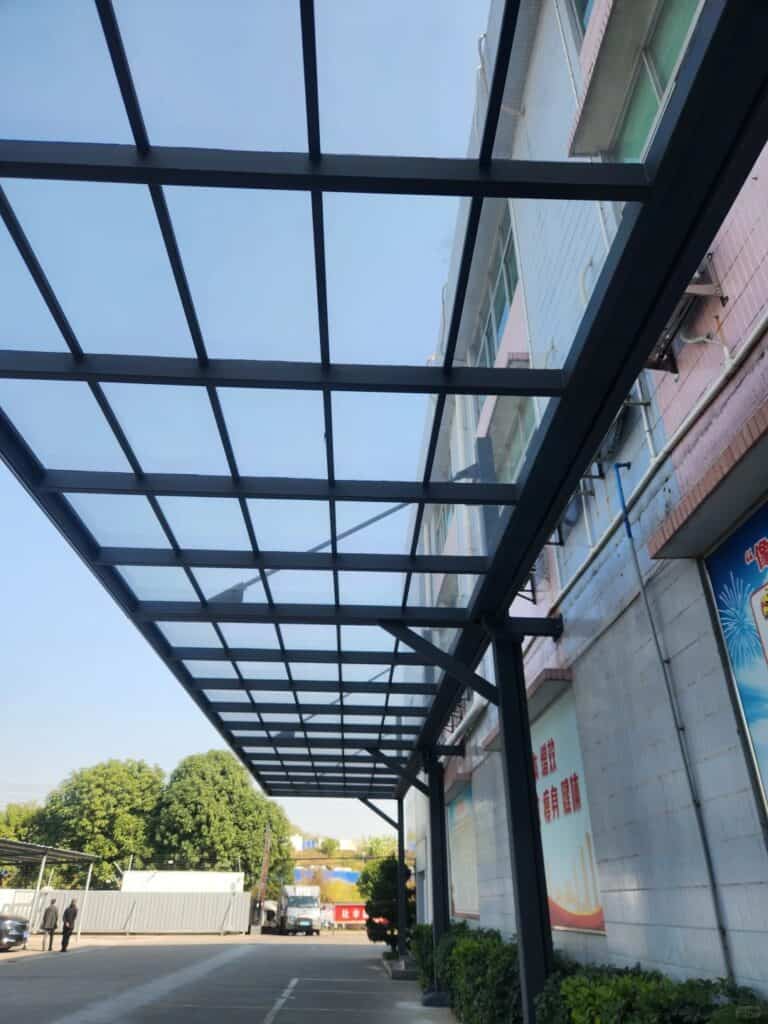
Structural Design of Steel Shelter
Our steel shelters are built with your needs in mind—versatile, durable, and easy to install. Whether you’re designing a bus stop or a larger public shelter, we ensure every shelter meets your specific requirements, providing long-lasting value and minimal maintenance. Designed for the real world, our shelters prioritize safety and functionality, making sure they stand up to time and the elements.
1. Foundation and Steel Columns
We start with a strong foundation, pouring concrete and securing it with anchor bolts to make sure your shelter stays solid, even in tough conditions. The steel columns are crafted from high-strength materials, so they’re built to carry heavy loads and last through all kinds of weather. This means your shelter will stay stable, secure, and worry-free for years to come.
2. Main Structural Frame
Our shelters typically adopt portal frame construction, using steel columns and H-shaped roof beams connected by high-strength bolts. This design is tough enough for shelters of all sizes—whether it’s a small bus stop or a larger waiting area. What’s even better? The simplicity of this design allows for quicker and easier installation, helping you save time and money on your project.

3. Purlins and Bracing Systems
For added stability, we install purlins that support the roof and integrate bracing systems that keep the structure steady, even in high winds or seismic conditions. These systems make sure your shelter remains strong and secure, no matter the weather or external forces.
4. Roof Design Options
We offer a range of roof designs to meet your project’s needs. While a double-slope roof is the most common choice for efficient water drainage, we also provide single-slope and flat roofs depending on your project needs. All our roof designs are engineered to last, providing reliable protection from the elements and reducing the need for costly maintenance.
5. Corrosion Resistance and Durability
To ensure your shelter lasts, we coat all steel components with corrosion-resistant materials, like hot-dip galvanization or anti-corrosion paints. This protects the shelter from rust, so it can stand up to tough conditions, whether you’re in a humid, coastal area or an industrial zone. It also helps cut down on future maintenance costs, giving you peace of mind for the long haul.
6. Flexibility and Future Expansion
We understand that your needs may change over time, which is why our shelters are designed with flexibility in mind. Our modular system makes it easy to expand or modify the structure as required—whether you want to increase size, add features, or update the design. This adaptability ensures that your shelter can grow with you, providing value for years to come.
Components of Steel Structure Shelters
Essential Components
- Foundation Base (including concrete foundation, reinforcement, etc., such as strip foundations, isolated foundations, or pile foundations depending on soil conditions)
- Steel Columns (typically made of hot-rolled steel or steel pipes, material choice depends on load requirements and design specifications)
- Anchor Bolts (typically high-strength bolts such as hexagonal bolts)
- Roof Beams (steel beams, typically I-beams or H-beams, or tubular columns)
- Purlins (typically C-shaped or Z-shaped steel, profiles like U or Omega may also be used)
- Fasteners (including bolts, nuts, washers, etc.)
- Roof Bracing (steel tie rods, diagonal steel rods, or steel pipe bracing)
- Roof Panels (typically metal sheets, such as color steel sheets, aluminum panels, or corrugated steel sheets)
Optional or Conditional Components
- Gutters and Downpipes (optional)
- Steel Trusses (for large spans)
- Wall Bracing (typically in shelters with enclosed walls)
- Horizontal Bracing (for large spans or significant lateral loads)
- Cross Bracing (for earthquake-prone or high-wind areas)
- Diagonal Bracing (for large spans, high wind or seismic zones)
- Cladding Panels (optional)
- Expansion Joints (typically in large-span structures or areas with significant temperature variation)
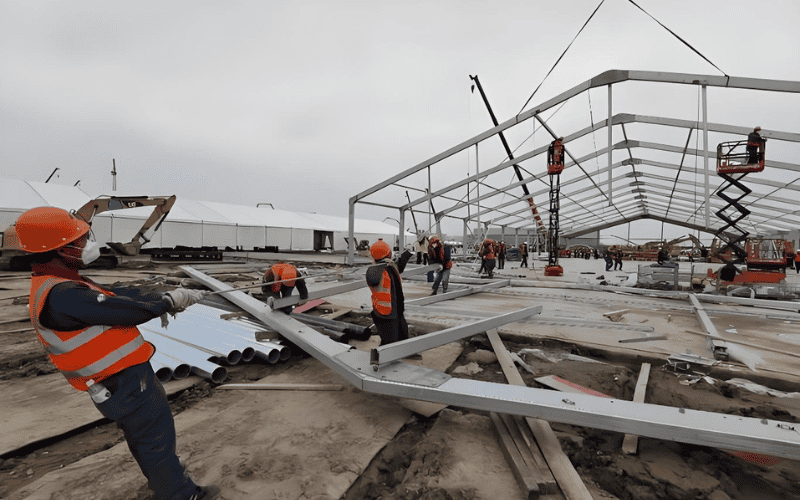
Construction Process of Steel Structure Shelters
The general construction process of steel structure shelters includes the following steps:
1. Preparation:
- Clear the construction site
- Conduct geological surveys and measurements
- Determine foundation locations
- Develop construction plans and safety assessments
2. Foundation Construction:
- Excavate foundation pits
- Lay the base layer and foundation reinforcement
- Pour concrete for the foundation
- Allow curing and conduct tests
3. Transportation and Staging of Steel Materials:
- Transport steel components (such as columns, beams, roof trusses, etc.) to the site
- Organize and arrange materials according to design requirements
4. Steel Structure Installation:
- Install steel columns and beams
- Assemble steel columns, beams, crossbeams, and roof trusses according to the construction drawings
- Use lifting equipment for heavy steel components
5. Connections and Fixing:
- Connect using bolts or welding
- Reinforce joints and connections
- Install support systems, such as connections between columns and beams, and trusses and columns
6. Roof and Wall Installation:
- Install roof panels and wall materials (e.g., metal panels, glass, insulation materials)
- Apply waterproofing and insulation layers for the roof and walls
7. Installation of Doors, Windows, and Auxiliary Facilities:
- Install door and window frames and windows
- Set up other auxiliary systems (e.g., ventilation, electrical systems)
Applications of Steel Structure Shelters
Steel shelters can be applied in various industries and applications as follows:
- Public Transportation: Bus stops, bicycle parking shelters.
- Residential: Community rest areas, shaded seating in parks and neighborhoods.
- Educational and Recreational: School waiting zones, sports facility shade.
- Commercial: Advertising kiosks, vending booths, outdoor retail spaces.
- Industrial: Storage covers, loading bay shelters.
- Tourism and Emergency: Scenic observation pavilions, temporary shelters for disaster relief.
Advantages of Steel Structure Shelters
Here’s what you get from steel shelters:
- High strength and durability ensure safety and reliability in all weather conditions.
- Cost-effective materials and modular design reduce initial and maintenance expenses.
- Quick installation minimizes construction time and disruption to public spaces.
- Customizable designs enhance functionality while meeting aesthetic demands.
- Modular structure supports future upgrades and expansions as needed.
- Long service life and recyclable materials support sustainability goals.
- Resistant to corrosion, extreme temperatures, and UV exposure for lasting performance.
- Supports smart features like real-time displays and integrated lighting for user convenience.
- Efficient ventilation and thoughtful design improve comfort and usability.
Common Issues of Steel Shelters and Solutions
Corrosion
Issue: Steel shelters are susceptible to rust, especially in humid, coastal, or high-moisture environments.
Solution: Use galvanized steel or apply powder-coated finishes to prevent rust. For added protection, apply anti-corrosion paints (e.g., epoxy or polyurethane) to exposed surfaces. Regularly inspect and reapply coatings as necessary, especially after harsh weather events.
Roof Leaks
Issue: Leaks can occur at roof joints, seams, or due to poor sealing, which leads to water damage and maintenance issues.
Solution: Ensure proper sealant application during installation, especially at joints and seams. Use butyl or silicone sealants for high-performance waterproofing. Consider overlapping roof panels to prevent water infiltration. Perform routine inspections and maintenance to detect early signs of leaks.
Structural Deformation
Issue: Shelters may sag, warp, or experience distortion under heavy loads, extreme weather, or insufficient bracing.
Solution: Design with stronger steel (e.g., high strength steel) and adequate load-bearing capacity. Implement roof and column bracing systems (e.g., cross bracing, roof horizontal bracing) to prevent deformation. Regularly inspect for signs of strain or bending and reinforce as needed.
Wind Damage
Issue: Shelters with large spans or exposed locations may suffer from wind pressure, causing structural instability.
Solution: Use wind-resistant designs, such as cross bracing or diagonal bracing in both roof and wall sections. Ensure anchor bolts are sufficiently strong and spaced to resist high wind forces. In high-wind areas, opt for low-profile designs to reduce wind load, and conduct wind-load analysis during the design phase.
Thermal Expansion
Issue: Steel expands or contracts due to temperature fluctuations, which can lead to stress or joint misalignment.
Solution: Integrate expansion joints into the design, particularly in long-span shelters. These joints allow for movement without damaging the structure. Use temperature-resistant fasteners and ensure proper alignment during installation to accommodate thermal expansion.
Foundation Settling
Issue: Poorly prepared or uneven foundations may cause settling, leading to misalignment of the structure.
Solution: Perform site soil testing to determine foundation requirements. Use reinforced concrete for the foundation, ensuring it is deep enough to handle the shelter’s weight and prevent settling. In areas with unstable soil, consider piling foundations or concrete footings for added stability.
