As global temperatures rise and climate patterns shift, the urgency for sustainable agricultural practices intensifies. Traditional farming methods contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating climate change. In 2024, global carbon emissions increased by 0.8%, reaching 41.2 billion tons of CO₂.
Solar greenhouses present a transformative solution, harnessing renewable energy to cultivate crops efficiently. By integrating solar technology, these greenhouses reduce reliance on fossil fuels, lower operational costs, and support year-round production. Embracing such innovations is crucial for mitigating environmental impact and ensuring food security in a changing climate.
What’s Expected in This Blog:
What is a Solar Greenhouse?
A solar greenhouse is a type of greenhouse that uses the sun’s energy to control the temperature inside and create a better environment for plants to grow. The main idea is simple: it takes advantage of natural sunlight to reduce the need for extra heating or lighting, making it more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
In a solar greenhouse, sunlight is captured and trapped inside. This helps to keep the greenhouse warm, even when it’s cold outside. Special materials like clear glass or plastic are used for the walls and roof, letting sunlight in while preventing heat from escaping. This keeps the temperature steady and comfortable for the plants.
By using sunlight in this way, a solar greenhouse not only helps plants grow in a controlled climate but also lowers energy costs, offering an eco-friendly solution for growing crops all year round.
How Does a Solar Greenhouse Work?
A solar greenhouse works by capturing and using sunlight to keep the environment inside warm and stable, making it ideal for plant growth. Here’s a breakdown of how it functions:
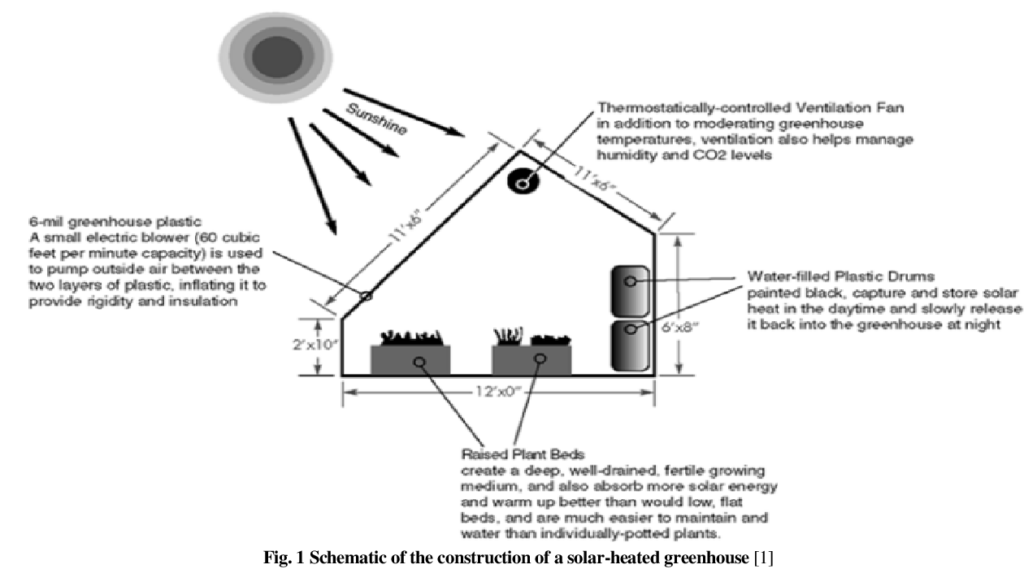
- Sunlight Entry: The greenhouse is designed with transparent materials like glass or clear plastic for the roof and walls. These materials let sunlight enter the greenhouse freely.
- Solar Heat Trapping: Once sunlight enters, it heats the air and surfaces inside the greenhouse. The structure of the greenhouse helps trap this heat, preventing it from escaping quickly. This keeps the inside temperature warmer, even when it’s cold outside.
- Temperature Regulation: Solar greenhouses often use special designs to balance the temperature. For example, they may have a thermal mass—materials like water barrels or stone floors—that absorb heat during the day and release it at night. This keeps the temperature steady without needing extra heating.
- Passive Solar Heating: Most solar greenhouses rely on passive solar heating. This means they don’t use any mechanical or electrical systems to heat the greenhouse. Instead, they depend on the sun’s natural energy to maintain warmth. By using smart design, such as positioning the greenhouse to maximize sunlight, you can keep the plants warm without needing an extra power source.
- Ventilation: To avoid overheating during sunny days, solar greenhouses often have adjustable windows or vents. These allow hot air to escape when needed, preventing the temperature from getting too high for plants.
In short, a solar greenhouse works by taking full advantage of sunlight to warm the space and keep it at an ideal temperature for plants. It’s an efficient way to use natural resources, saving energy and providing a sustainable growing environment.
Advantages of Solar Greenhouses
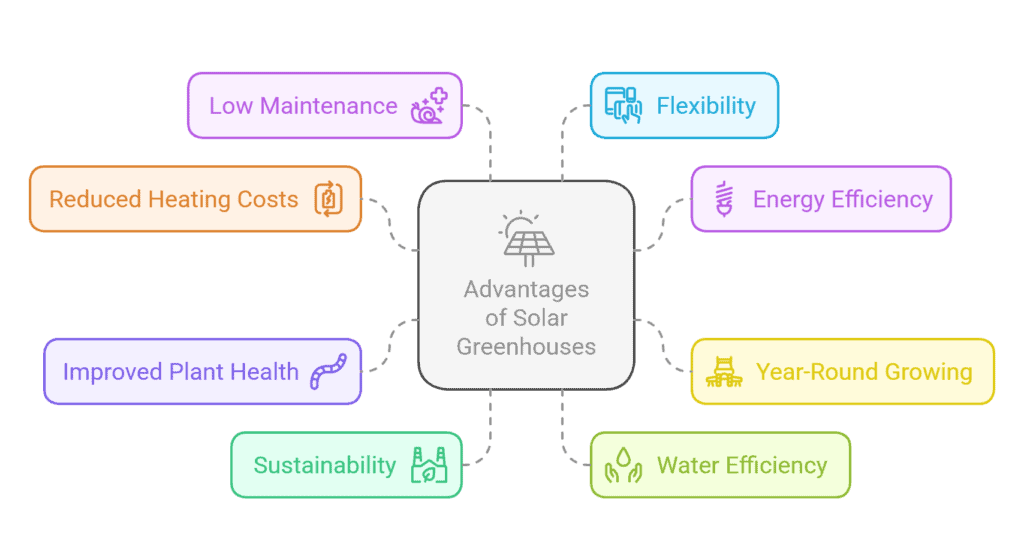
- Reduced Heating Costs
Since they capture and store sunlight, solar greenhouses require little or no extra heating. This lowers energy consumption and operational costs. - Energy Efficiency
Solar greenhouses use sunlight to maintain a warm environment, which reduces the need for external heating. This cuts energy costs and minimizes reliance on electricity or gas. - Year-Round Growing
The temperature inside remains stable, which allows crops to grow even in colder months. This extends the growing season and makes year-round production possible. - Improved Plant Health
A stable temperature inside helps plants grow better and healthier, reducing stress from fluctuating temperatures. This results in more efficient growth and higher-quality crops. - Sustainability
By relying on solar energy, solar greenhouses reduce carbon emissions, making them an eco-friendly choice. They support sustainable farming by using clean, renewable energy. - Water Efficiency
Solar greenhouses often include systems for collecting rainwater or designs that reduce water loss. This improves water use and helps conserve resources, especially in dry regions. - Low Maintenance
After setup, solar greenhouses typically need less maintenance compared to traditional greenhouses with complex systems. Their reliance on sunlight makes them simpler to manage. - Flexibility
Solar greenhouses can be customized to suit different crops or climates. Whether for small gardens or large farms, they offer adaptable solutions for various needs.
Related Reading:
Should You Build a Solar Greenhouse? Key Benefits and Drawbacks
Disadvantages of Solar Greenhouses
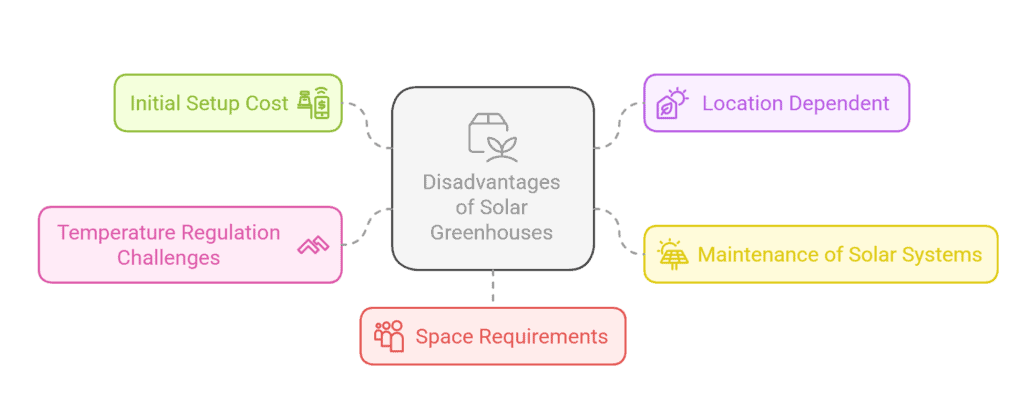
- Initial Setup Cost
Building a solar greenhouse can be expensive upfront, especially with high-quality materials and specialized designs. While it saves money in the long run, the initial investment may be higher than that of traditional greenhouses. - Location Dependent
Solar greenhouses depend on sunlight to function effectively. In regions with limited sunlight, long winters, or frequent cloudy weather, their efficiency can be reduced. Proper positioning and design are crucial for maximizing solar energy use. - Maintenance of Solar Systems
While solar greenhouses generally require less maintenance than traditional greenhouses, the solar panels and energy systems still need regular checks. Over time, solar panels may require cleaning or replacing to maintain optimal performance. - Temperature Regulation Challenges
In areas with extreme temperatures, the greenhouse may not be able to keep the internal climate ideal for plants year-round. Supplemental heating or cooling systems might be needed during exceptionally cold or hot periods, adding extra costs. - Space Requirements
To maximize sunlight capture, solar greenhouses may require more space compared to traditional greenhouses. This could be a challenge in areas where land is limited or expensive.
Types of Solar Greenhouses
There are several types of solar greenhouses, each designed to meet specific needs and environmental conditions. The choice of design depends on factors such as climate, the types of crops you want to grow, and the resources available. Below, we’ll explore the most common types of solar greenhouses.
1. Passive Solar Greenhouse
A passive solar greenhouse relies entirely on natural sunlight and the greenhouse’s design to maintain a stable temperature. It uses materials that allow sunlight to enter but limit heat loss, such as transparent walls and roofs. Passive solar greenhouses don’t require any external energy sources or mechanical systems for heating, which makes them the most energy-efficient option. However, their performance is highly dependent on location and positioning to capture maximum sunlight.
2. Active Solar Greenhouse
An active solar greenhouse incorporates solar panels or other mechanical systems to collect and store energy. These systems can be used to power heating elements, fans, or other equipment inside the greenhouse. While active solar greenhouses are more expensive to set up, they can provide better control over the environment, especially in areas with less sunlight. They also allow for greater flexibility in greenhouse design and operation.
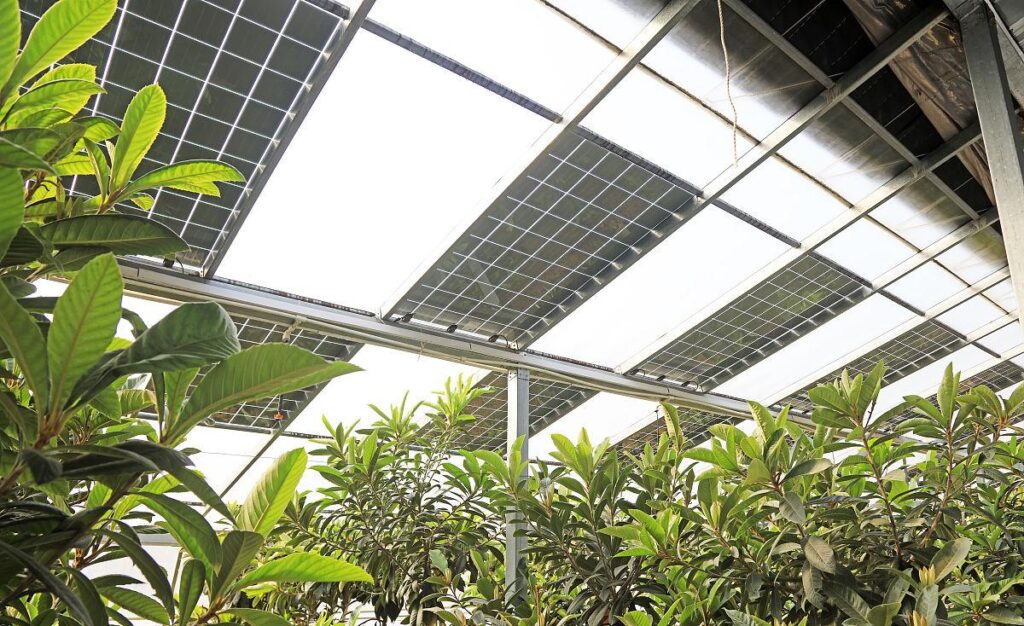

3. Hybrid Solar Greenhouse
A hybrid solar greenhouse combines the features of both passive and active solar designs. This type uses natural sunlight and passive heating methods for most of the year but incorporates active systems like solar panels or heat pumps during colder months or when additional heating is needed. Hybrid greenhouses are suitable for a wide range of climates and can be a good choice for those who want to balance energy efficiency with more control over temperature regulation.
4. Geodesic Solar Greenhouse
A geodesic solar greenhouse is a dome-shaped structure designed to maximize sunlight exposure. The unique geometric shape of the greenhouse allows sunlight to reach all areas of the structure, improving heat distribution and reducing shadowing. This design is particularly effective in areas with shorter days or limited sunlight. Geodesic solar greenhouses are often more expensive to build, but their efficient use of space and sunlight makes them ideal for growing a variety of crops year-round.
5. Lean-to Solar Greenhouse
A lean-to solar greenhouse is built against an existing structure, such as a house or barn, to take advantage of its heat. The greenhouse typically has one side that is attached to a wall, and the other three sides are open to sunlight. This design is especially beneficial for homeowners who want to grow food while using the heat from the attached building. It’s an excellent option for small-scale operations or personal gardens.
Debunking Common Myths About Solar Greenhouses
“Solar greenhouses are too expensive and not worth the investment.”
While the initial cost is higher, solar greenhouses pay for themselves in 5-10 years through energy savings and increased crop yield—up to 40% higher in colder climates.
“Solar greenhouses can only be used in areas with abundant sunlight.”
Solar greenhouses work even in low-light regions. By using double-glazed glass and thermal mass, they store heat during the day and release it at night, keeping crops warm—even in Scandinavia’s winters.
“Solar greenhouses require frequent maintenance and are complicated to manage.”
Solar greenhouses are easier to maintain than traditional ones. Solar panels need only annual cleaning and last 5-10 years, reducing maintenance costs by 50-60% compared to traditional systems.
“Solar greenhouses are only suitable for certain types of crops.”
Solar greenhouses support a wide range of crops. Farms are successfully growing tomatoes, herbs, and strawberries year-round, proving their versatility in various climates.
“Solar panels take up too much space and block sunlight, affecting plant growth.”
Modern designs integrate transparent or semi-transparent panels that allow 70-80% sunlight for optimal plant growth, with no significant yield loss.
Applications of Solar Greenhouses
Solar greenhouses have many uses that can benefit both farmers and everyday people. They help grow food all year round and support sustainable farming. Here are the main ways solar greenhouses are used:
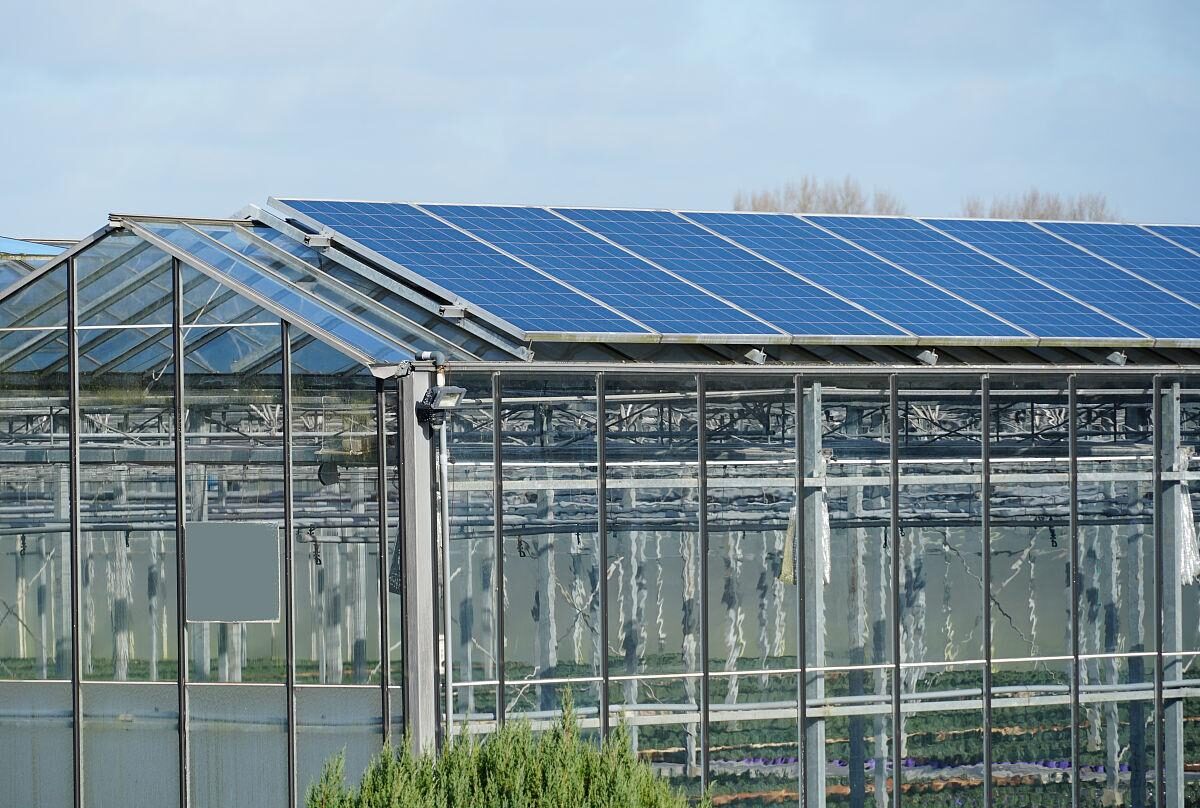

- Agricultural Production
Solar greenhouses are perfect for growing crops throughout the year, even in colder regions. They keep the temperature stable inside, helping crops grow during winter and extending the growing season. This is especially useful for vegetables, herbs, and flowers that need controlled conditions. - Urban Farming
In cities with limited space for farming, solar greenhouses offer a great solution. People can use rooftops or empty lots to grow fresh food in solar-powered greenhouses. This helps reduce transportation costs and supports local food production. - Sustainable Agriculture
Solar greenhouses are a good way to farm sustainably. They use solar energy instead of fossil fuels, reducing the environmental impact of farming. They also save water by using efficient watering systems and can collect rainwater to support the crops. - Research and Education
Solar greenhouses are used in research and education. Schools and universities use them to study plant growth and test new farming methods. They also teach students about renewable energy and how to grow food in eco-friendly ways. - Community and Home Gardening
For people who want to grow their own food, solar greenhouses offer an easy solution. Home gardeners can grow fresh vegetables and fruits all year round. Communities can also use them to grow food for local markets or schools.
Related Reading:
What Is a Solar Greenhouse Used For? A Practical Guide
Common Materials Used in Solar Greenhouses
- Glass
Glass is a popular choice for the walls and roof of solar greenhouses due to its transparency and high light transmission. It allows sunlight to enter while providing excellent insulation. However, it can be heavier and more expensive than other materials. - Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate panels are durable, lightweight, and offer good insulation properties. They are often used in place of glass because they are more cost-effective and provide better heat retention. Double or triple layers are commonly used for better insulation. - Polyethylene Film
This is a flexible plastic material often used as a covering for solar greenhouses. It is affordable and lightweight, offering good light transmission. While it may not be as durable as glass or polycarbonate, it is easy to replace and ideal for smaller setups. - Solar Panels
Solar panels are integrated into the roof or walls of the greenhouse to capture sunlight and generate electricity. They can either be transparent or semi-transparent, allowing light to pass through while producing energy for the greenhouse’s needs. - Thermal Mass Materials (e.g., Water, Stone)
Materials like water barrels or stones are used inside solar greenhouses to store heat during the day. They absorb sunlight and release it at night, helping maintain a stable temperature inside the greenhouse.
Best Structural Framework Materials for Solar Greenhouses
The framework of a solar greenhouse is typically made from materials like steel, aluminum, wood, or PVC, depending on the size and needs of the structure.
- Steel is the most common choice for its strength and durability, capable of supporting heavy glass or polycarbonate panels and withstanding harsh weather.
- Aluminum is a lightweight, rust-resistant alternative that’s ideal for smaller greenhouses.
- Wood is used for smaller, residential greenhouses or decorative purposes, offering good insulation but requiring more maintenance.
- PVC is a budget-friendly option, suitable for small, temporary setups, though it’s less durable for long-term use.
The choice of framework material depends on the greenhouse’s size, expected lifespan, and budget.
Solar Greenhouse and Solar Power
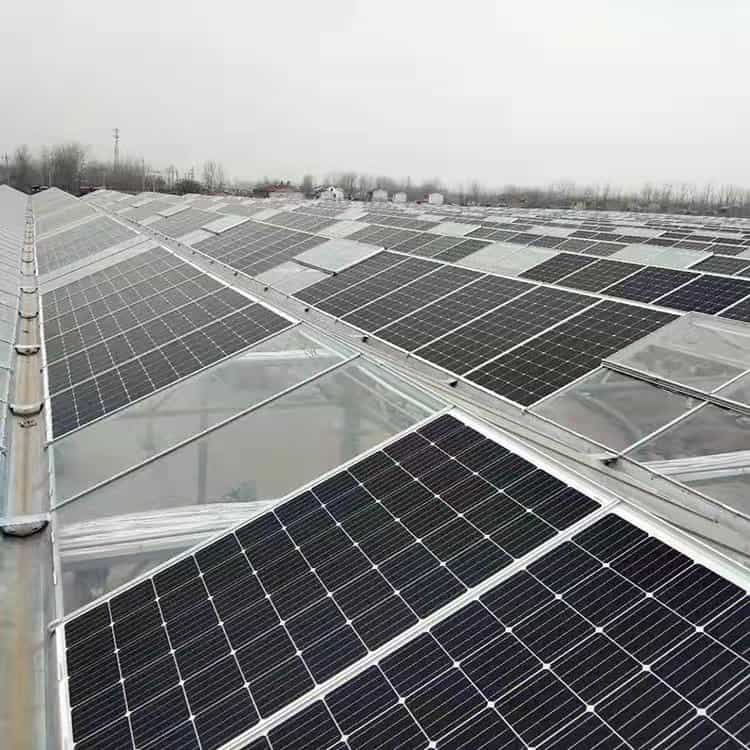

Solar greenhouses use solar power to create a stable growing environment for plants by capturing sunlight. This natural energy plays a key role in maintaining the greenhouse’s temperature and reducing the need for external heating or electricity.
A solar greenhouse captures sunlight through transparent walls and roofs. The sunlight warms the air and surfaces inside, helping to regulate temperature. In passive solar greenhouses, this heat is retained naturally, keeping the space warm without additional energy sources. Active solar greenhouses, on the other hand, incorporate solar panels to generate electricity, which can power ventilation, heating systems, or other equipment.
Solar panels installed on the roof or nearby can also provide additional energy. They convert sunlight into electricity, which can be used for lighting, cooling fans, or other systems within the greenhouse. The number of solar panels needed depends on factors such as the size of the greenhouse and the specific energy demands. While smaller greenhouses may only require a few panels, larger structures may need more to meet their energy needs.
It’s important to note that solar panels are typically placed outside the greenhouse to maximize exposure to sunlight. Placing them inside may limit their efficiency, as they need direct sunlight to generate sufficient energy.
Cost Considerations of Solar Greenhouses
Building and maintaining a solar greenhouse involves several cost factors. While the initial investment may be higher than traditional greenhouses, the long-term savings and environmental benefits make it a worthwhile investment. Below, we’ll explore the main factors that affect the cost of a solar greenhouse.
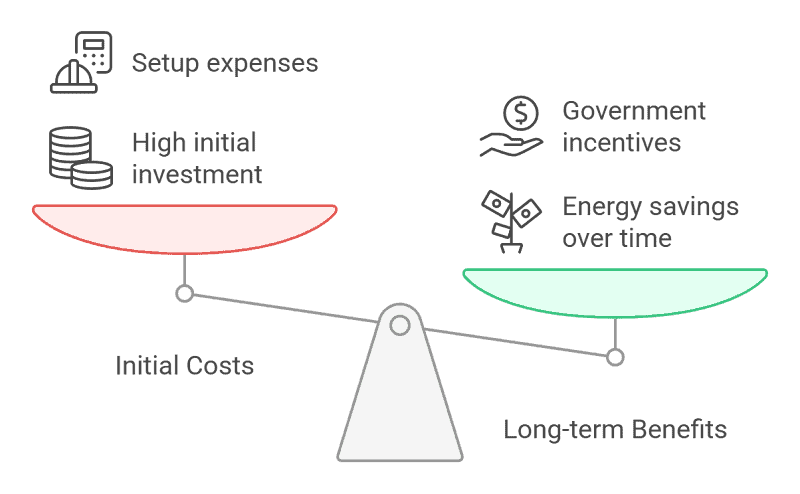
Initial Setup Costs
The initial cost of building a solar greenhouse depends on its size, design, and the materials used. High-quality transparent materials, such as special glass or durable plastic, are typically more expensive but are necessary to ensure the greenhouse is energy-efficient. Additionally, if you choose to install solar panels or other active solar systems, the upfront costs can increase significantly. However, these systems help reduce energy costs in the long run.
Size of the Greenhouse
The larger the greenhouse, the higher the cost. A larger structure requires more materials, a bigger solar panel system, and possibly additional infrastructure like ventilation and heating. However, larger greenhouses also allow for greater crop production, which can offset the initial costs over time.
Location and Site Preparation
The location of the greenhouse plays a big role in its cost. Areas with difficult terrain, poor soil, or challenging weather conditions may require extra work to prepare the site for construction. Additionally, proper positioning to maximize sunlight exposure is crucial for the greenhouse’s effectiveness, which may require additional planning and setup.
Maintenance Costs
While solar greenhouses generally require less maintenance than traditional greenhouses, there are still some ongoing costs. Solar panels may need cleaning or replacement after several years, and other systems like ventilation or heating may need periodic checks. However, these costs are generally lower compared to the maintenance of traditional heating systems.
Energy Savings
One of the main advantages of a solar greenhouse is its energy efficiency. Solar greenhouses can significantly reduce energy bills by relying on sunlight for heating and lighting. Over time, the savings on energy bills can offset the initial setup costs, making it a cost-effective option in the long run.
Government Incentives
Some regions offer incentives, subsidies, or tax breaks for building energy-efficient structures like solar greenhouses. These incentives can help reduce the initial investment and make solar greenhouses more affordable for individuals and businesses.
Conclusion
Solar greenhouses offer an innovative solution for sustainable farming by harnessing solar energy to create optimal growing conditions. They reduce energy costs, promote year-round production, and support environmentally friendly practices. While the initial investment can be higher, the long-term savings, combined with the environmental benefits, make them a worthwhile choice. By understanding the types, applications, and costs of solar greenhouses, you can make an informed decision on whether this eco-friendly option fits your agricultural needs.

