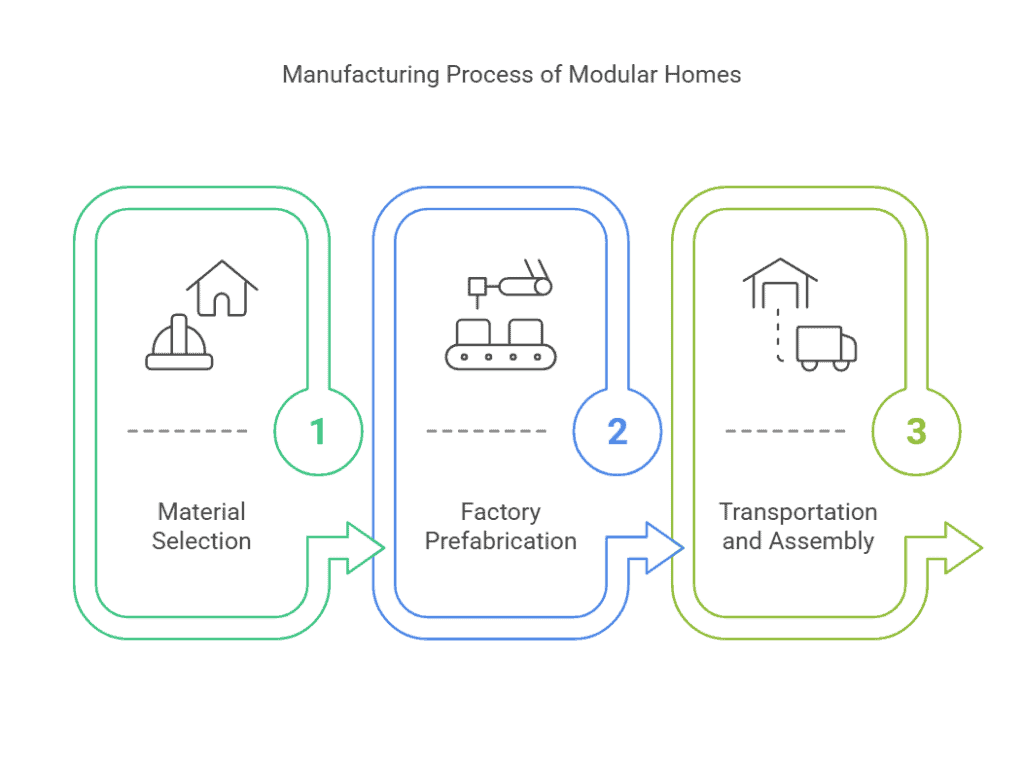
The Manufacturing Process of Modular Homes
1. Material Selection
The materials used in modular homes are chosen for their quality, sustainability, and energy efficiency. Common materials include:
- Steel: Provides a strong structural frame for the home, offering excellent resistance to natural disasters such as earthquakes or strong winds, ensuring long-term safety.
- Wood: Used for walls and interior elements, wood is both aesthetically pleasing and offers good insulation properties to enhance energy efficiency.
- Concrete: It is utilized for building solid foundations, thereby guaranteeing the stability and durability of the home.
- Energy-efficient materials: Materials like polyurethane foam and expanded polystyrene (EPS) insulation boards effectively reduce energy consumption, complying with green building standards.
In our modular home production, each material is carefully selected to ensure the quality of the building and its environmental performance, while also ensuring a high return on investment for our clients over the long term.
2. Factory Prefabrication
The prefabrication of modular homes takes place in specialized factories, ensuring that each module meets standardized high-quality requirements:
- Design and Planning: First, our designers and engineers work with clients to develop a customized design based on their needs and budget. After that, the prefabrication of the modules begins according to the precise design drawings.
- Module Production: Each module is constructed in the factory. The factory uses advanced production lines and tools to ensure that the dimensions, structure, and quality of each module meet industry standards. Our production process also includes strict quality control to ensure that every part of the home is built to last.
- Quality Inspection: After the modules are completed, our engineers perform exhaustive quality inspections. These checks include material compliance, structural strength of the modules, and safety of the connection points, ensuring that the home meets the highest construction standards.
Through this highly efficient and standardized factory prefabrication process, we are able to provide high-quality homes to clients at a lower cost and faster delivery time, meeting the growing market demand for quick delivery and customized solutions.
3. Transportation and Assembly
Upon completion of the modules, they are then transported to the construction site. The transportation and assembly process is as follows:
- Transportation preparation: All modules are securely packed and reinforced to prevent any damage during transportation. The transportation method is usually a special low-bed trailer, and the appropriate transportation tool is selected according to the size and weight of the module.
- On-site assembly: After the modules arrive at the site, a professional team will use a crane or other equipment to lift the modules to the designated location. The installers will splice and connect the modules according to the design drawings to ensure seamless connection between modules. Generally, the assembly process of modular houses is much faster than traditional house construction, and can be completed within a few days to a few weeks.
The speed and efficiency of assembly make modular houses more time-saving than traditional construction methods, especially effective when housing is urgently needed.
4. Self-Build Possibilities and Challenges
Parts that can be operated independently:
- Interior decoration (wall paint, floor laying)
- Exterior landscape (terrace, green planting)
- Furniture installation and intelligent system configuration
Parts that require professionals:
- Module hoisting and structural connection (special equipment operation certificate required)
- Foundation construction (allowable error ≤3mm/m)
- Water and electricity system connection (certified electrician/plumber required)
Main challenges of self-construction:
- It is necessary to apply for factory production license and land construction license at the same time
- The cost of purchasing hoisting equipment is as high as $15,000/day
- Module interface misalignment exceeds 5mm and needs to be returned to the factory for adjustment
5. Standardization and Building Codes
- Internationally accepted: ISO 22459 (modular building performance evaluation)
- North America:
- ICC-ES AC478 (structural safety certification)
- HUD specification Chapter 24 (factory-produced housing standards)
- Europe: EN 1090 (steel structure execution standard) + CE certification
- China requirements: GB/T 51232 (assembly housing acceptance specifications)
We guarantee that every modular home we deliver complies with local regulations, ensuring a safe and comfortable living environment for our clients.
Can You Put a Modular Home in City Limits?
Yes, modular homes can be placed within city limits in most areas, but it depends on local zoning laws and building codes.
Related Reading: Modular manufacturing
Advantages and Disadvantages of Modular Homes
Advantages:
- Fast construction: Modular homes are prefabricated in factories and can be swiftly assembled once transported to the site, significantly cutting down on traditional construction time.
- Cost-effective: Modular homes are generally cheaper than traditional homes due to factory production and reduced labor costs.
- Environmental protection: The utilization of energy-efficient materials and minimized construction waste aids in decreasing the environmental footprint.
- High quality control: Construction in the factory can strictly control quality and avoid unforeseen problems in on-site construction.
- Flexible customization: The design and layout can be personalized based on customer requirements, offering a diverse range of options.
Disadvantages:
- Transportation restrictions: The transportation of modules is limited by size and weight, which may affect construction in some remote areas.
- Land requirements: Suitable land and infrastructure are required, and some terrain or land conditions may not be suitable for modular homes.
- Resale issues: The resale market for modular homes may be limited in some areas, affecting long-term value.
Related Reading: Pros and cons of modular homes
Guide for modular house price
1. Price range
The price of modular houses is usually 10%-20% lower than that of traditional houses, mainly due to the material and labor costs saved by standardized factory production.
- Basic model: suitable for simple needs, the total price of a single-story house is about 70%-80% of that of a traditional house.
- Customized model: after adding personalized design (such as floor-to-ceiling windows, smart systems), the price is close to that of a traditional house, but the construction period is still shortened by half.
Main cost factors: transportation distance (more than 500 kilometers, the cost increases significantly), foundation construction complexity and local policy subsidies.
2. Loans and financing
- Conventional mortgages: If the house is fixed on a permanent foundation and meets local building regulations, you can apply for the same mortgage loan as a traditional house.
- Construction loans: issued in stages (factory production period and on-site assembly period), and the qualification certificate of the module supplier must be provided.
Note: Some banks require a higher down payment ratio (about 25%) for modular houses. It is recommended to consult a lending institution familiar with modular construction in advance.
3. Mortgage and property rights
- Property rights: No different from traditional houses, two points must be met:
- The house is fixed on a permanent foundation and cannot be moved as a whole;
- Obtain a property certificate issued by the local government.
- Mortgage risk: If you choose a non-famous supplier, you need to confirm its financial stability to avoid the house being unable to be completed due to the bankruptcy of the supplier.
4. Market acceptance
- Advantage areas: In cities with high housing prices and housing shortages (such as San Francisco and Berlin), modular houses are more acceptable due to their high cost-effectiveness.
- Main concerns: Some buyers still mistakenly believe that they are of poor quality or have a single design, and they need to break their prejudices by visiting model houses on site.
- Future trends: Young home buyers and environmentalists are more inclined to choose modular houses, which will drive the market to grow steadily.

Common uses for modular homes
| Application Area | Description |
| Residential Use | Affordable long-term housing, suitable for first-time buyers, small families, or those with limited budgets. |
| Commercial Use | Used for small offices, shops, clinics, restaurants, and more, customizable and quickly built. |
| Vacation and Tourism | Used in resorts, seaside vacation spots, and other tourist destinations, offering flexible accommodation options. |
| Emergency and Temporary Housing | Used for emergency housing after disasters, military bases, or temporary worker dormitories, quick to deploy and durable. |
| Educational Use | Used for classrooms, dormitories, and other educational facilities, providing quick construction and flexible space. |
| Medical Use | Used for temporary hospitals, clinics, or rehabilitation centers, quickly deployed for emergency medical needs. |
| Agricultural and Industrial Use | Used for warehouses, greenhouses, factories, and office facilities to meet agricultural and industrial needs. |
Related Reading: Modular construction helps the renewable energy industry
Modular Homes vs Other Housing Types
1. Modular Homes vs Traditional Homes
| Comparison Aspect | Modular Homes | Traditional Homes |
| Construction Time | 4-6 months (factory + on-site) | 12-18 months |
| Cost Control | Budget deviation ≤5% | Average cost overrun: 18% (Associated General Contractors of America 2023 Data) |
| Material Waste | ≤5% (precision cutting) | 30%-40% (U.S. EPA Data) |
| Quality Control | Factory-controlled environment reduces defects by 60% | Weather-dependent on-site risks |
| Design Flexibility | Modular innovations (e.g., Dutch Cube modular apartments) | Higher structural modification freedom |
2. Modular Homes vs Manufactured Homes
| Comparison Aspect | Modular Homes | Manufactured Homes |
| Building Codes | Complies with local residential codes (e.g., IRC) | Meets HUD Federal Manufactured Home Standards |
| Foundation | Permanent concrete foundation (min. 200mm thickness) | Can be placed on metal frames/wheels |
| Ownership Type | Same as traditional real estate, eligible for mortgages | Classified as personal property (higher loan rates) |
| Resale Value | 3-5% annual appreciation (matches traditional homes) | 2-4% annual depreciation (Zillow 2024 Report) |
| Lifespan | 50+ years (anti-corrosion steel) | 30-35 years average |
Related Reading: which is better modular or manufactured homes
3. Target Clientele for Modular Homes
- Budget-Conscious Buyers
- Time-Sensitive Buyers
- Remote Area Developers
- Policy Incentive Beneficiaries
- Specialized Needs
4. Scenarios Where Modular Homes Are Less Suitable
- High-value land areas
- Frequent remodelers
- Aesthetic customization seekers
Who makes the best modular homes?
When it comes to choosing the best modular homes, quality, design flexibility, and affordability are key factors. At SteelPRO PEB, we specialize in creating customizable, high-quality modular homes that suit your lifestyle and budget. Whether you’re looking for a modern design, energy-efficient features, or a personalized layout, we offer a range of options to ensure your new home meets all your needs.
Ready to explore your modular home options? Contact us today to discuss your dream home and get a free consultation!

