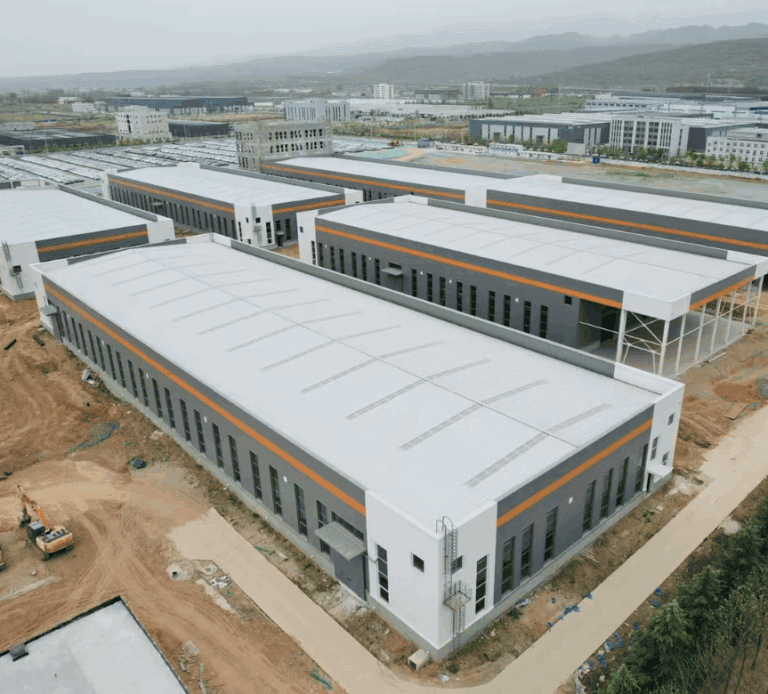
La cadena de suministro B2B global está bajo más presión que nunca. Eventos como pandemias, guerras y fenómenos meteorológicos extremos han puesto de manifiesto la fragilidad de los sistemas de fabricación tradicionales.
Quizás se pregunte: ¿existe una forma más inteligente y flexible de crear y entregar productos? Empresas como la suya se enfrentan a costos crecientes, una demanda impredecible y constantes retrasos en las entregas. Está claro: la forma tradicional de hacer las cosas ya no funciona.
En este artículo, presentamos la fabricación modular, un enfoque moderno que está transformando la industria global. Descubrirá qué es, cómo se compara con los métodos tradicionales y cómo puede mejorar su cadena de suministro. Desde sus ventajas hasta sus desafíos, esta guía le ayudará a decidir si la fabricación modular es la solución adecuada para su negocio.
¿Qué es la fabricación modular?
La fabricación modular es una estrategia de producción que descompone productos complejos en módulos más pequeños y estandarizados. Estos módulos están diseñados para producirse de forma independiente y luego ensamblarse, creando un sistema completo. Este enfoque es fundamentalmente diferente de la fabricación integrada o lineal tradicional, donde el producto se construye como un todo, de principio a fin, en secuencia.
La idea central de la fabricación modular reside en la estandarización y la producción en paralelo. Cada módulo sigue un conjunto predefinido de reglas de diseño y estándares de interfaz, lo que permite que distintos equipos, o incluso distintas fábricas, trabajen en varios módulos simultáneamente. De esta forma, las empresas pueden reducir significativamente el tiempo de producción, mitigar los riesgos en la cadena de suministro y simplificar las actualizaciones o la personalización de productos.
Piense en la fabricación modular como si armara un rompecabezas, donde cada pieza se fabrica por separado, pero se diseña para encajar a la perfección en el conjunto. Para las industrias B2B, especialmente aquellas que manejan productos complejos o de alto valor, este concepto está revolucionando la gestión de la producción y la logística.
La fabricación modular suele encontrarse en:
- Industria automotriz (por ejemplo, módulos de motor, sistemas de tablero)
- Productos electrónicos de consumo (por ejemplo, teléfonos inteligentes con unidades reemplazables)
- Equipos industriales (por ejemplo, sistemas de transporte y celdas de mecanizado modulares)
Comprender el funcionamiento de la fabricación modular es fundamental para reconocer su valor. No solo proporciona eficiencia, sino también mayor flexibilidad para satisfacer las cambiantes necesidades de los clientes y escalar la variedad de productos. En SteelPRO Peb, nos apasiona aplicar este enfoque para crear soluciones de acero industrial optimizadas, rentables y personalizables para clientes de todo el mundo.
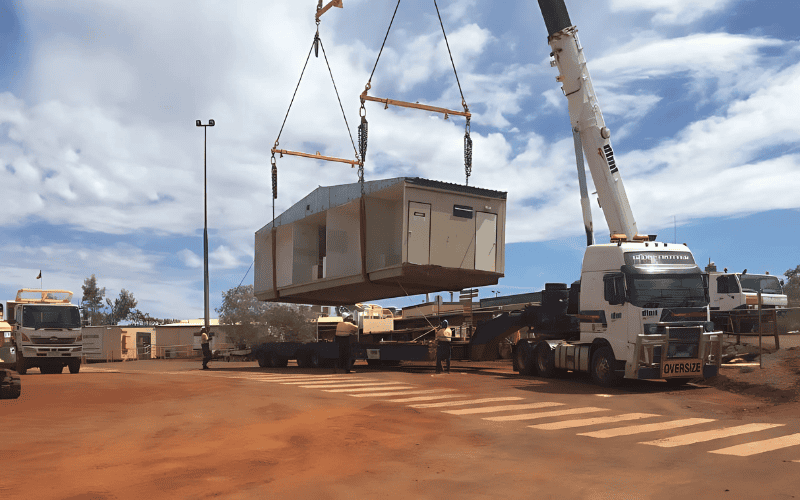
Proceso de fabricación modular
El proceso de fabricación modular implica la creación de módulos estandarizados en un entorno controlado, que posteriormente se ensamblan in situ o se integran en productos finales. Este enfoque mejora la eficiencia, reduce los costes y mejora la flexibilidad. Los pasos clave incluyen:
- Diseño y estandarizaciónLos módulos estandarizados están diseñados para una fácil integración y una calidad consistente en todos los productos o proyectos. Se crean configuraciones flexibles, manteniendo la interoperabilidad y la escalabilidad.
- PrefabricaciónLos módulos se prefabrican en fábrica mediante procesos automatizados y mano de obra cualificada. Componentes como paredes, motores o placas de circuito se construyen según estándares precisos, lo que garantiza un mejor control de la calidad de la producción.
- Conjunto de componentesLos módulos prefabricados se ensamblan en subconjuntos más grandes o productos finales. La estandarización de los módulos simplifica el ensamblaje final y reduce los errores.
- Control de calidadLos módulos se someten a estrictos controles de calidad para garantizar su integridad estructural, funcionalidad y rendimiento, lo que garantiza resultados consistentes y confiables debido al entorno controlado.
- Transporte y EntregaTras el ensamblaje, los módulos terminados se transportan a la obra final o a las instalaciones del cliente. En sectores como la construcción, los módulos prefabricados se ensamblan rápidamente in situ, lo que acorta los plazos del proyecto.
- Integración y personalización finalLos módulos se integran en sistemas más grandes en la obra final, con personalización según las necesidades del cliente. En la construcción, los módulos se unen para formar edificios; en la industria automotriz, se instalan en vehículos.
- Mantenimiento y actualizaciones continuasLa fabricación modular permite un fácil mantenimiento y actualizaciones, ya que los módulos individuales se pueden reemplazar o actualizar sin afectar todo el sistema, lo que resulta especialmente beneficioso en industrias como las de dispositivos médicos o electrónica.
Este proceso ofrece mayor eficiencia, ahorro de costos, escalabilidad y un tiempo de comercialización más rápido, lo que lo hace ideal para industrias como la construcción, la automotriz, la electrónica, los dispositivos médicos y la aeroespacial.
Desafíos actuales en las cadenas de suministro B2B
Las cadenas de suministro B2B han enfrentado presiones crecientes en los últimos años debido a la complejidad del comercio global y a interrupciones inesperadas, lo que expone vulnerabilidades en los sistemas tradicionales de fabricación y logística.
Interrupciones de la cadena de suministro global: Eventos como el COVID-19, tensiones geopolíticas y condiciones climáticas extremas han provocado retrasos y paradas de producción, afectando a empresas de todo el mundo.
Demanda imprevisibilidad: La volatilidad del mercado, las expectativas cambiantes de los clientes y los rápidos cambios tecnológicos dificultan que las empresas alineen la producción con la demanda, lo que genera exceso de inventario o faltantes de existencias.
Aumento de los costos: El aumento de los costos de las materias primas (por ejemplo, acero, aluminio) y de la logística (combustible, flete) presiona los márgenes, y las empresas más pequeñas son particularmente vulnerables debido a su limitado poder de negociación.
A medida que las empresas buscan una mayor resiliencia, nuevos modelos como la fabricación modular están ganando terreno para crear cadenas de suministro más eficientes.
¿Cuáles son los beneficios de la fabricación modular?
La fabricación modular no es solo una tendencia: está transformando el funcionamiento de las cadenas de suministro B2B en todos los sectores. Al permitir a los fabricantes descomponer sus productos en módulos estandarizados e intercambiables, las empresas pueden obtener importantes ventajas operativas.
Veamos cómo la fabricación modular mejora la eficiencia en las dimensiones centrales de la cadena de suministro:
1. Mayor flexibilidad del producto para satisfacer las demandas del mercado
En la fabricación tradicional, responder a las nuevas necesidades de los clientes o a los cambios del mercado suele implicar un rediseño completo. Los enfoques modulares transforman esta dinámica. Cuando los componentes del producto se modularizan, resulta mucho más fácil intercambiar o actualizar piezas sin tener que revisar todo el producto. Para los compradores B2B, esto significa que los proveedores pueden personalizar soluciones rápidamente sin largos plazos de entrega.
2. Reducción de los costes de I+D y producción
Los sistemas modulares permiten a las empresas reutilizar componentes probados en diferentes productos. Esto minimiza el tiempo dedicado al diseño y desarrollo, a la vez que reduce el riesgo de errores durante la producción. Gracias a las economías de escala en módulos de uso común, las empresas pueden reducir su coste unitario y mejorar la rentabilidad general del producto.
3. Plazos de producción acelerados mediante la fabricación paralela
Al separar un producto en módulos independientes, los fabricantes permiten que diferentes equipos o instalaciones produzcan piezas simultáneamente. A diferencia de la producción lineal, los flujos de trabajo paralelos reducen drásticamente el tiempo de comercialización, una ventaja en entornos B2B dinámicos, donde ser el primero puede significar cerrar el trato.
4. Mejor colaboración mediante la estandarización
La fabricación modular fomenta el desarrollo de estándares internos unificados. Esto facilita una colaboración más fluida entre departamentos, simplificando la entrega de proyectos y reduciendo las ineficiencias. Externamente, también simplifica la integración con socios de la cadena de suministro, como ensambladores o proveedores de servicios.
5. Soporte para modelos de fabricación distribuida
La inestabilidad geopolítica, los desastres naturales y los cuellos de botella logísticos pueden interrumpir la producción centralizada. La fabricación modular permite la producción distribuida, donde los módulos pueden construirse en diferentes ubicaciones y ensamblarse más cerca de los mercados finales. Esto reduce los riesgos de transporte y garantiza la continuidad del negocio incluso en condiciones impredecibles.
Empresas como SteelPRO Peb aprovechan esta ventaja modular para ofrecer soluciones de estructuras de acero personalizables y de alta calidad a clientes internacionales. Con sistemas modulares escalables y capacidad de entrega global, minimizamos la complejidad y maximizamos la capacidad de respuesta para nuestros socios en todo el mundo.
Lectura relacionada: Beneficios de la construcción modular

Desafíos a considerar al implementar la fabricación modular
Si bien la fabricación modular ofrece agilidad y eficiencia, su adopción conlleva varios desafíos. Comprender estos posibles obstáculos es esencial para una implementación exitosa.
Alta inversión inicial en diseño
La creación de módulos estandarizados e interoperables requiere un importante enfoque de ingeniería y de sistema. La fase inicial del desarrollo de productos modulares suele requerir más tiempo y recursos que la fabricación tradicional, ya que las empresas deben rediseñar sus líneas de productos y reestructurar sus flujos de trabajo para adaptarse a la modularidad.
Presiones del ecosistema de la cadena de suministro
La fabricación modular requiere una estrecha integración en toda la cadena de suministro. Cada módulo debe ser compatible con los demás, lo que exige una colaboración más estrecha tanto con los proveedores de la cadena de suministro como con los socios de la cadena de suministro. Sin estándares consistentes y protocolos compartidos, los módulos pueden convertirse en cuellos de botella en lugar de acelerar la producción.
Cambios culturales y procedimentales internos
Adoptar la fabricación modular requiere transformaciones culturales y procedimentales dentro de la empresa. La transición de los métodos tradicionales a enfoques modulares exige una gestión del cambio a todos los niveles, incluyendo la capacitación de los empleados y una mayor colaboración interdisciplinaria. La resistencia al cambio puede ralentizar el progreso si los equipos internos no están preparados para el cambio de mentalidad.
En definitiva, migrar a la fabricación modular implica más que rediseñar procesos: requiere previsión estratégica, una coordinación eficaz con las partes interesadas y un compromiso de toda la empresa con la innovación. Si bien las recompensas son considerables, las empresas deben ser conscientes de los desafíos y planificar en consecuencia.
¿Para qué industria es adecuada la fabricación modular?
Aplicación de la fabricación modular en la industria de la construcción
La fabricación modular se utiliza ampliamente en la industria de la construcción, incluidos edificios residenciales, comerciales, educativos e instalaciones médicas.
- La construcción residencial es una aplicación fundamental de la fabricación modular. Al prefabricar módulos como paredes, techos y pisos en fábricas y transportarlos a la obra para su ensamblaje, los promotores pueden construir rápidamente viviendas asequibles, apartamentos y casas unifamiliares.
- En la construcción comercial, el diseño modular se utiliza en edificios de oficinas, hoteles y centros comerciales. La construcción in situ es sencilla y eficiente, y los edificios pueden completarse rápidamente para satisfacer las necesidades de proyectos comerciales de rápido crecimiento.
- Las instalaciones educativas, como escuelas y residencias universitarias, también se construyen modularmente, especialmente para proyectos que requieren una rápida expansión o construcción temporal. El diseño modular permite a las escuelas construir rápidamente aulas, laboratorios y residencias para resolver el problema de la escasez de recursos educativos.
- En el sector médico, la fabricación modular facilita la rápida construcción de hospitales y clínicas, especialmente en zonas con recursos médicos limitados. Los hospitales pueden ampliar con flexibilidad departamentos y salas según sea necesario.
Además, la construcción modular también se utiliza en instalaciones públicas como centros comunitarios, bibliotecas, comisarías de policía y estaciones de bomberos para garantizar una entrega rápida y una construcción eficiente.
Aplicaciones de fabricación modular en otras industrias
En el industria automotrizEl diseño modular divide los vehículos en módulos estandarizados (por ejemplo, chasis, carrocería, motor) que pueden producirse en paralelo, lo que reduce el tiempo de ensamblaje y mejora la eficiencia.
En fabricación de productos electrónicosEl diseño modular permite que productos como smartphones y electrodomésticos se adapten rápidamente a la demanda del mercado. La estandarización de componentes como pantallas, procesadores y cámaras permite opciones personalizadas, a la vez que simplifica la producción y reduce costos.
El industria de dispositivos médicos Utiliza el diseño modular en productos como escáneres de tomografía computarizada y máquinas de rayos X. La estandarización de módulos (por ejemplo, sistemas eléctricos, pantallas, sensores) acorta los ciclos de producción, mejora el control de calidad y simplifica el mantenimiento y las actualizaciones.
En el industria aeroespacialEl diseño modular se aplica a la fabricación de aeronaves y satélites, donde componentes como fuselajes, alas y motores se prefabrican y ensamblan in situ. Esto acelera la producción, reduce costos y aumenta la flexibilidad, facilitando las reparaciones.
La fabricación modular no es solo una técnica nueva: es una forma más inteligente de construir cadenas de suministro resilientes y flexibles.
En SteelPRO Peb, estamos listos para ayudarle a convertir estas ideas en resultados. Si busca simplificar sus operaciones, mejorar los plazos de entrega y reducir costes, contáctenos. Construyamos juntos algo más sólido.

