If you’re planning on building or buying a modular home, you might be wondering: Do prefab homes need a foundation? The short answer is yes. Just like any traditional house, a modular home needs a solid, secure foundation to ensure stability, safety, and compliance with local building codes.
But choosing the right foundation isn’t always straightforward. In this article, we’ll answer this question and cover everything from understanding the types of foundations available to installation steps and common issues to watch out for.
What is a Modular Home Foundation?
A modular home foundation is the structure that supports a modular home, providing a stable base for the house. Modular homes are built in sections within a factory setting and then transported to the designated location for final assembly. These sections need a solid, level foundation to ensure they stay stable and secure over time.
Do Prefab Homes Need a Foundation?
Yes, prefab homes, which encompass modular, manufactured, and panelized homes, do require a foundation. These homes undergo construction in a factory environment before being transported to the site for their final assembly. Regardless of the type of prefab home, it requires a foundation to ensure safety and stability.
Common Misconceptions About Prefab Foundations
Some people believe that prefab homes don’t require a solid foundation, thinking that they are like mobile homes or trailers, which can sit on simple skids or blocks. However, even though prefab homes are factory-built, they still need a secure foundation.
The required foundation type depends on location, climate, and the specific prefab home model. Skipping the proper foundation could lead to structural problems, and in some cases, may even violate local building codes.
Why is a Foundation Important for Modular Homes?
A strong foundation is crucial for ensuring the stability, safety, and durability of modular homes. Here’s the reasoning behind it:
Stability and Structural Integrity: Ensuring a Solid, Level Base for Safety
The foundation provides a stable, level base to keep the modular home secure and upright. Without it, the home could shift or settle, leading to structural issues. A solid foundation is crucial for safety, especially in areas with severe weather like high winds or flooding.
Building Codes and Regulations: Legal Requirements for Foundation in Different Areas
Local building codes require modular homes to have a proper foundation to meet safety standards. These regulations ensure the home is secure and compliant with the law. Skipping or using an improper foundation could lead to legal problems, fines, or even the need to redo the work.
Long-term Performance: How Foundation Impacts the Lifespan of the Home
A strong foundation supports the home’s long-term durability. A poor foundation can lead to problems like uneven floors, cracks, or shifting, which can worsen over time. A well-built foundation helps ensure the home lasts longer, protecting your investment and minimizing future repairs.
In short, a proper foundation ensures a modular home’s stability, legal compliance, and long-term performance. It is crucial for maintaining the safety, comfort, and durability of the home.
Types of Foundations for Modular and Prefab Homes
A solid foundation ensures the stability and security of modular and prefabricated homes. Depending on the type of home, site conditions, and budget, common foundation options are:
1. Slab Foundation
A slab foundation comprises a flat, solid concrete layer poured directly onto the ground, regarded as one of the most cost-effective and swift installation methods. It is ideal for flat, stable land and provides a simple, durable base for modular and prefab homes.
- Pros: Low cost, fast installation, minimal maintenance.
- Cons: Limited space for utilities or storage underneath; not suitable for areas with frost or unstable soil.
2. Crawl Space Foundation
A crawl space foundation raises the home above the ground, providing a below-access area usually surrounded by concrete or masonry walls. This type of foundation is suitable for regions with unstable soil or where access to plumbing and utilities is required.
- Pros: Easier access to utilities, better ventilation, and moisture control.
- Cons: Higher cost and installation time compared to a slab foundation; potential for pests in the crawl space.
3. Basement Foundation
A basement foundation provides an entire lower level for additional living or storage space, typically constructed using poured concrete or concrete blocks. This type of foundation is suitable for colder climates, where frost depths are a concern, or when extra living space is desired.
- Pros: Provides extra living space, ideal for colder climates.
- Cons: Higher cost and longer installation time; more complex construction.
4. Pier Foundation
A pier foundation utilizes concrete or steel piers to support the home, leaving the area beneath the home open and unenclosed. This is commonly used for modular or prefab homes in areas prone to flooding or in regions with uneven terrain.
- Pros: Suitable for uneven terrain, provides elevated clearance for flood-prone areas.
- Cons: Less stable than other foundations; may require more maintenance over time.

Differences Between Modular and Traditional Home
| Foundation Type | Flexible options like slab, crawl space, or basements | Full poured concrete foundation |
| Construction Process | Foundation prepared in advance, home placed on-site | Foundation poured and set before construction begins |
| Cost | More affordable, quicker installation | More expensive, requires more labor and materials |
| Flexibility and Customization | Limited customization, but flexible for future changes | Greater flexibility for custom foundation work |
| Speed of Construction | Faster construction with parallel foundation preparation and home build | Slower construction, sequential process of foundation and building |
How to Choose the Right Foundation for Your Modular Home
Choosing the right foundation for your modular home is essential for both cost-efficiency and long-term stability. Here are the key factors to consider:
Budget Considerations: Which Foundation Type Fits Your Financial Plan?
The cost of the foundation will fluctuate based on its type and degree of complexity. A slab foundation is usually the most affordable option, while a basement foundation is more expensive due to the additional labor and materials required. If you’re working within a tight budget, the crawl space foundation may offer a good balance between cost and accessibility.
It’s vital to take into account not just the upfront installation cost but also the ongoing maintenance expenses over the long term. Some foundations, like slab foundations, require less maintenance, while others, like crawl spaces, may need regular checks for moisture or pests. Choose a foundation that fits your current budget and long-term financial plans.
Terrain and Climate: Matching Foundation Type with Local Conditions
- Cold Climates: In areas with frost, a basement foundation or crawl space is often recommended to avoid issues like frost heave, which can shift the foundation.
- Wet or Flood-Prone Areas: In regions with high moisture levels or flooding risks, a pier foundation can elevate the home and keep it safe from water damage.
- Flat, Stable Land: A slab foundation works well in areas with stable soil and no risk of flooding or shifting.
It’s important to consider your terrain’s stability and any environmental factors that might affect your home’s foundation in the long term.
Future Plans: Will You Need Extra Space or Utilities Down the Road?
Consider how your needs may evolve in the future. If you plan to expand your home or add additional utilities, a basement or crawl space foundation might be the right choice as they provide space for expansion and easy access to plumbing and electrical systems.
For those who may need extra storage or living space in the future, a basement foundation offers more flexibility. If expansion is unlikely, a slab foundation could be a practical, low-maintenance option.
Ultimately, the right foundation depends on balancing your current needs, future plans, budget, and the local environment. By taking these factors into account, you can ensure a foundation that will support your modular home for years to come.
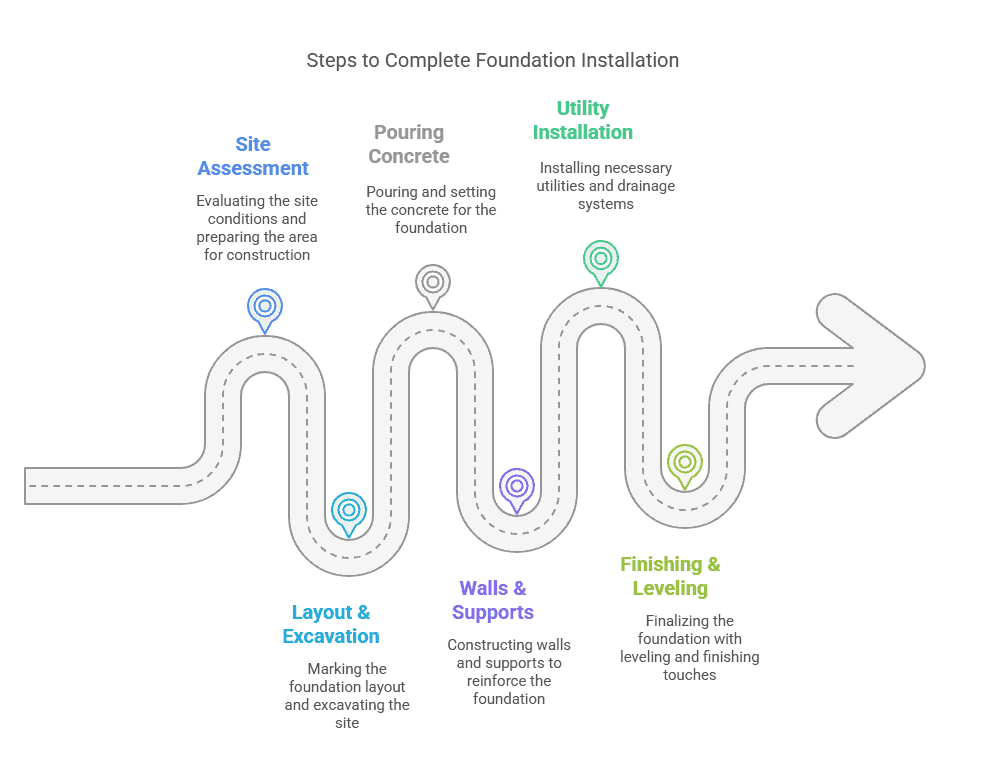
The Foundation Installation Process
Installing the foundation for your modular home is a crucial step in the overall construction process. Foundation installation timelines and complexity depend on the foundation type, site conditions, and local regulations. Here’s a step-by-step overview of the foundation installation process:
Step-by-Step Overview of Foundation Preparation and Installation
- Site Assessment and Preparation
- Before any foundation work begins, a professional will assess the site to determine the best foundation type for the land. This entails assessing the soil, inspecting for drainage issues, and confirming that the site is level. Any necessary clearing, grading, or excavation work will be done to prepare the site.
- Before any foundation work begins, a professional will assess the site to determine the best foundation type for the land. This entails assessing the soil, inspecting for drainage issues, and confirming that the site is level. Any necessary clearing, grading, or excavation work will be done to prepare the site.
- Foundation Layout and Excavation
- After the site preparation is complete, the foundation layout is marked according to the home’s size and design. For slab foundations, the area must be excavated to the required depth. For crawl spaces or basements, additional excavation is done to create the necessary space for the foundation walls.
- After the site preparation is complete, the foundation layout is marked according to the home’s size and design. For slab foundations, the area must be excavated to the required depth. For crawl spaces or basements, additional excavation is done to create the necessary space for the foundation walls.
- Pouring the Concrete (if applicable)
- For slab foundations, concrete is poured to create the base. For crawl space and basement foundations, concrete footings are poured first, followed by foundation walls. This process requires proper setting of the concrete, which can take several days, depending on the prevailing weather conditions.
- Foundation Walls and Supports
- In the case of a crawl space or basement foundation, the next step is to build the walls and supports. This could involve the installation of concrete blocks, poured concrete walls, or other materials depending on the foundation type.
- In the case of a crawl space or basement foundation, the next step is to build the walls and supports. This could involve the installation of concrete blocks, poured concrete walls, or other materials depending on the foundation type.
- Utility and Drainage Installation
- Before finishing the foundation, utilities such as plumbing and electrical lines may be installed if needed. Additionally, proper drainage systems are put in place to prevent water accumulation and soil erosion, especially for crawl spaces and basements.
- Before finishing the foundation, utilities such as plumbing and electrical lines may be installed if needed. Additionally, proper drainage systems are put in place to prevent water accumulation and soil erosion, especially for crawl spaces and basements.
- Finishing and Leveling
- Once the foundation walls are in place, the final finishing touches, including backfilling and leveling, are completed. This step guarantees that the foundation is sturdy and that the site is adequately prepared to accommodate the modular home.
- Once the foundation walls are in place, the final finishing touches, including backfilling and leveling, are completed. This step guarantees that the foundation is sturdy and that the site is adequately prepared to accommodate the modular home.
Timeline and Expectations for Foundation Work and Modular Home Setup
The timeline for foundation installation depends on several factors, such as foundation type, site conditions, and weather. On average:
- Slab foundations take about 1–2 weeks to complete, depending on the complexity of the site and weather conditions.
- Crawl space foundations can take 2–3 weeks, as excavation and additional work are required for the space.
- Basement foundations typically take 3–4 weeks due to the increased complexity of excavation and wall construction.
After the foundation is complete, the modular home can typically be set up within a few days. The home is delivered, placed on the foundation, and then connected to utilities and final inspections are done.
Key Factors Affecting Installation Time and Complexity
Several factors can impact the installation time and complexity of the foundation:
- Site Preparation: If the land is uneven, has a lot of trees, or requires significant excavation, it will take more time and effort to prepare the site for foundation work.
- Foundation Type: More complex foundations like crawl spaces and basements take longer to install than slab foundations. The extra excavation, structural work, and utilities contribute to this.
- Weather Conditions: Weather can significantly impact the timeline, especially if there are delays in concrete curing or if the site is difficult to work in due to rain or snow.
- Local Regulations: Building codes and permits required by local authorities can also affect the timeline, as inspections may be needed at various stages of the process.
By comprehending these factors, you can more effectively manage expectations and plan for a seamless installation process.
Maintaining Your Modular Home Foundation
Proper maintenance of your modular home foundation is essential for ensuring its long-term stability and performance. A well-maintained foundation aids in preventing significant structural problems and can prevent the need for expensive repairs in the future. Here’s how to keep your foundation in good condition:
Importance of Regular Foundation Inspections
Performing regular inspections of the foundation is crucial for identifying potential problems early. It’s recommended to check your foundation at least annually, especially after extreme weather events like heavy rain or snowfall. Inspections help detect early signs of settling, cracking, or water damage, allowing for timely repairs before they become major issues.
Key areas to inspect include:
- Cracks or gaps in the foundation walls
- Shifting or settling of the foundation
- Water damage or pooling around the foundation
- Pest infestations in crawl spaces or basements
If you’re unsure how to inspect the foundation yourself, consider hiring a professional to perform a thorough assessment.
Common Foundation Issues and How to Prevent or Address Them
- Settling: Over time, foundations may settle due to soil movement or inadequate drainage. To prevent settling, it is important to ensure proper grading around the foundation to divert water away from the house. If settling occurs, you may need to lift the house and add more support under the foundation.
- Cracking: Cracks in the foundation can arise due to settling, temperature variations, or moisture fluctuations. Small cracks can usually be sealed with waterproof sealants, but larger cracks may necessitate professional repairs. To prevent cracking, make sure the foundation is properly supported and the site has proper drainage.
- Water Damage: Water infiltration can compromise the foundation’s strength and result in the development of mold or mildew. To prevent this, ensure that gutters are clean and operational, and that water is directed away from the foundation through adequate drainage systems. If water does penetrate the foundation, it’s essential to address the issue swiftly to prevent additional damage.
- Pest Infestations: In crawl spaces or basements, pests like termites or rodents can damage the foundation and affect the structural integrity of the home. Conducting regular inspections and sealing any cracks or gaps can help deter pests from invading your home.
Tips for Maintaining the Foundation’s Integrity Over Time
- Control Moisture Levels: Ensure the soil around the foundation remains stable by managing moisture levels. Avoid letting water pool near the foundation and fix any drainage issues. Proper landscaping techniques, such as sloping the ground away from the foundation, can also be beneficial in preventing pest entry.
- Monitor for Signs of Movement: Be on the lookout for signs of shifting or settling, such as uneven floors, doors that don’t close properly, or cracks in the walls. These could be signs of foundation problems that need to be addressed.
- Ensure Proper Ventilation: If you have a crawl space or basement, make sure it’s well-ventilated. This helps prevent the accumulation of moisture, which can gradually weaken the foundation.
- Fix Small Issues Immediately: Small cracks or minor shifts might seem insignificant, but ignoring them can lead to bigger, more expensive problems. Promptly addressing small issues can help preserve the foundation’s structural integrity.
By taking care of your modular home’s foundation and conducting regular inspections, you can ensure it remains strong and stable for years to come. Maintaining the foundation properly not only safeguards your home but also retains its value and structural integrity.
At SteelPRO PEB, we recognize the significance of a sturdy foundation. If you’re ready to take the next step in building or maintaining your modular home, our team is here to guide you. We offer expert advice, high-quality foundations, and reliable solutions tailored to your specific needs. Contact us today to get started!